Abstract
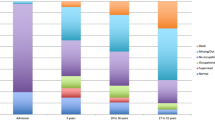
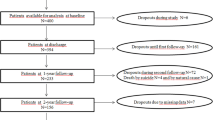
The effect of long-term treatment with clozapine in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder was evaluated in a retrospective study comprising 96 patients treated with the drug during the period 1974–1986 at the Psychiatric Research Center in Uppsala. All patients had previously been treated with different kinds of antipsychotic drugs but with insufficient clinical effect or distressing extrapyramidal side effects. When clozapine treatment was initiated, the mean duration of the illness was 8 years and 9 months. In 36% of the patients clozapine treatment was discontinued, the main reasons being lack of efficacy, poor compliance or temporary withdrawal from the market in 1975. Clinical evaluation of the effect revealed that 85% of the patients could be discharged from the hospital within a year and that 43% of the patients were significantly and 38% moderately improved compared to previous treatments. Of those patients who were still on clozapine 2 years after the treatment was initiated, 39% had employment compared to only 3% before clozapine. In ten patients a transient decrement in white blood cells (WBC) was noted but normalized during ongoing treatment. One patient developed leukopenia and one agranulocytosis, none with fatal outcome. Common side effects were sedation, hypersalivation, weight gain and obstipation. In one patient clozapine treatment was stopped because of grand mal seizures. No extrapyramidal side effects were observed or reported during clozapine treatment. It is concluded that clozapine offers particular advantages for many “therapy-resistant” schizophrenic patients when compared to classical neuroleptics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anden NE, Stock G (1973) Effect of clozapine on the turnover of dopamine in the corpus striatum and in the limbic system. J Pharm Pharmacol 25:346–348
Anderman B, Griffith RW (1977) Clozapine-induced agranulocytosis: a situation report up to August 1976. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 11:199–201
Angst J (1971) Ergebnisse eines Doppelblindversuches von HF 1854 (8-chlor-1-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo(b,e) 1,4)diazepin im Vergleich zu Levomepromazine. Pharmacopsychiatry 4:192–200
Bartholini G, Haefely W, Jalfre M, Keller HH, Pletcher A (1972) Effects of clozapine on cerebral catecholaminergic neuron systems. Br J Pharmacol 46:736–740
Davis JM, Schaffer CB, Killian GA, Kinard C, Chan C (1980) Important issues in the drug treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophren Bull 6:70–87
Ekblom B, Häggström JE (1974) Clozapine (Leponex) compared with chlorpromazine: a double-blind evaluation of pharmacological and clinical properties. Curr Ther Res 16:945–957
Fog R (1975) Neuroleptic action of clozapine injected into various brain areas in rats. Int Pharmacopsychiatry 10:89–93
Gerlach J, Koppelhus P, Helweg E, Monrad A (1974) Clozapine and haloperidol in a single-blind cross-over trial: therapeutic and biochemical aspects in the treatment of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 50:410–424
Kane JM, Lieberman J (1987) Maintenance pharmacotherapy in schizophrenia. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology, the third generation of progress: the emergence of molecular biology and biological psychiatry. Raven Press, New York, pp 1103–1109
Kane JM, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H (1988) Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic; a double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:789–796
Kuha S, Miettinen E (1986) Long-term effect of clozapine in schizophrenia: a retrospective study of 108 chronic schizophrenics treated with clozapine for up to 12 years. Nord Psychiatr Tidskr 40:225–230
Leon CA (1979) Therapeutic effect of clozapine. A 4-year follow-up of a controlled clinical trial. Acta Psychiatr Scand 59:471–480
Nybäck H, Sedvall G (1976) Effects of neuroleptics on striatal dopamine synthesized from 14C-tyrosine. Pharmacol Ther 2:49–63
Povlsen UJ, Noring U, Fog R, Gerlach J (1985) Tolerability and therapeutic effect of clozapine; a retrospective investigation of 216 patients treated with clozapine for up to 12 years. Acta Psychiatr Scand 71:176–185
Sayers AC, Burki HR, Ruch W, Aspen A (1975) Neuroleptic-induced hypersensitivity of striatal dopamine receptors in the rat as a model of tardiv dyskinesias. Effects of clozapine, haloperidol, loxapine and chlorpromazine. Psychopharmacologia 41:97–104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindström, L.H. A retrospective study on the long-term efficacy of clozapine in 96 schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients during a 13-year period. Psychopharmacology 99 (Suppl 1), S84–S86 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442567
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442567