Abstract
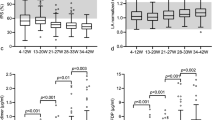
The following tests were performed within the first week of life in 129 newborn infants: determination of alpha1-antitrypsin, alpha2-macroglobulin, antithrombin III, fibrinogen, prothrombin, accelerin, convertin and plasminogen. The newborns were divided into three groups: group (a), healthy newborns with a normal obstetric history (n=62); group (b), newborns without clinical signs of illness, but a complicated obstetric history (n=49); group (c), newborns suffering from various diseases (n=18). For statistical analysis correlation coefficients and t-tests were used. The mean values of the coagulation factors showed no significant differences between the three groups, but the standard deviation, was found to be markedly greater in group (c). This can be explained by higher production and an increased turnover of coagulation factors in these newborns.
Significant correlations were found between fibrinogen, prothrombin, plasminogen and the inhibitors alpha1-antitrypsin, alpha2-macroglobulin and antithrombin III.
According to this investigation the fibrin forming system and fibrinolysis are influenced by many complications in the newborn period. Alpha2-macroglobulin was found to be significantly reduced in 15 out of 18 sick newborn infants and appears to be a sensitive indicator for various coagulation defects. Alpha1-antitrypsin was reduced in infants with severe disturbances of the clotting system. Therefore, alpha2-macroglobulin and alpha1-antitrypsin may be useful for the determination of mild and severe coagulation disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abildgaard, U.: Inhibition of the thrombin-fibrinogen reaction by alpha2-macroglobulin, studied by N-terminal analysis. Thromb. Diathes. Haem. 21, 173–180 (1969)
Aronsen, K.-F., Ekel, G., Kindmark, C.-O., Laurell, C.-B.: Sequential changes of plasma proteins after surgical trauma. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 29, Supply. 124, 127–136 (1972)
Deutsch, E., Marschner, I.: Antifibrinolysine. Folia. Haematol. (Frankfurt) 8, 74–83 (1963)
Deykin, D.: The clinical challenge of disseminated intravascular coagulation. New Engl. J. Med. 283, 636–644 (1970)
Ekelund, H., Finnström, O.: Fibrin degradation products and plasminogen in newborn infants with respiratory disturbances and postnatal asphyxia. Acta Paediat. Scand. 61, 661–669 (1972)
Fischer, M.: Verhalten menschlicher Thrombininhibitoren (Alpha2-Macroglobulin und Antithrombin III) während und nach chirurgischen, und gynäkologisch-geburtshiflichen Eingriffen. Folia Haematol (Leipzig) 98, 397–407 (1972)
Ganrot, P. O.: Variation of the concentrations of some plasma proteins in normal adults, in pregnant women and in newborns. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 29, Suppl. 124, 83–88 (1972)
Ganrot, P. O., Nilehn, J. E.: Competition between plasmin and thrombin for Alpha2-macroglobulin. Clin. Chim. Acta 17, 511–513 (1967)
Göbel, U.: Pathophysiologie der Blutgerinnung bei Neugeborenen. Bücherei des Pädiaters, Band 78. Erworbene Gerinnungsstörungen im Kindesalter, 27–32, Hrsg. U. Göbel. Stuttgart: Enke 1977
Göbel, U., Petrich, C., Voss, H. v., Schmelzer, L.: Alpha1-antitrypsin and alpha2-macroglobulin in newborn infants. I. The influence of perinatal complications. Eur. J. Pediatr. 129, 117–124 (1978)
Göbel, U., Riech, P.: Partielle Thromboplastinzeit, Thromboplastinzeit, Fibrinogen, Thrombinzeit und Thrombocytenzahl bei gesunden und kranken Neugeborenen. Mschr. Kinderheilk. 120, 484–488 (1972)
Harpel, P. C.: Human plasma alpha2-macroglobulin. An inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. J. Exp. Med. 132, 329–352 (1970)
Haverback, B. J., Dyce, B., Bundy, H. F., Wirtschafter, S. K., Edmondson H. A.: Protein binding of pancreatic proteolytic enzymes. J. clin. Invest. 41, 972–980 (1962)
Heimburger, N.: Proteinase inhibitors of human plasma. — Their properties and control functions. Proteases and Biological Control, pp. 367–386. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory 1975
James, K., Taylor, F. B. jr., Fudenberg, H. H.: The effect of alpha2-macroglobulin in human serum on trypsin, plasmin, and thrombin activities. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 133, 374–376 (1967)
Johansson, B. G., Kindmark, C.-O., Tyrell, E. Y., Wollheim, F. A.: Sequential changes of plasma proteins after myocardial infarction. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 29, Suppl. 124, 117–126 (1972)
Lanchantin, G. F., Plesset, M. L., Friedmann, J. A., Hart, D. W.: Dissociation of esterolytic and clotting activities of thrombin by trypsin-binding macroglobulin. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 121, 444–449 (1966)
Lennert, K. A., Kollmar, M., Hupe, H.: Verhalten der Immunglobuline G, A und M, des Alpha1-C-Globulins, des Alpha1-Antitrypsins und des Alpha2-Macroglobulins bei Kindern vor und nach operativen Eingriffen. Mschr. Kinderheilk. 121, 151–154 (1973)
Mancini, G., Carbonara, A. O., Heremans, J. F.: Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Int. J. Immunochem. 2, 235–254 (1965)
Nie, N. H., Bent, D. H., Hull, C. H.: SPSS — Statistical package for the social sciences (Provisional users manual). Norc, University of Chicago 1969
Refvem, O., Fagerhol, M. K., Abildgaard, U.: Changes in antithrombin III levels following cessation of anticoagulant therapy. Acta med. Scand. 193, 307–309 (1973)
Rimon, A., Shamash, Y., Shapiro, B. S.: The plasmin inhibitor of human plasma. IV. Its action on plasmin, trypsin, chymotrypsin and thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 241, 5102–5107 (1966)
Schwick, H. G., Heimburger, N., Haupt, H.: Purification and chemical physical properties of some proteinase inhibitors of plasma. Thrombos. Diathes. haemorrh. 18, 302 (1967)
Schröer, H.: Physiologische Inhibitoren des Thrombins und der Thrombinbildung. Folia Haematol. (Leipzig) 99, 212–222 (1973)
Suzuki, S., Wake, N., Yoshiaki, K.: New neonatal problems of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. I. The change of plasmin inhibitor levels in the newborn infant. J. Perinat. Med. 4, 213–220 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Göbel, U., Triebel, A., Petrich, C. et al. Alpha1-antitrypsin and alpha2-macroglobulin in newborn infants. Eur J Pediatr 129, 125–132 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442372
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442372