Abstract
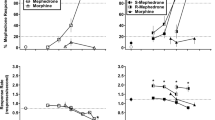
Biochemical, electrophysiological, and behavioral experiments suggest that the dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptor subtypes functionally interact. In rats trained to discriminate 1.0 mg/kg d-amphetamine, substitution with the D-2 agonist quinpirole (0.1–2.0 mg/kg) produces amphetaminelever responding, whereas the D-1 agonist SKF 38393 (0.3–10.0 mg/kg) elicits only saline-appropriate responding. Combining either quinpirole (0.05–0.5 mg/kg) or SKF 38393 (0.5–10.0 mg/kg) with 0.3 mg/kg d-amphetamine results in dose-dependent increases in amphetamine-lever responding. Conversely, the D-1 antagonist SCH 23390 (0.02–0.1 mg/kg) antagonizes the discrimination produced by 0.7 mg/kg d-amphetamine. Additional combination studies examined the effect of DA receptor drugs on discrimination when quinpirole is substituted in d-amphetamine trained rats. SKF 38393 (0.5–7.0 mg/kg) fails to increase the amphetamine-appropriate lever response produced by either 0.05 or 0.2 mg/kg quinpirole. Similarly, SCH 23390 (0.01–0.1 mg/kg) fails to antagonize the amphetamine-lever responding produced by either 0.2 or 0.5 mg/kg quinpirole. Haloperidol (0.02–0.2 mg/kg) does antagonize the amphetamine-appropriate response produced by quinpirole substitution. The d-amphetamine discrimination studies indicate that stimulating D-2 receptors alone or D-1 receptors in the presence of d-amphetamine yields d-amphetamine-lever responding, and suggests that D-1/D-2 receptors can functionally interact to alter discrimination behavior. Quinpirole substitution, on the other hand, shows an insensitivity to D-1 receptor manipulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barone P, Devin DA, Brown AR, Chase TN (1986) Dopamnergic mechanisms and motor function: characterization of D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptor interactions. Eur J Pharmacol 123:109–114.
Boyar WC, Altar CA (1987) Modulation of in vivo dopamine release by D-2 but not D-1 receptor agonists and antagonists. J Neurochem 48:824–831.
Carlson JH, Bergstrom DA, Walters JR (1986) Neurophysiological evidence that dopamine receptor blockade attenuates postsyn-aptic but not autoreceptor-mediated effects of dopamine agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 23:237–251.
Colpaert FC, Neimegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1978a) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine and d-amphetamine, and antagonism by haloperidol: a comparative study. Neuropharmacology 17:937–942.
Colpaert FC, Neimegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1978b) Neuroleptic interference with the cocaine cue: internal stimulus control of behavior and psychosis. Psychopharmacologia 58:247–255.
Colpaert FC, Neimegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1979) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: neuropharmacological characteristics as derived from stimulus generalization experiments. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:535–546.
Cunningham KA, Callahan PM, Appel JB (1987) Discriminative stimulus properties of lisuride revisited: involvement of dopamine D-2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:147–151.
Jarbe TUC (1978) Cocaine as a discriminative cue in rats: interactions with neuroleptics and other drugs. Psychopharmacologia 59:183–187.
Jarbe TUC (1984) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: effects of apomorphine, haloperidol, procaine and other drugs. Neuropharmacology 23:899–907.
Kelle E, Nahorski SR (1987a) Endogenous dopamine functionally activates D-1 and D-2 receptors in striatum. J Neurochem 49:115–120.
Kelly E, Nahorski SR (1987b) Dopamine D-2 receptors inhibit D-1 stimulated cAMP accumulation in striatum but not limbic forebrain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 335:508–512.
Koob GF, Le HT, Creese I (1987) The D-1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH 23390 increases self-administration in the rat. Neurosci Lett 79:315–320.
Lehmann J, Briley M, Langer SZ (1983) Characterization of dopamine autoreceptor and [3H] spiperone binding studies in vitro with classical and novel dopamine receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 88:11–26.
Leone P, Chiara GD (1987) Blockade of D-1 receptors by SCH 23390 antagonizes morphine- and amphetamine-induced place preference conditioning. Eur J Pharmacol 135:251–254.
Longoni R, Spina L, Chiara GD (1987) Permissive role D-1 receptor stimulation for the expression of D-2 mediated behavioral response: a quantitative phenomenological study in rats. Life Sci 41:2135–2145.
Mashurano M, Waddington JL (1986) Stereotyped behavior in response to the selective D-2 dopamine receptor agonist RU 24213 is enhanced by pretreatment with the selective D-1 agonist SKF 38393. Neuropharmacology 25:947–949.
McKenna ML, Ho BT (1980) The role of dopamine in the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine. Neuropharmacology 19:297–303.
Nielsen EB, Jespen SA (1985) Antagonism of the amphetamine cue by both classical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 11:167–176.
Plantje JF, Dijcks FA, Verheijden PFHM, Stoof JC (1985) Stimulation of D-2 dopamine receptors in rat mesocortical areas inhibits the release of [3H] dopamine. Eur J Pharmacol 114:401–402.
Pugh MT, O'Boyle, Molloy AG, Waddington JL (1985) Effects of the putative D-1 antagonist SCH 23390 on stereotyped behavior induced by the D-2 agonist RU 24213. Psychopharmacology 87:308–312.
Robertson GS, Robertson HA (1986) Synergistic effects of D-1 and D-2 dopamine agonists on turning behavior in rats. Brain Res 384:387–390.
Saller CF, Salama AI (1985) Dopamine receptor subtypes: in vivo biochemical evidence for functional interaction. Eur J Pharmacol 109:297–300.
Saller CF, Salama AI (1986) D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptor blockade: interactive effects in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 236:714–720.
Schechter MD (1977) Amphetamine discrimination as a test for antiparkinsonism drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 44:51–56.
Schechter MD, Greer NL (1987) Evidence that the stimulus properties of apomorphine are mediated by both D-1 and D-2 receptor activation. Life Sci 40:2461–2471.
Setler PE, Saraw HM, Zirkle CL, Saunders HL (1978) The central effects of a novel dopamine agonist Eur J Pharmacol 50:419–430.
Stoof JC, Verheijden PFHM (1986) D-2 receptor stimulation inhibits cyclic AMP formation brought about by D-1 receptor stimulation in rat neostriatum but not nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharmacol 129:205–206.
Walters JR, Bergstrom DA, Carlson JH, Chase TN, Brown AR (1987) D-1 dopamine receptor activation required for postsynaptic expression of D-2 agonist effects. Science 236:719–722.
Weathersby RT, Appel JB (1986) Dopamine D-2 receptor mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of (LY 171555) quinpirole. Eur J Pharmacol 132:87–91.
White FJ (1987) D-1 dopamine receptor stimulation enables the inhibition of nucleus accumbens neurons by a D-2 receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 135:101–105.
Woolverton WL (1986) Effects of a D-1 and D-2 dopamine antagonist on the self-administration of cocaine and piribedil by Rhesus monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:531–535.
Woolverton WL, Kamien KB, Goldberg LI (1985) Effects or selective dopamine receptor agonists in rats trained to discriminate apomorphine from saline. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:577–581.
Zetterstrom T, Sharp T, Ungerstedt U (1986) Effect of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptor selective drugs on dopamine release and metaboism in rat striatum in vivo. Nauyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 334:117–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, F.L., John, C.S., Yang, T.F.T. et al. Role of specific dopamine receptor subtypes in amphetamine discrimination. Psychopharmacology 97, 501–506 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439555
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439555