Abstract
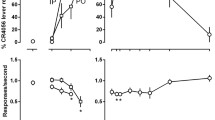
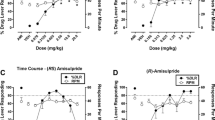
Rats (N=12) were trained to discriminate midazolam (1 mg/kg, IP) from vehicle in a food reinforced operant conditioning procedure. Midazolam, flunitrazepam, diazepam, chlordiazepoxide and pentobarbital showed dose-dependent substitution for midazolam. Buspirone and Ro 15-1788 did not substitute for midazolam. The midazolam cue was dose-dependently antagonized by Ro 15-1788. In rats (N=12) trained to discriminate chlordiazepoxide (3 mg/kg, IP) from vehicle midazolam, flunitrazepam, diazepam and chlordiazepoxide substituted completely and dose dependently for chlordiazepoxide. The relative potency of chlordiazepoxide and diazepam was three times less in the midazolam-trained animals than in the chlordiazepoxide-trained animals. Response rate and latency data further support the main finding that the midazolam cue is similar, but not identical to the cue of classical benzodiazepines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ator NA, Griffiths RR (1983) Lorazepam and pentobarbital drug discrimination in baboons: cross-drug generalization and interaction with Ro 15-1788. Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:776–782.
Ator NA, Griffiths RR (1986) Discriminative stimulus effect of atypical anxiolytics in baboons and rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:393–403.
Barry III H (1974) Classification of drugs according to their discriminative effects in rats. Fed Proc 33:1814–1824.
Colpaert FC, Desmedt LKC, Janssen PAJ (1976) Discriminative stimulus properties of benzodiazepines, barbiturates and pharmacologically related drugs: relation to some intrinsic and anticonvulsant effects. Eur J Pharmacol 37:113–123.
De Vry J, Slangen JL (1986a) Effects of chlordiazepoxide training dose on the mixed agonist-antagonist properties of benzodiazepine receptor antagonist Ro 15-1788 in a drug discrimination procedure. Psychopharmacology 88:177–183.
De Vry J, Slangen JL (1986b) Specificity of chlordiazepoxide discrimination as a function of alternative training condition. Psychopharmacology 89:S45.
Draper NR, Smith H (1981) Applied regression analysis, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Extance K, Goudie AJ (1981) Inter-animal olfactory cues in operant drug discrimination procedures in rats. Psychopharmacology 73:363–371.
Garcha HS, Rose IC, Stolerman IP (1985) Midazolam cue in rats: generalization tests with anxiolytic and other drugs. Psychopharmacology 87:233–237.
Garret C, Blanchard JC, Bardone MC, Julou L (1981) Discriminative properties of zopiclone in the rat. Eight International Congress of Pharmacology, Tokyo, Abstract 810
Hendry JS, Balster RL, Rosecrans JA (1983) Discriminative stimulus properties of buspirone compared to central nervous system depressants in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 19:97–101.
Herling S, Shannon HE (1982) Ro 15-1788 antagonizes the discriminative stimulus effects of diaepam in rats but not similar effects of pentobarbital. Life Sci 31:2105–2112.
Kuhn DM, Appel JB, Greenberg J (1974) An analysis of some discriminative properties of d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacologia 39:57–66.
McElroy JF, Feldman RS (1982) Generalization between benzodiazepine-and triazolopyridazine-elicited discriminative cues. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:709–713.
Pieri L, Schaffner R, Scherschlicht R, Polc P, Sepinwall J, Davidson A, Mohler H, Cumin R, Da Prada M, Burkhard WP, Keller HH, Muller RKM, Gerold M, Pieri M, Cook L, Haefely W (1981) Pharmacology of midazolam. Arzneimittelforschung Drug Res 31:2180–2201.
Rauch RJ, Stolerman IP (1987) Midazolam cue in rats: effects of drugs acting on GABA and 5-hydroxytryptamine systems, anticonvulsants and sedatives. J Psychopharmacol 2:71–80.
Shannon HE, Herling S (1983) Discriminative stimulus effects of diazepam in rats: evidence for a maximal effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:160–166.
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical methods, 7th edn. Iowa University Press, Iowa
Spealman RD (1985) Discriminative stimulus effects of midazolam in squirrel monkeys: comparison with other drugs and antagonism by Ro 15-1788. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:456–462.
Stolerman IP, D'Mello GD (1981) Role of training conditions in discrimination of central nervous system stimulants by rats. Psychopharmacology 73:295–303.
Stolerman IP, Garcha HS, Rose IC (1986) Midazolam cue in rats: effects of Ro 15-1788 and picrotoxin. Psychopharmacology 89:183–188.
Teal JJ, Holtzman SG (1980) Stimulus effects of morphine in the monkey: quantitative analysis of antagonism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:587–593.
Young R, Dewey WL (1982) Differentiation of the behavioural responses produced by barbiturates and benzodiazepines by the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788. In: Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) Drug discrimination: applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 235–240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woudenberg, F., Slangen, J.L. Discriminative stimulus properties of midazolam: comparison with other benzodiazepines. Psychopharmacology 97, 466–470 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439549
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439549