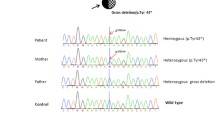
Abstract
The genetic transmission of X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) can be determined with high probability using closely linked DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP's). In a family known to be at risk for XLA in male offspring, RFLP analysis demonstrated that the mother was an XLA carrier and her newborn son was affected. The infant developed immunological deficiencies a few months later, confirming the diagnosis. RFLP analysis provides a method for carrier detection, prenatal diagnosis and presymptomatic diagnosis of XLA, which plays a significant role in prevention of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- XLA:
-
X-linked agammaglobulinaemia
- RFLP:
-
restriction fragment length polymorphism
- PBMC:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- Ig:
-
Immunoglobulin
- PWM:
-
pokeweed mitogen
- SAC:
-
Staphylococcus aureus cowan A strain
References
Blom J, Harrisson CMH, Schuurman RKB, Schot JDL (1986) A comparison of two fluorescence-activated cell sorters, the FACS IV (laser) and the FACS Tm (mercury lamp), as research analyzers for the quantification of T and B cell subsets in human peripheral blood. J Immunol Methods 95:39–46
Conley ME (1985) B cells in patients with X-linked agammaglobulineamia. J Immunol 134:3070–3074
Dosch HM, Schuurman RKB, Gelfand EW (1980) Polyclonal activation of human lymphocytes in vitro II. Reappraisal of T and B cell-specific mitogens. J Immunol 125:827–832
Kwan SP, Kunkel L, Bruns G, Wedgwood RJ, Latt S, Rosen FS (1986) Mapping of the X-linked agammaglobulinemia locus by use of restriction fragment-length polymorphism. J Clin Invest 77: 649–652
Ledermann HM, Winkelstein JA (1985) X-linked agammaglobulinemia: an analysis of 96 patients. Medicine 64:145–156
Leickley FE, Buckley R (1986) Variability in B cell maturation and differentiation in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Clin Exp Immunol 65:90–99
Mensink EJBM, Schot JDL, Tippett P, Ott J, Schuurman RKB (1984) X-linked agammaglobulinemia and the red bloodcell determinants Xg and 12E7 are not closely linked. Hum Genet 68:303–309
Mensink EJBM, Schuurman RKB, Schot JDL, Thompson A, Alt FW (1986) Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangements in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Eur J Immunol 16:963–967
Mensink EJBM, Thompson A, Schot JDL, van de Greef WMM, Sandkuyl LA, Schuurman RKB (1986) Mapping of a gene for X-linked agammaglobulinemia and evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Hum Genet 73:327–332
Mensink EJBM, Thompson A, Schot JDL, Kraakman MEM, Sandkuyl LA, Schuurman RKB (1987) Genetic heterogeneity in X-linked agammaglobulinemia complicates carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis. Clin Genet 31:91–96
Ott J, Mensink EJBM, Thompson A, Schot JDL, Schuurman RKB (1986) Heterogeneity in the map distance between X-linked agammaglobulinemia and a map of nine RFLP loci. Hum Genet 74:280–283
Pearl ER, Vogler LB, Okos AJ, Christ WM, Lawton III AR, Cooper MD (1978) B lymphocyte precursors in human bone marrow: an analysis of normal individuals and patients with antibody deficiency states. J Immunol 120:1169–1175
Schot JDL, Elferink BG, Hooijkaas H, Neyens HJ, Schuurman RKB (1987) Deficiency of immunity to mycobacterium avium that can be restored by allogenic lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol 68:48–57
Schuurman RKB, Gelfand EW, Dosch HM (1980) Polyclonal activation of human lymphocytes in vitro. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte response to a T cell independent B cell mitogen. J Immunol 125:820–826
Sedgwick JD, Holt PG (1983) A solid phase immunoenzymatic technique for the enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods 57:301–309
Stiehm ER, Fudenberg HH (1966) Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics 37:715–727
Wedgwood R, Ochs D (1980) Variability in the expression of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. The co-existence of classic XLA (Bruton type) and common variable immunodeficiency in the same families. In: Seligmann M, Hitzig WH (eds) Primary immunodeficiencies. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam New York, pp 69–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuurman, R.K.B., Mensink, E.J.B.M., Sandkuyl, L.A. et al. Early diagnosis in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia. Eur J Pediatr 147, 93–95 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442622