Abstract
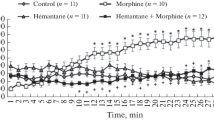
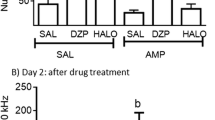
The influence of lisuride on naloxone-induced withdrawal signs (wet shakes, escape attempts) was studied in morphine-dependent rats. Lisuride, injected IP at doses of 12.5 and 25 μg/kg, inhibited wet shakes while not significantly altering escape attempts induced by naloxone (4 mg/kg IP). At higher doses (50 and 100 μg/kg IP), lisuride's inhibitory effect on wet shakes persisted while escape attempts were actually potentiated with respect to control withdrawal rats. Increases in aggressive behavior were seen at all doses, and were dose-related. Haloperidol (0.3 mg/kg IP), administered 40 min before lisuride, did not modify the antagonistic effect on wet shakes, unlike sulpiride (40 mg/kg IP 30 min before lisuride), but at the same time blocked the increase in escape attempts and aggressiveness induced by lisuride. We suggest that lisuride modulates withdrawal signs by stimulation of dopamine receptors in the CNS. The effect of the dopamine mimetic N-n-propylnorapomorphine (NPA) on the same variables is reported as well as the influence of haloperidol on NPA, and a comparison between the effects of the two drugs is made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ary M, Cox B, Lomax P (1977) Dopaminergic mechanisms in precipitated withdrawal in morphine-dependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 200:271–276
Baggio G, Ferrari F (1980) Role of brain dopaminergic mechanisms in rodent aggressive behavior: Influence of (+)N-n-propylnor-apomorphine on three experimental models. Psychopharmacology 70:63–68
Benassi-Benelli A, Ferrari F (1979) Comparazione tra apomorfina ed N-n-propylnorapomorfina per l'induzione della sindrome di stiramento e sbadiglio, di erezione peniena e di stereotipie nel ratto. Riv Farmacol Ter 10:121–137
Benassi-Benelli A, Ferrari F, Pellegrini Quarantotti B (1979) Penile erection induced by apomorphine and N-n-propylnorapomorphine in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 242:241–247
Gianutsos G, Hynes MD, Puri SK, Drawbaugh RB, Lal H (1974) Effect of apomorphine and nigrostriatal lesions on aggression and striatal dopamine turnover during morphine withdrawal: Evidence for dopaminergic supersensitivity in protracted abstinence. Psychopharmacologia 34:37–44
Herz A, Bläsig J, Papeschi R (1974) Role of catecholaminergic mechanisms in the expression of the morphine abstinence syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia 39:121–143
Iwamoto ET, Loh HH, Way EL (1976) Circling behavior after narcotic drugs and during naloxone-precipitated abstinence in rats with unilateral nigral lesions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:503–516
Lal H, Puri SK, Karkalas Y (1971) Blockade of opioid-withdrawal symptoms by haloperidol in rats and humans. Pharmacologist 13:263
Lal H, Numan R (1976) Blockade of morphine-withdrawal body shakes by haloperidol. Life Sci 18:163–168
Lison L (1961) Statistica applicata alla biologia sperimentale. Casa editrice Ambrosiana, Milan
Maggiolo C, Huidobro F (1961) Administration of pellets of morphine to mice: Abstinence syndrome, Acta Physiol Lat Am 11:70–78
Martin WR, Sloan JW (1977) Neuropharmacology and neurochemistry of subjective effects, analgesia, tolerance and dependence produced by narcotic analgesics. In: Martin WR (ed) Drug addiction, vol 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 43–158
Maruyama Y, Takemori AE (1973) The role of dopamine and norepinephrine in the naloxone-induced abstinence of morphine-dependent mice. J. Pharmacol Exp Ther 185:602–608
Schwartz AS, Eidelberg E (1970) Role of biogenic amines in morphine dependence. Life Sci 9:613–624
Spano PF, Stefanini E, Trabucchi M, Fresia P (1979) Stereospecific interaction of sulpiride with striatal and nonstriatal dopamine receptors. In: Spano PF, Trabucchi M, Corsini GU, Gessa GL (eds) Sulpiride and other benzamides. Italian Brain Research Foundation, Milan, pp 11–13
Tseng LF, Loh HH, Wei ET (1975) Effects of clonidine on morphine withdrawal signs in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 30:93–99
Wei E, Loh HH, Way EL (1973) Quantitative aspects of precipitated abstinence in morphine-dependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 184:398–403
Wei E, Tseng LF, Loh HH, Way EL (1974) Similarity of morphine abstinence signs to thermoregulatory behaviour. Nature 247:398–400
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrari, F., Baggio, G. Influence of lisuride on morphine withdrawal signs in the rat: A dopamine-mimetic effect. Psychopharmacology 78, 326–330 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433735
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433735