Abstract
Thirteen acute schizophrenic patients aged 14–18 years were treated with gradually increasing doses of diazepam to a maximum of 100–400 mg/day/p.o. with a total duration of treatment of 4 weeks. The clinical antipsychotic effect was evaluated by the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), while the impact on the hypothalamic hypophyseal pathway was evaluated by monitoring the serum prolactin levels (SPL) determined by a highly sensitive homologous radioimmunoassay (RIA).
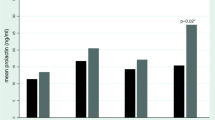
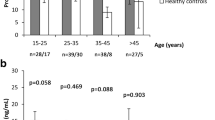
High diazepam doses (100–400 mg/day) caused sedation but no clinical antipsychotic effect was observed. Diazepam treatment with doses up to 250 mg/day caused no significant rise in SPL, while the treatment with doses of higher than 250 mg/day resulted in a mild but still significant increase in SPL.
The clinical and laboratory data suggest that diazepam has no direct antidopaminergic activity. The mild hyperprolactinemia achieved with the extremely high doses of diazepam (>250 mg/day) is possibly due to activation of the GABA system which stimulates prolactin release directly or by inhibiting the dopaminergic neurons or alternatively to activation of the endopphinergic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arato M (1980) Promethazine and diazepam potentiate the haloperidol induced prolactin responses. Commun Psychopharmacol 4:317–322
Beckman H, Hass S (1980) High dose diazepam in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 71:79–82
Ben David M, Chrambach A (1977) Preparation of bio- and immuno-active human prolactin in milligram amounts from amniotic fluid in 60% yield. Endocrinology 101:250–261
Ben David M, Chrambach A (1980) A method for isolation by gel electrofocussing of isohormones B and C of human prolactin from amniotic fluid. J Endocrinol 84:125–133
Braestrup C, Albrechston R, Squires EF (1977) High densities of benzodiazepines receptors in human cortical areas. Nature 269:702–704
Bunney BS, Aghajanian GK (1976) The effect of antipsychotic drugs on the firing of dopaminergic neurons: a reappraisal. In: Sedvall G, Uvans B, Zotterman Y (eds) Antipsychotic drugs, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Wenner-Gren Center International Symposium Series. Pergamon Press, New York
Costa E, Guidotti A, Mao CC, Suria A (1975) New concepts of the mechanisms of action of benzodiazepines. Life Sci 17:167–170
Grandison L (1981) Anterior pituitary Gaba receptors and their regulation of prolactin section. In: Costa E (ed) Gaba and benzodiazepine receptors. Raven Press, New York, pp 219–227
Haas S, Emrich HM, Beckman H (1982) Analgesic and euphoric effects of high dose diazepam in schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 8:123–128
Haefely WE (1978) Behavioral and neuropharmacological aspects of drugs used in anxiety and related states. In: Lipton MA, Dimascio A, Killam KF (eds) Psychopharmacology: A generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 1359–1374
Jimerson DC, Van Kammen DP, Post RM, Docherty JP, Bunney WE Jr (1982) Diazepam in schizophrenia: a preliminary double-blind trial. Am J Psychiatry 139:489–491
Lautin A, Angrist B, Stanley M, Gershon S, Heckl K, Karobath M (1980) Sodium valproate in schizophrenia: some biochemical correlates. Br J Psychiatry 137:240–244
Lerner Y, Lwow E, Levitin A, Belmaker RH (1979) Acute high dose parenteral halperidol treatment of psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 136:1061–1064
Nestoros JN, Suranyi-Cadotte BE, Spees RC, Schwartz G, Nair NPV (1982) Diazepam in high doses is effective in schizophrenia. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 6:513–517
Nestoros JN, Nair NVP, Pulman JR, Schwartz G, Bloom D (1983) High doses of diazepam improve neuroleptic-resistant chronic schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 81:42–47
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Racagni G, Apud JA, Cocchi D, Locatelli V, Muller EE (1982) GABAergic control of anterior pituitary hormones secretion. Life Sci 31:823–838
Rastrogi RB, Agarwal RA, Lapierre YD, Singhal RL (1977) Effects of acute diazepam and clobazam on spontaneous locomotor activity and central amine metabolism in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 43:91–98
Roberts E (1972) A hypothesis suggesting that there is a defect in the GABA system in schizophrenia. Neurosci Res Prog Bull 10:468–480
Spitzer RL, Endicott J, Robins E (1978) Research diagnostic criteria (RDC) for a selected group of functional disorders 3rd edn. New York State Psychiatric Institute, Biometrics Res
Stubbs WA, Delitala G, Jones A, Jeffcoate WY, Edwards CRW, Ratter SJ, Besser BM, Bloom SR, Albert KGMM (1978) Hormonal and metabolism responses to an enkephalin analogue in normal man. Lancet 2:1225–1227
Szara S (1982) Opiate receptors and endogenous opiats. Panorama of opiate research. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 8:3–15
Tamminga CA, Crayton JW, Chase TN (1978) Muscimol: GABA agonist therapy in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 36:595–598
Van Kammen DP (1977) γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) hypothesis of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 134:138–143
Weizman R, Weizman A, Tyano S, Wijsenbeek H, Ben David M (1979) The biphasic effect of gradually increased doses of diazepam on prolactin secretion in acute schizophrenic patients. Isr Ann Psychiatry 17:233–240
Wise CD, Berger BB, Stein L (1972) Benzodiazepines: anxiety-reducing activity by reduction of serotonin turnover in the brain. Science 177:180–183
Wuster M, Duka T, Herz A (1980) Diazepam-induced release of opioid activity in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 26:335–337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weizman, A., Tyano, S., Wijsenbeek, H. et al. High dose diazepam treatment and its effect on prolactin secretion in adolescent schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 82, 382–385 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427690
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427690