Abstract
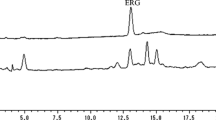
The mycotoxin, cyclopiazonic acid (CPA), was detected at concentrations as high as 9 ppm in 21 of 26 corn samples from a Bogor poultry feedmill. This is the first demonstration of the natural occurrence of CPA in Indonesia. CPA was always accompanied by other mycotoxins, especially aflatoxins, suggesting that the interactive toxicity of these mycotoxins to poultry should be investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allcroft R, Carnaghan RBA, Sargeant K, O'Kelly J. A toxic factor in Brazilian groundnut meal. Vet Rec 1961; 73:428–9.
Blaney BJ. Aflatoxin survey of maize from the 1978 crop in the South Burnett region of Queensland. Qld J Ag Amin Sc 1981; 38:7–11.
Blaney BJ, Moore CJ, Tyler AL. Mycotoxins and fungal damage in maize harvested during 1982 in Far North Queensland. Aust J Agric Res 1984; 35:463–71.
Blaney BJ, Ramsey MD, Tyler AL. Mycotoxins and toxigenic fungi in insect damaged maize harvested during 1983 in Farm North Queensland. Aust J Agric Res 1986; 37:235–44.
Cole RJ. Etiology of turkey ‘X’ disease in retrospect: a case for the involvement of cyclopiazonic acid. Mycotoxin Res 1986; 2:3–7.
Dorner JW, Cole RJ, Lomax LG, Gosser HS, Diener UL. Cyclopiazonic acid production by Aspergillus flavus and its effects on broiler chickens. Appl Envir Microbiol 1983; 46:698–703.
Dorner JW, Cole RJ, Diener UL. The relationship of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus with reference to production of aflatoxins and cyclopiazonic acid. Mycopathologia 1984; 87:13–5.
Dutton MF, Westlake K. Occurrence of mycotoxins in cereals and animal feedstuffs in Natal, South Africa. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 1985; 68:839–42.
Gallagher RT, Richard JL, Stahr HM, Cole RJ. Cyclopiazonic acid production by aflatoxigenic and non-aflatoxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus. Mycopathologia 1978; 66:31–6.
Ginting N. Variasi kejadian dan kandungan aflatoksin pada jagung yang bersumber dari Tegal, Thailand dan Lampung pada satu pabrik makanan ternak di Bogor. Penyakit Hewan 1986; 18:79–81.
Hetzel DJS, Hoffman D, Van de Ven J, Soeripto S. Mortality rate and liver histopathology in four breeds of chicks following long term exposure to low level of aflatoxin. Sing Vet J 1984; 8:6–14.
Hinton DM, Morrissey RE, Norred WP, Cole RJ, Dorner J. Effects of cyclopiazonic acid on the ultrastructure of rat liver. Toxicol Lett 1985; 25:211–8.
Huff WE, Doerr JA. Synergism between aflatoxin and ochratoxin A in broiler chickens. Poultry Sci 1981; 60:550–5.
Lansden JA. Liquid chromatographic analysis system for cyclopiazonic acid in peanuts. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 1984; 67:728–31.
Lansden JA. Determination of cyclopiazonic acid in peanuts and corn by thin layer chromatography. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 1986; 69:964–6.
Lansden JA, Davidson JL. Occurrence of cyclopiazonic acid in peanuts. Appl Envir Microbiol 1983; 45:766–9.
Le Bars J. Cyclopiazonic acid production by Penicillium camemberti Thom and natural occurrence of this mycotoxin in cheese. Appl Envir Microbiol 1979; 38:1052–5.
Lee Y-W, Mirocha CJ, Shroeder DJ, Walser MM: TDP-1, a toxic component causing tibial dyschondroplasia in broiler chickens, and trichothecenes from Fusarium roseum ‘Gaminearum’. Appl Environ Microbiol 1985; 50:102–7.
Lindenfelser LA, Lillehoj EB, Burmeister HR. Aflatoxin and trichothecene toxins: skin tumor induction and synergistic toxicity in white mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 1974; 52:113–6.
Lomax LG, Cole RJ. Effects of cyclopiazonic acid on poultry and swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc 1983; 183:349.
Lomax LG, Cole RJ, Dorner JW. The toxicity of cyclopiazonic acid in weaned pigs. Vet Pathol 1984; 21:418–24.
Morrisey RE, Norred WP, Cole RJ, Dorner J. Toxicity of the mycotoxin, cyclopiazonic acid, to Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1985; 77:94–107.
Morrissey RE, Norred WP, Hinton DM. Combined effects of the micotoxins aflatoxin B1 and cyclopiazonic acid on Sprague-Dawley rats. Fd Chem Toxic 1987; 25:837–42.
Muhilal, Karyadi D. Aflatoxin in nuts and grains. Gizi Indonesia 1985; 10:75–9.
Nuehring LP, Rowland GN, Harrison LR, Cole RJ, Dorner JW: Cyclopiazonic acid mycotoxicosis in the dog. Am J Vet Res 1985; 46:1670–6.
Purchase IFH. The acute toxicity of the mycotoxin cyclopiazonic acid to rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1971; 18:114–23.
Rao LB, Husain A. Presence of cyclopiazonic acid in kodo millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum) causing ‘kodua poisoning’ in man and its production by associated fungi. Mycopathologia 1985; 89:177–80.
Rathinavelu A, Shanmugasundaram ERB. Simple colorimetric estimation of cyclopiazonic acid in contaminated food and feeds. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 1984; 67:38–40.
Richard JL, Peden WM, Fichtner RE, Cole RJ. Effect of cyclopiazonic acid on delayed hypersensitivity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, complement activity, serum enzymes, and bilirubin in guinea pigs. Mycopathologia 1986; 96:73–7.
Sansing GA, Lillehoj EB, Detroy RW, Miller MA. Synergistic toxic effects of citrinin, ochratoxin A and penicillic acid in mice, Toxicon 1976; 14:213–20.
Stoltz DR. Carcinogenic and mutagenic mycotoxins. In: Stich, HF, ed. Carcinogens and mutagens in the environment, vol. III, Naturally occurring compounds. Florida: CRC Press, Inc 1983:129–36.
Sutton JC. Epidemiology of wheat head blight and maize ear rot caused by Fusarium graminearum. Can J Plant Pathol 1982; 4:195–209.
Trucksess MW, Mislivec PB, Young K, Brace VR, Page SW. Cyclopiazonic acid production by cultures of Aspergillus and Penicillium species isolated from dried beans, corn meal, macaroni, and pecans. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 1987;. 70:123–6.
Van Rensburg SJ. Subacute toxicity of the mycotoxin cyclopiazonic acid. Fd Chem Toxic 1984; 22:993–8.
Widiastuti R, Maryam R, Salfina, Blaney BJ, Stoltz DR. Corn as a source of mycotoxins in Indonesian poultry feeds and the effectiveness of visual examination methods for detecting contamination. Mycopathologia 1988; 102:45–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Widiastuti, R., Maryam, R., Blaney, B.J. et al. Cyclopiazonic acid in combination with aflatoxins, zearalenone and ochratoxin A in Indonesian corn. Mycopathologia 104, 153–156 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437430
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437430