Abstract
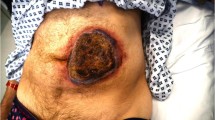
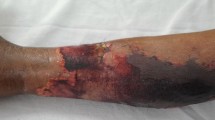
We report the unusual complication of focal necrotizing skin lesions accompanied by moderate thrombocytopenia in a female patient undergoing thromboprophylaxis with low-molecular-weight heparin after total knee arthroplasty. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia was suspected and confirmed using the heparin-induced platelet activation assay. The skin lesions improved gradually after the discontinuation of heparin application. In addition to the description of this exceptionally rare adverse effect of low-molecular-weight heparin, a brief discussion of previously reported cases is provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balestra B, Quadri P, Biasiutti FD et al (1994) Low molecular weight heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and skin necrosis distant from injection sites. Eur J Haematol 53:61–63
Cordoliani F, Saiag P, Guillaume J-C et al (1987) Nécroses cutanées étendues induites par la fraxiparine. Ann Dermatol Venereol 114:1366–1368
Cunningham M, Torrente A de, Ekeo JM et al (1984) Vascular spasm and gangrene during heparin-dihydroergotamine prophylaxis. Br J Surg 71:829–831
Cziraky MJ, Spinler SA (1993) Low-molecular-weight heparins for the treatment of deep-vein thrombosis. Clin Pharm 12:892–899
Eby CS (1993) Warfarin-induced skin necrosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 7:1291–1300
Eichinger S, Kyrle PA, Brenner B et al (1991) Thrombocytopenia associated with low-molecular-weight heparin. Lancet 337:1425–1426
Greinacher A, Michels I, Kiefel V et al (1991) A rapid and sensitive test for diagnosing heparin-associated thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost 66:734–736
Hirsh J (1993) Low molecular weight heparin. Thromb Haemost 70:204–207
Lieberman JR, Geerts WH (1994) Prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 76:1239–1250
Manoharan A (1993) Heparin-induced skin reaction with low molecular weight heparin. Eur J Haematol 84:349–350
Montserrat I, Lopez D, Zuazu-Jausoro I et al (1990) Low-molecular-weight subcutaneous heparin-induced skin necrosis. Blood Coag Fibrinol 1:751–752
Ojeda E, Perez MC, Mataix R et al (1992) Skin necrosis with a low molecular weight heparin. Br J Haematol 83:620
Phillips JK, Majumdar G, Hunt BJ et al (1993) Heparin-induced skin reaction due to two different preparations of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH). Br J Haematol 84:349–350
Rem JA, Gratzl O, Follath F et al (1987) Ergotism as complication of thromboembolic prophylaxis with heparin-dihydroergotamine. Lancet 1:219
Warkentin TE, Kelton JG (1989) Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Ann Rev Med 40:31–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plath, J., Schulze, R., Barz, D. et al. Necrotizing skin lesions induced by low-molecular-weight heparin after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 116, 443–445 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00434012
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00434012