Abstract
Each of 40 fasting human subjects (20 men and 20 women) consumed 1 g ethanol (absolute) per kilogram body weight as a 20% solution by volume in organge juice. The time to peak BAC was found to be 24.0 min later than the time to peak alcohol effect as measured by magnitude estimation. This difference is both large and statistically reliable. These data are compared with those in the literature which usually show these events to be synchronous. Discussion includes reasons for this empirical discrepancy, implications of the theory of acute tolerance, and plans for future research.
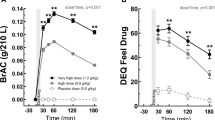
Examination of group data shows the same general trends obtained in the analysis of individual data: alcohol-effect scores reach peak earlier than BAC for the group as a whole (n=40), or for men alone, or for women alone. Moreover, alcohol-effect scores decline more rapidly in later trials than BAC scores, as has been reported earlier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conway TL, Radlow R (1979) Weight-adjusted alcohol dosage: effects of body fat. Presented at the Western Psychological Association Convention, San Diego, CA
Durnin JVGA, Womersley J (1974) Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Br J Nutr 32: 77–97
Ekman G, Frankenhaeuser M, Goldberg L, Bjherver K, Jarpe G, Myrsten A-L (1963) Effects of alcohol intake on subjective and objective variables over a five-hour period. Psychopharmacologia 4: 28–38
Ekman G, Frankenhaeuser M, Goldberg L, Hagdahl R, Myrsten A-L (1964) Subjective and objective effects of alcohol as functions of dosage and time. Psychopharmacologia 6: 399–409
Goldberg L (1943) Quantitative studies on alcohol tolerance in man. Acta Physiol Scan (Suppl 16) 5: 1–128
Grossberg JM, Grant BF (1978) Clinical psychophysics: applications of ratio scaling and signal detection methods to research on pain, fear, drugs, and medical decision making. Psychol Bull 85: 1154–1176
Hurst PM, Bagley SK (1972) Acute adaptation to the effects of alcohol. Q J Stud Alc 33: 358–378
Jellinek EM (1960) The disease concept of alcoholism. Hillhouse Press, Highland Park NJ
Jones BM (1973) Memory impairment on the ascending and descending limbs of the blood alcohol curve. J Abnorm Psychol 82: 24–32
Jones BM, Jones MK (1976a) Alcohol effects in women during the menstrual cycle. Ann NY Acad Sci 273: 576–587
Jonses BM, Jones MK (1976b) Women and alcohol: intoxication, metabolism, and the menstrual cycle. In: Greenblatt M, Schuckit MA (eds) Alcoholism problems in women and children. Grune & Stratten, New York, pp 103–136
Jones BM, Jones MK (1977) Interaction of alcohol, oral contraceptives and the menstrual cycle with stimulus-response compatibility. In: Seixas FA (ed) currents in alcoholism, v II. Grune & Stratton, New York, pp 457–477
Kelley M, Myrsten A-L, Neri A, Rydberg U (1970) Effects and after-effects of alcohol on physiological and psychological functions in man — a controlled study. Blutalkohol 7: 422–436
Mellanby E (1919) Alcohol: its absorption and disappearance from the blood under different conditions. Special report series No. 31. Medical Research Committee, London
Moskowitz H (1971) A behavioral mechanism of alcohol-related accidents. In: Proceedings of the First Annual Alcoholism Conference of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. DHEW Publication No. (NIH) 74-675
Myrsten A-L, Hollstedt C, Holmberg N (1975) Alcohol-induced changes in mood and activation in males and females. Scand J Psychol 16: 303–310
Myrsten A-L, Lamble R, Frankenhaeuser M, Lundberg U (1979) Interaction of alcohol and reward in an achievement situation. Psychopharmacology 62: 211–215
Radlow R, Conway TL (1978) Consistency of alcohol absorption in human subjects. Presented at the American Psychological Association Convention, Toronto, Ont
Vogel-Sprott MD (1979) Acute recovery and tolerance to low doses of alcohol. Psychopharmacology 61: 287–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radlow, R., Hurst, P.M. Temporal relations between blood alcohol concentration and alcohol effect: an experiment with human subjects. Psychopharmacology 85, 260–266 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428184
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428184