Abstract
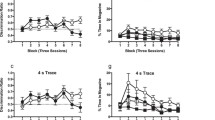
Rats were trained to perform light-dark discrimination learning for a period of 6 consecutive days. GABA, an inhibitory transmitter, was administered into the lateral ventricle either immediately or 60 min after the completion of each training session. GABA, in dose levels of 100 and 150 μg and injected immediately after the completion of the session, significantly increased correct responses in comparison with the corresponding control group, while 200 μg of the drug had no further effect on the correct responses. When the administration of the drug was delayed by 60 min, neither 100 nor 150 μg of GABA significantly increased correct response. Intraventricular GABA did not affect total activity or water intake, which could be considered indexes corresponding to motility and motivational state, respectively. It was concluded that under these conditions GABA improves discrimination learning by its action as an inhibitory transmitter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agranoff, B. W., Davis, R. E., Brink, J. J.: Chemical studies on memory fixation in goldfish. Brain Res. 1, 303–309 (1966)
Barondes, S. H.: Agents that block memory. In: The neurosciences, G. C. Quarton, T. Melnechuk, and F. O. Schmitt, eds., pp. 756–764. New York: The Rockefeller University Press 1967
Curtis, D. R., Phillis, J. W., Watkins, J. C.: The depression of spinal neurons by γ-amino-n-butyric acid and β-alanine. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 146, 185–203 (1959)
Eccles, J. C., Schmidt, R., Willis, W. D.: Pharmacological studies on presynaptic inhibition. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 168, 500–530 (1963)
Engberg, I., Thaller, S.: On the interaction of picrotoxin with GABA and glycine in the spinal cord. Brain Res 19, 151–154 (1970)
Garg, M., Holland, H. C.: Consolidation and maze learning: a comparison of several post-trial treatments. Life Sci. 6, 1987–1997 (1967)
Hydén, H.: Biochemical changes accompanying learning. In: The neurosciences G. C. Quarton, T. Melnechuk, and F. O. Schmitt, eds., pp. 765–771. New York: The Rockefeller University Press 1967
Ishikawa, K.: Time requirement for memory consolidation. Nihon Univ. J. Med. 17, 19–29 (1975)
Ishikawa, K., Saito, S.: Differences in the effects of post-trial chlorpromazine reserpine, and amphetamine on discrimination learning in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 48, 45–51 (1976)
Iwama, K., Jasper, H. H.: The action of γ-aminobutyric acid upon cortical electrical activity in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 138, 365–380 (1957)
Kornhuber, H. H.: Neural control of input of long term memory: limbic system and amnestic syndrome in man. In: Memory and transfer of information, H. P. Zippel, ed. pp. 1–22. New York: Plenum Press 1973
Krnjević, K.: Chemical nature of synaptic transmission in vertebrates. Physiol. Rev. 54, 418–540 (1974)
McGaugh, J. L.: Drug facilitation of learning and memory. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 13, 229–241 (1973)
McGaugh, J. L., Petrinovich, L. F.: Effects of drugs on learning and memory. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 8, 135–149 (1965)
Obata, K., Highstein, S. M.: Blocking by picrotoxin of both vestibular inhibition and GABA action on rabbit oculomotor neurons. Brain Res. 18, 538–541 (1970)
Roberts, E.: γ-Aminobutyric acid and nervous system function—a perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23, 2637–2649 (1974)
Sherwood, N. M., Timiras, P. S.: A stereotaxic atlas of the developing rat brain. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press 1970
Squire, L. R., Barondes, S. H.: Inhibition of cerebral protein or RNA synthesis and memory. In: Macromolecules and behavior, 2nd ed., J. Gaito, ed., pp. 61–82. New York: Appletion-Century-Crofts 1972
Squire, L. R., Barondes, S. H.: Anisomycin, like other inhibitors of cerebral protein synthesis, impairs ‘long-term’ memory of a discrimination taks Brain Res. 66, 301–308 (1974)
Yamamoto, T.: Studies on the central effects produced by the intra-cerebral injections of various drugs and its analysis in mice. Pharmacometrics 5, 891–904 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, K., Saito, S. Effect of intraventricular γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on discrimination learning in rats. Psychopharmacology 56, 127–132 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431837
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431837