Abstract
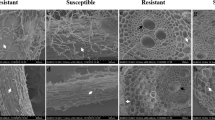
Seedlings of an inbred line of male-fertile corn possessing the gene rhm for resistance to Southern corn leaf blight were inoculated with conidia of Helminthosporium maydis race O. Histological observations at 1 day revealed that lesions were comprised of several dead mesophyll cells bordered by a pair of vascular bundles. By 4 days, lesions had only spread to a width of three vascular bundles. Ultrastructural observations revealed that although mesophyll cells degenerated at an early stage, bundle sheath and phloem cells remained intact even in 4-day-old lesions. It appears that the gene rhm imparts a resistance to bundle sheath and phloem cells against toxic substances released by the fungus. Addition key words: Zea mays L., ultrastructure, gene rhm, Southern corn leaf blight.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanchard, R. O., 1973. Two cytological responses in corn resistant to Helminthosporium maydis. Can. J. Bot. 51: 2520–2521.
Brotzman, H. G., Calvert, O. H., White, J. A. & Brown, M. F., 1975. Southern corn leaf blight: ultrastructure of host-pathogen association. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 7: 209–211.
Graig, J. & Daniel-Kalio, L. A., 1968. Chlorotic lesion resistance to Helminthosporium maydis in maize. Plant Dis. Rep. 52: 134–136.
Evert, R. F., Eschrich, W. & Heyser, W., 1978. Leaf structure in relation to solute transport and phloem loading in Zea mays L. Planta 138: 279–294.
Jennings, P. R. & Ullstrup, A. J., 1957. A histological study of three Helminthosporium leaf blights of corn. Phytopathology 47: 707–714.
Pate, J. B. & Harvey, P. H., 1954. Studies on the inheritance of resistance in corn to Helminthosporium maydis leaf spot. Agron. J. 46: 442–445.
Smith, D. R. & Hooker, A. L., 1973. Monogenic chloroticlesion resistance in corn to Helminthosporium maydis. Crop Sci. 13: 330–331.
Smith, D. R., 1975. Expression of monogenic chloroticlesion resistance to Helminthosporium maydis in corn. Phytopathology 65: 1160–1165.
Toth, R. & Smith, D. R., 1980. Histopathological changes in susceptible corn leaves inoculated with Helminthosporium maydis race O. Mycopathologia.
Walsh, M. A., 1974. Late-formed metaphloem sieve elements in Zea mays L. Planta 121: 17–25.
White, J. A., Calvert, O. H. & Brown, M. F., 1973. Ultrastructural changes in corn leaves after inoculation with Helminthosporium maydis race T. Phytopathology 63: 296–300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, D.R., Toth, R. Histopathological changes in resistant (rhm) corn inoculated with Helminthosporium maydis race O. Mycopathologia 77, 83–88 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437388
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437388