Abstract
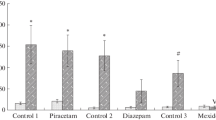
In a single session, naive female 250-g Wistar rats were trained to remain for 3 min on a platform located above an electrifiable grid. During training, animals were shocked (4 mA) after they stepped down. Retention of the step-down avoidance was tested 24 h later in rats treated SC 30 min before the session with saline or a subconvulsive dose of metrazol (40 mg/kg). During the retention test no shock was delivered. The latency to step down and the time on the grid were recorded. The metrazol rats significantly failed to retain the avoidance task. Groups of six rats per dose were trained and 24 h later pretreated, 5 min before metrazol, with an IP injection of the following antiepileptics (dose range in mg/kg): Ethosuximide (20–320); trimethadione (20–320); clonazepam (0.04–0.63); sodium valproate (20–320); carbamazepine (1.25–20); phenobarbital (5–80); or diphenylhydantoin (5–80); or a high dose of haloperidol (0.16) and amphetamine (0.63). Only ethosuximide, trimethadione, and clonazepam significantly increased the latency to step down and significantly shortened the time on the grid. Sodium valproate only shortened the time spent on the grid. The results suggest that only anti-petit mal drugs antagonize the retention impairment of passive avoidance produced by metrazol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Browne, T. R., Penry, J. K.: Benzodiazepines in the treatment of epilepsy. A review. Epilepsia 14, 277–310 (1973)
Desmedt, L. K. C., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Lewi, P. J., Janssen, P. A. J.: Antagonism of maximal metrazol seizures in rats and its relevance to an experimental classification of antiepileptic drugs. Arzneim. Forsch. 26, 1592–1602 (1976)
Gastaut, H., Roger, J., Lob, H.: Medical treatment of epileptic diseases. In: International encyclopedia of pharmacology and therapeutics, vol. 2, C. Radouco-Thomas, ed., pp. 535–599. Oxford: Pergamon 1973
Jeavons, P. N., Clark, J. E.: Sodium valproate in treatment of epilepsy. Br. Med. J. 2, 584–586 (1974)
Krall, R. L., Penry, J. K., White, B. G., Kupferberg, H. J., Swinyard, E. A.: Antiepileptic drug development: Anticonvulsant drug screening. Epilepsia 19, 409–428 (1978)
Kurtz, P., Palfai, T.: State-dependent learning produced by metrazol. Physiol. Behav. 10, 91–95 (1973)
MacLeod, C. N., Dekaban, A. S., Hunt, E.: Memory impairment in epileptic patients. Selective effects of phenobarbital concentration. Science 202, 1102–1104 (1978)
Martin, D., Hirt, H. R.: Clinical experience with clonazepam (Rivotril) in the treatment of epilepsies in infancy and childhood. Neuropaediatrie 4, 245–266 (1973)
Myslobodsky, M.: Petit mal epilepsy. A search for the precursors of wave-spike activity. New York-San Francisco-London: Academic 1976
Pinder, R. M., Brogden, R. N., Speight, T. M., Avery, G. S.: Clonazepam: A review of its pharmacological properties of therapeutic efficacy in epilepsy. Drugs 12, 321–361 (1976)
Pinder, R. M., Brogden, R. N., Speight, T. M., Avery, G. S.: Sodium valproate: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in epilepsy. Drugs 13, 81–123 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clincke, G., Wauquier, A. Metrazol-produced impairment of passive avoidance retention specifically antagonized by anti-petit mal drugs. Psychopharmacology 66, 243–246 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428313
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428313