Abstract
Albumin-binding capacity and the concentration of unbound bilirubin after separation by gel filtration were determined in the sera of 20 newborn infants aged 1 to 7 days. Total serum bilirubin level ranged between 12.0 and 23.8 mg/100 ml. The results are as follows:
-
1.
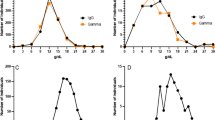
The albumin-binding capacity ranged between 48 and 100% without any relation to the level of total serum bilirubin.
-
2.
The mean concentration of unbound bilirubin was 0.11 mg/100 ml. No significant correlations were found between unbound bilirubin levels and the albumin-binding capacity or the concentration of total bilirubin.
Zusammenfassung
Bei 20 Neugeborenen, deren Serum-Bilirubin-Konzentrationen zwischen 12,0 und 23,8 mg/100 ml lagen, wurden während der ersten 7 Tage die Albuminbindungskapazität und die Konzentration des freien Bilirubins nach Sephadexgelfiltration bestimmt. Die Untersuchung zeigte folgende Ergebnisse:
-
1.
Die Albuminbindungskapazität bewegte sich zwischen 48 und 100%. Es fand sich keine gesicherte Abhängigkeit von der Höhe des Gesamtbilirubins imSerum.
-
2.
Unter den Probanden wurde eine mittlere Konzentration an freiem Bilirubin von 0,11 mg/100 ml ermittelt. Die Konzentration an freiem Bilirubin erwies sich als unabhängig sowohl von der Höhe des Gesamtbilirubins als auch von der Höhe der Albuminbindungskapazität.
An Hand der Ergebnisse wird der Wert der Bestimmung der Albuminbindungskapazität für die Präzisierung der Austauschindikation diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun, W., Kosloswki, H., Weidemann, H.: Die Farbstoffbindungskapazität der Plasmaalbumine ikterischer Neugeborener und Frühgeborener. Pädiat. u. Grenzgeb. 9, 353–358 (1970)
Chunga, F., Lardinois, R.: Separation by gel filtration and microdetermination of unbound bilirubin. Acta paediat. scand. 60, 27–32 (1971)
Corkery, J. J., Dubowitz, V., Lister, J., Moosa, A.: Colonic perforation after exchange transfusion. Brit. med. J. 1968 14, 345–349
Diamond, I., Schmid, R.: Experimental bilirubin encephalopathie. The mode of entry of bilirubin — 14C into the central nervous system. J. clin. Invest. 45, 678–689 (1966).
Hennemann, U.: Die Bedeutung des Albuminsättigungsindex für Bilirubin bei der Beurteilung des Neugeborenenikterus. Z. Kinderheilk. 112, 68–78 (1972)
Keller, E., Theile, H.: Komplikationen nach Austauschtransfusion über die Nabelvene in Abhängigkeit von prophylaktischen Antibiotikagaben. Kinderärztl. Prax. 38, 52–58 (1970)
Kerr, A. A.: Neonatal colonic perforation after exchange transfusion. N. Z. med. J. 72, 18–21 (1970)
Odell, G. B.: The distribution of bilirubin between albumin and mitochondria. J. Pediat. 68, 164 (1966)
Odell, G. B.: The distribution and toxicity of bilirubin. Pediatrics 46, 16 (1970)
Odell, G. B., Cohen, S. N., Kelly, P. C.: Studies in kernicterus. II. The determination of the saturation of serum albumin with bilirubin. J. Pediat. 74, 214–230 (1969)
Odievre, M., Pinon, F., Schirar, M., Luzeau, R., Sauvageot, M.: La fraction de bilirubine non conjugeé et non lieé a l'albumine au cours des hyperbilirubinemies neonatales, mesure et premiers resultats. Arch. Pediat. 27, 225–235 (1970)
Panagopoulos, G., Valaes, T., Doxiadis, S. A.: Morbidity and mortality related to exchange transfusion. J. Pediat. 74, 247 (1969)
Ploussard, J.-P., Poliot, A., Christoforov, B., Etienne, J.-P., Housset, E.: Contribution a l'etude des criteres d'evalution du risque d'ictere nucleaire du nouveausne. Arch. franç. Pédiat. 28, 797–816 (1971)
Porter, E. G., Waters, J. W.: A rapid micromethod for measurement the reserve albumin binding capacity in serum from newborn infants with hyperbilirubinemia. J. Lab. clin. Med. 67, 660–668 (1966)
Rossipal, E., Teubl, I., Rosegger, H.: Untersuchungen über die Bindungsreserve des Serumalbumins für Bilirubin beim Ikterus gravis neonatorum. Pädiat. u. Pädol. 6, 205–212 (1971)
Schiff, D., Chan, G., Stern, L.: Fixed drug combinations and the displacement of bilirubin from albumin. Pediatrics 48, 139–141 (1971)
Schiff, D., Chan, G., Stern, L.: Sephadex G-25 quantitative estimation of free bilirubin potential in jaundiced newborn infants' sera: a guide to the prevention of kernicterus. J. Lab. clin. Med. 80, 455–462 (1972)
Theile, H., Künzel, R.: Farbstoffbindungskapazität im Serum Neugeborener und Indikation zur Austauschtransfusion. Pädiat. u. Grenzgeb. 8, 245–253 (1969)
Weldon, V. V., Odell, G. B.: Mortality risk of exchange transfusion. Pediatrics 41, 797–801 (1968)
Zamet, P., Chunga, F.: Separation by gel filtration and microdetermination of unbound bilirubin. Acta paediat. scand. 60, 33–38 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frenzel, J., Sander, I. & Schramm, D. Comparative analysis between albumin-binding capacity and the concentration of unbound bilirubin in hyperbilirubinemic sera of newborn infants. Z. Kinder-Heilk. 115, 187–192 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00440543
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00440543