Abstract
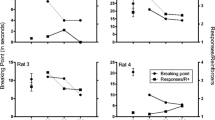
d-Amphetamine (0.5 and 1.0 mg/kg) and dl-fenfluramine (2.0 and 4.0 mg/kg) reduced food intake in a short exposure feeding test, and their effects were counteracted by chlordiazepoxide, particularly at 5.0 mg/kg. Chlordiazepoxide reduced latency to eat, extended the duration of feeding and depressed the rate of feeding. Antagonism occurred in combination with d-amphetamine in relation to latency and duration, but in this experiment d-amphetamine did not affect feeding rate. Antagonism also occurred in combination with fenfluramine, with latency and duration measures, but only at the lower chlordiazepoxide dose. Instead, chlordiazepoxide (10.0 mg/kg) enhanced fenfluramine's effects to reduce feeding duration and feeding rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah AH, White HD, Kulkarni AS (1974) Interaction of d-amphetamine with central nervous system depressants on food intake and spontaneous motor activity of mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 26:119–121
Antelman SM, Caggiula AR, Black CA, Edwards DJ (1978) Stress reverses the anorexia induced by amphetamine and methylphenidate but not fenfluramine. Brain Res 143:580–585
Blundell JE, Latham CJ (1978) Pharmacological manipulations of feeding behavior: Possible influences of serotonin and dopamine on food intake. In: Garattini S, Samanin R (eds) Central mechanisms of anorectic drugs. Raven Press, New York, p 83
Blundell JE, Latham, CJ (1979) Pharmacology of food and water intake. In: Brown K, Cooper SJ (eds) Chemical influences on behaviour. Academic Press, London, p 201
Borella LE, Paquette R, Herr F (1969) The effect of some CNS depressants on the hypermotility and anorexia induced by amphetamine in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 47:841–847
Braestrup C, Squires RF (1977) Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterised by high affinity 3H-diazepam binding Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3805–3809
Burton, MJ, Cooper, SJ, Popplewell DA (1980) Fenfluramine: continuous monitoring of its effects on feeding and drinking in rats. Br J Pharmacol 68:157–158
Cooper SJ (1979) Behavioural studies of drug interactions. In: Brown K, Cooper SJ (eds) chemical influences on behaviour. Academic Press, London, p 553
Cooper SJ (1980) Benzodiazepines as appetite-enhancing compounds. Appetite 1:7–19
Cooper SJ, Francis RL (1979) Feeding parameters with two food textures after chlordiazepoxide administration, alone or in combination with d-amphetamine or fenfluramine. Psychopharmacology 62:253–259
Cooper SJ, Sweeney KF (1980) Effects of spiperone alone and in combination with anorectic agents on feeding parameters in the rat. Neuropharmacology (in press)
Costa E, Guidotti A (1979) Molecular mechanisms in the receptor action of benzodiazepines. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 19:531–545
Fratta W, Mereu G., Chessa, P, Paglietti E, Gessa G (1976) Benzodiazepine-induced voraciousness in cats and inhibition of amphetamine-anorexia. Life Sci 18:1157–1166
Lidbrink P, Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Olson L (1973) The effects of benzodiazepines, meprobamate, and barbiturates on central monoamine neurons. In: Garattini S, Mussini E, Randall LO (eds) The benzodiazepines. Raven, New York, p 203
Möhler H, Okada T (1977) Properties of 3H-diazepam binding to benzodiazepine receptors in the rat cerbral cortex. Life Sci 20:2101–2110
Nakamura M, Fukushima H (1977) Effects of benzodiazepines on central serotonergic neuron systems. Psychopharmacology 53:121–126
Randall LO, Schallek W, Heise GA, Keith EF, Bagdon RE (1960) The psychosedative properties of methaminodiazepoxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 129:163–171
Soubrié P, Kulkarni S, Simon P, Boissier JR (1975) Effects des anxiolytiques sur la prise de nourriture de rats et de souris placés en situation nouvelle ou familière. Psychopharmacologia 45:203–210
Stein L, Wise CD, Berger BD (1973) Antianxiety action of benzodiazepines: Decrease in activity of serotonin neurons in the punishment system. In: Garattini S, Mussini M, Randall LO, (eds) The benzodiazepines. Raven, New York, p 299
Wiepkema PR (1971) Behavioural factors in the regulation of food intake. Proc Nutr Soc 30:142–149
Wise CD, Berger BD, Stein L (1972) Benzodiazepines: Anxietyreducing activity by reduction of serotonin turnover in the brain. Science 177:180–183
Wise RA, Dawson V (1974) Diazepam-induced eating and leverpressing for food in sated rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol 86:930–941
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, S.J., Francis, R.L. Interactions of chlordiazepoxide and anorectic agents on rate and duration parameters of feeding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 69, 261–265 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433092
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433092