Abstract
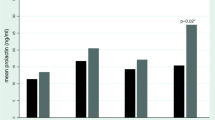
The effects of chronic sultopride treatment on endocrine systems were studied using five schizophrenic women. Sultopride, an antipsychotic drug, was administered orally three times daily for 5 weeks in a daily dose of 300–600 mg. The serum prolactin levels increased significantly after 1 day of treatment, reaching a maximum at 1 week and remaining elevated during treatment. The serum GH levels declined temporarily after 1 week of treatment and then returned to normal values after 3–5 weeks of treatment. Sultopride had no significant effects on LH, FSH, TSH, insulin, estradiol-17β and cortisol basal levels. Serum sultopride levels measured by radioimmunoassay remained steady during treatment. These results showed that sultopride stimulates prolactin secretion in schizophrenic women, probably by blocking pituitary dopamine receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beumont PJV, Corker CS, Friesen HG, Geldes MG, Harris GW, Kalakowska T, MacKinnon PCB, Mandelbrote BM, Marshall J, Murray MAF, Willes DH (1974) The effect of phenothiazines on endocrine function. Br J Psychiatry 124:413–422
Bjeerkenstedt L, Harnryd C, Sedval G (1979) Effect of sulpiride on monoaminergic mechanisms in psychotic women. Psychopharmacology 64:135–139
Borenstein P, Cujo P, Champion C, Olivenstein C (1968) Study of a new psychotic drug — sulpiride. Ann Med Psychol 2:90–100
Borenstein P, Cujo P, Soret C (1976) Clinical and electroencephalographic study of sultopride in psychiatry. Sem Hop Paris 52:81–88
Boyar RM, Kapen S, Finkelstein JW, Perlow M, Sassin JF, Fukushima DK, Weitzman ED, Hellman L (1974) Hypothalamic-pituitary function in diverse hyperprolactinemic states. J Clin Invest 53:1588–1591
Buvat J, Thomas K, Racadot A, Blacker C, Buvat-Herbaut M, Ferin F, Iinquette M (1978) Changes in pituitary gonadotropins during the amenorrhoea-galactorrhoea syndrome due to sulpiride. Clin Endocrinol 9:499–504
Clemens JA, Smalstig EB, Sawyer BD (1974) Antipsychotic drugs stimulate prolactin release. Psychopharmacology 40:123–127
Debeljuk L, Rozados R, Daskal H, Velez CV, Mancini AM (1975) Acute and chronic effects of sulpiride on serum prolactin and gonadotropin levels in castrated male rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 148:550–552
Jenner P, Elliott PNC, Clow A, Reavill C, Marsden CD (1978) A comparison of in vitro and in vivo dopamine receptor antagonism produced by substituted benzamide drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol 30:46–48
Jenner P, Marsden CD (1979) The mechanismus of action of substituted benzamide drugs. In: Spano PF, Trabucchi M, Corsini GU, Gessa GL (eds) Sulpiride and other benzamides. Raven Press, New York, pp 119–147
Kato Y, Ohgo S, Chihara K, Imura H (1975) Stimulation of human prolactin secretion by sulpiride. Endocrinol Jpn 22:457–460
L'Hermite M, MacLeod RM, Robyn C (1978) Effects of two substituted benzamides, tiapride and sultopride on gonadotrophins and prolactin. Acta Endocrinol 89:29–37
Linder HR, Perel E, Friedlander A, Zeitlin A (1972) Specificity of antibodies to ovarian hormones in relation to the site of attachment of the steroid hapten to the peptide carrier. Steroids 19:357–375
Lu KH, Koch Y, Amenomori Y, Chen CL, Meites J (1970) Effects of central acting drugs on serum and prolactin levels in rats. Endocrinology 87:667–672
Meites J, Clemens J (1972) Hypothalamic control of prolactin secretion. Vitam Horm 30:165–221
Mielke DH, Gallant DM, Kessler C (1977) An evaluation of a unique new antipsychotic agent, sulpiride: Effects on serum prolactin and growth hormone levels. Am J Psychiatry 134:1371–1375
Mizuchi A, Kitagawa N, Saruta S, Tokuda H, Miyachi Y (1984) Effect of sultopride on prolactin secretion in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn (in press)
Mizuchi A, Saruta S, Kitagawa N, Miyachi Y (1981) Development of radioimmunoassay for sultopride and sulpiride. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 254:317–326
Murasaki M, Yamazumi S, Okamoto K, Takahashi A, Miura S (1981) Phase 1 study of sultopride (new benzamide derivative). Clin Eval 9:577–627
Quickel Jr. KE, Feldman JM, Lebovitz HE (1971) Inhibition of insulin secretion by serotonin and dopamine: species variation. Endocrinology 89:1295–1302
Ruder HJ, Guy RL, Lipsett MB (1972) A radioimmunoassay for cortisol in plasma and urine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 35:219–224
Sharman L, Kim S, Benjamin F, Kolodny D (1971) Effect of chlorpromazine on serum growth hormone concentration in man. New Engl J Med 284:72–75
Turkington RW (1972) Prolactin secretion treated with various drugs. Arch Int Med 130:349–354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyachi, Y., Mizuchi, A., Hamano, H. et al. Effects of chronic sultopride treatment on endocrine systems in psychotic women. Psychopharmacology 82, 287–290 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427671
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427671