Abstract
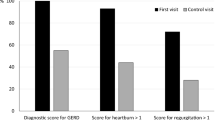
Respiratory symptoms were studied in 119 patients operated on for fundoplication and crural repair because of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The effect of antireflux surgery and of smoking habits on their respiratory symptoms was evaluated. A questionnaire was completed before and after surgery in connection with esophageal investigations. Chronic bronchitis was present in 20% of the patients, 38% of whom were smokers. In the rest of the patients, 18% were smokers. Cough was reported by 34% and expectoration by 21%. After surgery the number of patients with cough and chronic bronchitis was reduced significantly in nonsmokers and to some extent in smokers. It is believed that fundoplication with distal anchoring of the longitudinal esophageal muscle will improve pharyngoesophageal function and thereby decrease aspiration and respiratory symptoms due to mis-swallowing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ducoloné A, Vandevenne A, Jouin H, Grob JC, Coumaros D, Meyer C et al: Gastroesophageal reflux in patients with asthma and chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:327–332, 1987
Overholt RH, Voorhees RJ: Esophageal reflux as trigger in asthma. Dis Chest 49:464–466, 1966
Mansfield LE, Stein MR: Gastroesophageal reflux and asthma: a possible reflux mechanism. Ann Allergy 41:224–226, 1978
Boyle JT, Tuchman DN, Altschuler SM, Nixon TE, Pack AL, Cohen S: Mechanisms for the association for gastroesophageal reflux and bronchospasm. Am Rev Respir Dis 131(Suppl 13):16–20, 1985
Allen CJ, Newhouse MT: Gastroesophageal reflux and chronic respiratory disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:645–647, 1984
Sadoun D, Valeyre D, Cargill J, Volter F, Amouroux J, Battesti JP: Bronchiolite oblitérante avec pneumonie en voie d'organisation en apparence cryptogénétique. Mise en évidence d'un reflux gastro-oesophagien dans 5 cas. Presse Med 17:2383–2385, 1988
Kennedy JH: “Silent” gastroesophageal reflux: an important but little known cause of pulmonary complications. Dis Chest 42:42–45, 1962
Urschel HC, Paulson DL: Gastroesophageal reflux and hiatal hernia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 53:21–32, 1967
Larrain A, Carrasco I, Galleguillos F Sepulveda R, Pope II CE: Medical and surgical treatment of nonallergic asthma associated with gastroesophageal reflux. Chest 99:1330–1335, 1991
Pasquis P, Tardif C, Nouvet G: Reflux gastro-oesophagien et affections respiratoires. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir 19:645–658, 1983
Davis MV, Fiuzat J: Application of the Belsey hiatal hernia repair to infants and children with recurrent bronchitis, brochioloitis, and pneumonitis due to regurgitation and aspiration. Ann Thorac Surg 3:99–110, 1967
Jolley SG, Herbst JJ, Johnson DG, Matlak ME, Book LS: Surgery in children with gastroesophageal reflux and respiratory symptoms. J Pediatrics 96:194–198, 1980
DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Iascone C, Courtney JV, Skinner DB: Chronic respiratory symptoms and occult gastroesophageal reflux. A prospective clinical study and results of surgical therapy. Ann Surg 211:337–345, 1990
Pellegrini CA, DeMeester TR, Johnson LF, Skinner DB: Gastroesophageal reflux and pulmonary aspiration: incidence, functional abnormality and results of surgical therapy. Surgery 86:110–119, 1979
Mansfield LE, Hameister HH, Spaulding HS, Smoth NJ, Glab N: The role of the vagus nerve in airway narrowing caused by intraesophageal hydrochloric acid provocation and esophageal distension. Ann Allergy 47:431–434, 1981
Johansson K-E, Tibbling L: Maintenance, treatment with ranitidine compared to fundoplication in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 21:779–788, 1981
American Thoracic Society: Chronic bronchitis asthma and pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis 85:762–788, 1962
Ask P, Carlsson P, Öberg Å, Pettersson H, Törngren P, Tibbling L: Feedback system for control of abdominal compression in oesophageal investigations. Med Biol Eng Comput 19:501–503, 1981
Tibbling L: Wrong-way swallowing as a possible cause of bronchitis in patients with gastroesophageal, reflux, disease. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 113:405–408, 1993
DeMeester T: What are the relations between gastroesophageal reflux and pharyngoesophageal dysphagia: In: Giuli R, McCallum RW (eds.) Benign Lesions of the Esophagus and Cancer. Answers to 110 questions. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 143–144, 1988
Henderson RD, Woolf C, Marryatt G: Pharyngoesophageal dysphagia and gastroesophageal reflux. Laryngoscope 10:1531–1539, 1976
Surgeon General: Pharmacological and toxicological implications of smoke constituents on cardiovascular disease. In: U.S. Public, Health Service (eds.). The Health Consequences of Smoking. Cardiovascular Disease. A Report of the Surgeon General. Washington DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, DHHS Publication No. (PHS) 84-50204; 1983:203–240
Kiviloog J, Irnell L, Eklund G: The prevalence of bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis in smokers and non-smokers in a representative local Swedish population. Scand J Resp Dis 55:262–266, 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tibbling, L., Gibellino, F.M. & Johansson, KE. Is mis-swallowing or smoking a cause of respiratory symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease?. Dysphagia 10, 113–116 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00440081
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00440081