Abstract
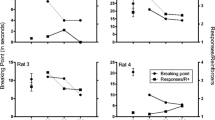
The effects of caffeine (1–100 mg/kg, IP), (-)N-((R)-1-methyl-2-phenylethyl)-adenosine (PIA) (0.01–1 mg/kg, IP), and of the two drugs in combination were studied in mice responding under a mult FR30 FI600 s schedule of food presentation. The lowest dose of caffeine, 1 mg/kg, had no effect on responding under either component of the mult schedule. Intermediate doses of caffeine (3 and 10 mg/kg) slightly increased responding under the FI component, while higher doses decreased responding. Caffeine only decreased responding, at doses above 30 mg/kg, under the FR component. PIA decreased responding under both components of the mult schedule in a dose-dependent, and similar, manner. In most cases, the rate-increasing effect of caffeine on FI responding was diminished when combined with a rate-decreasing dose of PIA. However, when 0.01 mg/kg PIA, a dose that had no effect alone, was combined with 3 mg/kg caffeine, the increase in rate exceeded that of caffeine alone. Rate-deceasing effects of PIA were antagonized by caffeine; with larger doses of PIA, larger doses of caffeine were required for antagonism. Thus, while the rate-increasing effects of caffeine can be either enhanced or diminished, when combined with different doses of PIA, the rate-decreasing effects of PIA are clearly antagonized by caffeine in a dose-dependent manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coffin VC, Carney J (1983) Behavioral pharmacology of adenosine analogs. In: Daly JW, Kuroda Y, Phillis JW, Shimizu H, Ui M (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of adenosine derivatives, Raven Press, New York, pp 267–274
Daly JW (1983) Role of ATP and adenosine receptors in physiologic processes: summary and prospectus. In: Daly JW, Kuroda Y, Phillis JW, Shimizu H, Ui M (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of adenosine derivatives, Raven Press, New York, pp 275–290
Davis TRA, Kensler JJ, Dews PB (1973) Comparison of behavioral effects of nicotine, d-amphetamine, caffeine and dimethylheptyl tetrahydrocannabinol in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacologia 32:51–65
Dews PB (1958) Studies on behavior. IV. Stimulant actions of methamphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 122:137–147
Katims JJ, Annau Z, Snyder SH (1983) Interactions in the behavioral effects of methylxanthines and adenosine derivatives. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:167–173
Kelleher RT, Morse WH (1968) Determinants of the specificity of the behavioral effects of drugs. Ergebnisse der Physiologic 60:1–56
Meliska CJ, Brown RE (1982) Effects of caffeine on schedulecontrolled responding in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 16:745–750
McKim WA (1980) The effects of caffeine, theophylline and amphetamine on operant responding of the mouse. Psychopharmacology 68:135–138
McMillan DE (1968) Some interactions between sympathomimetic amines and amine-depleting agents on schedule-controlled behavior of the pigeon and squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 163:172–187
Sattin A, Rall TW (1970) The effect of adenosine and adenosine nucleotides on the adenosine 3′,5′-phosphate content of guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol 6:12–23
Snyder SH, Katims JJ, Annau Z, Bruns RF, Daly JW (1981) Adenosine receptors and the behavioral actions of methylxanthines. Proc Natl Acad Sci 78:3260–3264
Vapaatalo H, Ohken D, Neuvonen PJ, Westerman E (1975) Stereospecificity in some central and circulatory effects of phenylisopropyl-adenosine (PIA). Arzneim-Forsch 25:407–410
Wenger GR, Dews PB (1976) The effects of phencyclidine, ketamine, d-amphetamine and pentobarbital on schedule-controlled behavior in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 196:616–623
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glowa, J.R., Sobel, E., Malaspina, S. et al. Behavioral effects of caffeine, (-)N-((R)-1-methyl-2-phenylethyl)-adenosine (PIA), and their combination in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 87, 421–424 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432506
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432506