Summary
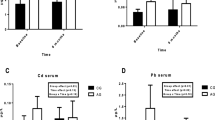
Twelve voluntary adult subjects twice took a 30-min sauna bath, at a temperature of 80‡ C with a 30-min rest between each, every 12 h for 1 week. Measurements of serum iron, copper, zinc, ferritin and ceruloplasmin were performed before the experiment, after the first and second 30 min in the sauna and at the end of the week. The first two sauna baths did not significantly change the concentrations of the trace elements measured. After the week the mean serum copper concentration had decreased from 15.0 (SD 1.7) Μmol·l−1 to 13.5 (SD 2.0) Μmol·l−1 (p<0.02). The mean zinc concentration decreased from 13.8 (SD 2.4) Μmol·l−1 to 9.8 (SD 1.8) Μmol·l−1 (p<0.001) during the week of the experiment. At the beginning of the study period two subjects had zinc concentrations below the reference values and after the week nine subjects had zinc concentrations below the reference values. The concentration of serum ferritin decreased from 142.2 (SD 103) Μg·l−1 to 111.3 (SD 89) Μg·l−1 (p<0.02) whereas the values of ceruloplasmin remained unchanged. Our findings confirm the earlier suggestion that heavy exposure to heat can cause a loss of some trace elements, especially zinc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coltman CA, Rowe NJ (1966) The iron content of sweat in normal adults. Am J Clin Nutr 18: 270–274
Golden MHN, Golden BE (1981) Trace elements. Potential importance in human nutrition with particular reference to zinc and vanadium. Br Med Bull 37: 31–36
Hess FM, King JC, Margen S (1977) Zinc excretion in young women on low zinc intakes and oral contraceptive agents. J Nutr 107: 1610–1620
Hietala J, Nurmi T, Uhari M, Pakarinen A, Kouvalainen K (1982) Acute phase proteins, humoral and cell mediated immunity in environmentally-induced hyperthermia in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 49: 271–276
Hohnadel DC, Sunderman FW, Nechay MW, McNeely MD (1973) Atomic absorption spectrometry of nickel, copper, zinc, and lead in sweat collected from healthy subjects during sauna bath. Clin Chem 19: 1288–1292
Mancini G, Garbonara AO, Heremans JF (1965) Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry 2: 235–254
Mitchell HH, Hamilton TS (1949) The dermal excretion under controlled environmental conditions of nitrogen and minerals in human subjects, with particular reference to calcium and iron. J Biol Chem 178: 345–354
Prasad AS, Schulert AR, Sandstead HH, Miale A, Farid A (1963) Zinc, iron, and nitrogen content of sweat in normal and deficient subjects. J Lab Clin Med 62: 84–89
Ritchey SJ, Korslund MK, Gilbert LM, Fay DC, Robinson MF (1979) Zinc retention and losses of zinc in sweat by preadolescent girls. Am J Clin Nutr 32: 799–803
Ruutu R (1975) Determination of iron and unsaturated ironbinding capacity in serum with ferrozine. Clin Chim Acta 61: 229–232
Solomons NW, Layden TJ, Rosenberg IH, Vo-Khactu K, Sandstead HH (1976) Plasma trace metals during total parenteral alimentation. Gastroenterology 70: 1022–1025
Varo P, Koivistoinen P (1980) Mineral element composition of Finnish foods. Acta Agr Scand [Suppl] 22: 165–171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Sigrid Juselius Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uhari, M., Pakarinen, A., Hietala, J. et al. Serum iron, copper, zinc, ferritin, and ceruloplasmin after intense heat exposure. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 51, 331–335 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00429069
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00429069