Abstract
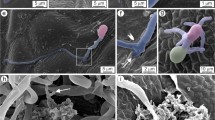
The behavior of rust fungi in their host plants has been elucidated by electron microscopy. However, most of the ultrastructural studies on rust fungi have focused on the uredial stage. In order to elucidate the features of the sporidial stage, we studied the fine structure of Kuehneola japonica, a short-cycle rust, in rose leaves. Infection pegs arising from appressoria penetrated the host walls. Papillae formed at the time of penetration against the outer epidermal cell walls. The papillae which had formed at the penetration sites grew extensively and partially surrounded the intracellular hyphae which were connected with the infection pegs. The intracellular hyphae in the epidermal cells developed further and entered adjacent parenchyma cells. Walls of parenchyma cells either invaginated or thin papillae formed at penetration sites and the invaginated walls or papillae surrounded the necks of the intracellular hyphae. Intracellular hyphae in both epidermal and parenchyma cells were not enveloped by the sheath before 20 days after inoculation. In specimens prepared 20 days after inoculation, some of the intracellular hyphae were enveloped by a sheath in both palisade and spongy parenchyma cells. The sheathed hyphae resembled haustoria of other rust fungi which had been described previously. Teliospore initials were formed in mycelial masses in intercellular spaces between the epidermal cells and palisade parenchyma cells 20 days after inoculation. Uninucleate teliospores developed from teliospore initials 30 days after inoculation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aist, J. R. 1976. Papillae and related wound plugs of plant cells. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 14: 145–163.
Allen, R. F. 1933. A cytological study of the teliospores, promycelia, and sporidia in Puccinia malvacearum. Phytopathology 23: 572–586.
Coffey, M. D. 1976. Flax rust resistance involving the K gene: an ultrastructural survey. Can. J. Bot. 54: 1443–1457.
Coffey, M. D., B. A. Palevitz & P. J. Allen. 1972. The fine structure of two rust fungi, Puccinia helianthi and Melampsora lini. Can. J. Bot. 50: 231–240.
Harder, D. E. 1976. Electron microscopy of urediospore formation in Puccinia coronata avenae and P. graminis avenae. Can. J. Bot. 54: 1010–1019.
Heath, M. C. 1972. Ultrastructure of host and nonhost reactions to cowpea rust. Phytopathology 62: 27–38.
Heath, M. C. & I. B. Heath. 1971. Ultrastructure of an immune and a susceptible reaction of cowpea leaves to rust infection. Physiol. Pl. Path. 1: 277–287.
Kajiwara, T. 1970. Structure and physiology of haustoria of various parasites. In: Morphological and biochemical events in plant-parasite interaction. S. Akai & S. Ouchi (eds.). The Phytopath. Soc. of Japan, Tokyo, pp. 255–277.
Kohno, M., T. Nishimura, H. Ishizaki & H. Kunoh. 1975. Cytological studies on rust fungi. (III) Nuclear behaviors during the process from teliospore stage through sporidial stage in two short-cycled rusts, Kuehneola japonica and Puccinia horiana. Bull. Fac. Agr. Mie Univ. 49: 21–29.
Kohno, M., H. Ishizaki & H. Kunoh. 1976. Cytological studies on rust fungi. (V) Intracellular hyphae of Gymnosporangium haraeanum Sydow in leaf cells of Japanese pear. Ann. Phytopath. Soc. Japan 42: 417–423.
Littlefield, L. J. & C. E. Bracker. 1972. Ultrastructural specialization at the host-pathogen interface in rust-infected flax. Protoplasma 74: 271–305.
Olive, L. S. 1949. Karyogamy and meiosis in the rust Coleosporium vernoniae. Amer. J. Bot. 36: 41–54.
Pady, S. M. 1946. The development and germination of the intraepidermal teliospores of Melampsorella cerastii. Mycologia 38: 477–490.
Rijkenberg, F. H. J. & S. J. Truter. 1973. Haustoria and intracellular hyphae in rusts. Phytopathology 63: 281–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 32.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohno, M., Ishizaki, H. & Kunoh, H. Cytological studies on rust fungi. (vi) fine structures of infection process of Kuehneola japonica (diet.) dietel. Mycopathologia 61, 35–41 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00440756
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00440756