Abstract
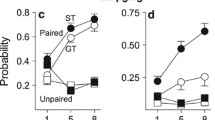
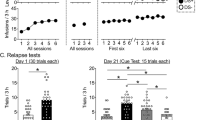
A two-choice discrimination task was used to evaluate the effects of psychoactive drugs on the discriminative stimulus properties of brain self-stimulation in rats. In these experiments, brain stimulation served both as a discriminative stimulus and as a reinforcing stimulus, but the two effects were manipulated separately. Animals were trained to a criterion of 95% correct in choosing between two levers, and when this levels of accuracy was reached, the ability to choose correctly remained stable over an 8-month period. Increasing the current strength of the discriminative stimulus from zero to 100% of the training current produced a graded increase in the number of trials completed on the appropriate lever. The discriminative effects produced by brain stimulation were evaluated pharmacologically by using three prototypical psychoactive drugs in an attempt to change the detection threshold for the discriminative stimulus. Morphine, d-amphetamine, and haloperidol, drugs that reliably alter reinforcement thresholds for brain stimulation, failed to change detection thresholds. These results demonstrated that: (1) brain stimulation produces potent and reliable discriminative effects and (2) the effects of psychoactive drugs on detection thresholds can be dissociated from their effects on reinforcement thresholds for brain stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Clincke GHC, Fransen JF, Wauquier A (1982) Drug induced changes of brain self-stimulation using a discrimination paradigm. In: Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology, Elsevier Biomedical, Amsterdam, pp 381–389
Colpaert FC, Rosecrans JA (1978) Stimulus properties of drugs: Ten years of progress, Elsevier Biomedical, Amsterdam
Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (1982) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier Biomedical, Amsterdam
Colpaert FC, Maroli AN, Meert T (1982) Parametric effects in the discrimination of intracranial stimulation: some methodological and analytical issues. Physiol Behav 28:1047–1058
Doty RW (1969) Electrical stimulation of the brain in behavioral context. Annu Rev Psychol 20:289–320
Hirschhorn ID, Hays RL, Rosecrans JA (1975) Discriminative control of behavior by electrical stimulation of the dorsal raphe nucleus: Generalization to lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Brain Res 86:134–138
Ho BT, Richards DW, Chute DL (1978) Drug discrimination and state-dependent learning. Academic, New York
Hodos W, Valenstein ES (1960) Motivational variables affecting the rate of behavior maintained by intracranial stimulation. J Comp Physiol Psychol 53:502–508
Kirk RE (1968) Experimental design: Procedures for the behavioral sciences. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, California
Ksir C, Slifer B (1982) Drug effects on discrimination performance at two levels of stimulus control. Psychopharmacology 76:286–290
Kornetsky C, Esposito RU (1981) Reward and detection thresholds for brain stimulation: dissociative effects of cocaine. Brain Res. 209:496–500
Lal H (1977) Disriminative stimulus properties of drugs. Plenum, New York
Litchfield JT Jr, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose effect experiments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 96:99–113
Marcus R, Kornetsky C (1974) Negative and positive intracranial reinforcement thresholds: Effects of morphine. Psychopharmacology 38:1–13
Olds J (1960) Differentiation of reward systems in the brain by self-stimulation technics. In: Ramey ER, O'Doherty D. S. (eds) Electrical studies on the unanesthetized brain. Paul B. Hoeber, New York, pp 17–51
Pellegrino LJ, Pellegrino AS, Cushman AJ (1979) A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain. Plenum, New York
Schaefer GJ, Holtzman SG (1977a) Discriminative effects of morphine in the squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 201:67–75
Schaefer GJ, Holtzman SG (1977b) Dose- and time-dependent effects of narcotic analgesics on intracranial self-stimulation in the rat. Psychopharmacology 53:227–234
Schaefer GJ, Holtzman SG (1979) Free-operant and auto-titration brain self-stimulation procedures in the rat: A comparison of drug effects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:127–135
Schaefer GJ, Michael RP (1980) Acute effects of neuroleptics on brain self-stimulation thresholds in rats. Psychopharmacology 67:9–15
Schaefer GJ, Bonsall RW, Michael RP (1982) An easily constructed biphasic constant-current stimulator for intracranial self-stimulation. Physiol Behav 29:163–165
Shannon HE, Holtzman SG (1976) Evaluation of the discriminative effects of morphine in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 198:54–65
Stein L (1980) The chemistry of reward. In: Routtenberg A (ed) Biology of reinforcement: Facets of brain stimulation reward. Academic, New York, pp 109–130
Stutz RM, Maroli AN (1978) Central mechanism of reward and the narcotic cue. In: Colpaert FC, Rosecrans JA (eds) Stimulus properties of drugs: Ten years of progress. Elservier Biomedical, Amsterdam, pp 517–534
Valenstein ES (1964) Problems of measurement and interpretation with reinforcing brain stimulation. Psychol Rev 71:415–437
Wise RA (1978) Neuroleptic attenuation of intracranial selfstimulation: Reward or performance deficits? Life Sci 22:535–542
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaefer, G.J., Michael, R.P. The discriminative stimulus properties and detection thresholds of intracranial self-stimulation: Effects of d-amphetamine, morphine, and haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 85, 289–294 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428189
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428189