Abstract
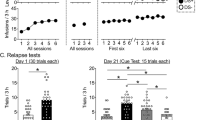
The ability of cocaine to exert internal stimulus control of behavior was investigated by training rats to discriminate 10 mg/kg cocaine from saline in a discrete-trial, two-lever, food-reward procedure. Acquisition of response control by cocaine (1) succeeded in all animals tested, (2) proceeded rapidly, and (3) was associated with a high Commission Error: Omission Error ratio. These findings support the hypothesis that cocaine, a prototype of drugs inducing a psychotic condition in humans, can act as a powerful internal stimulus in rats. The cocaine cue was also responsive to the action of the dopamine-receptor-blocking agents spiperone (ED50: 0.06 mg/kg), haloperidol (0.24 mg/kg), and pimozide (1.90 mg/kg). d,l-Amphetamine (1.25 mg/kg) induced stimulus generalization with cocaine, and this generalization was blocked by dosages of the same neuroleptics comparable to those of cocaine antagonism. The results are discussed in terms of internal stimulus control of behavior and its relevance to the psychophysiology of schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., Butcher, S. G., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Ungerstedt, U.: Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 11, 303–314 (1970)
Andén, N.-E., Roos, B. E., Werdenicus, B.: Effects of chlorpromazine, haloperidol and reserpine on the levels of phenolic acids in rabbit corpus striatum. Life Sci. 3, 149–158 (1964)
Angrist, B., Lee, H. K., Gershon, S.: The antagonism of amphetamine-induced symptomatology by a neuroleptic. Am. J. Psychiatry 131, 817–819 (1974)
Beamish, P., Kiloh, L. G.: Psychoses due to amphetamine consumption. J. Ment. Sci. 106, 337–343 (1960)
Borison, R. L., Mosnaim, A. D., Sabelli, H. C.: Brain 2-phenylethylamine as a major mediator for the central actions of amphetamine and methylphenidate. Life Sci. 17, 1331–1344 (1975)
Carlsson, A., Lindqvist, M.: Effect of chlorpromazine and haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxytyramine and normetanephine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 20, 140–144 (1963)
Colpaert, F. C.: Drug-produced cues and states: some theoretical and methodological inferences. In: Discriminative stimulus properties of drugs, H. Lal, ed., pp. 5–21. New York: Plenum 1977
Colpaert, F. C., Lal, H., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Janssen, P. A. J.: Investigations on drug produced and subjectively experienced discriminative stimuli. I. The fentanyl cue, a tool to investigate subjectively experienced narcotic drug actions. Life Sci. 16, 705–716 (1975)
Colpaert, F. C., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Janssen, P. A. J.: Theoretical and methodological considerations on drug discrimination learning. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 46, 169–177 (1976a)
Colpaert, F. C., Leysen, J. E. M. F., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Janssen, P. A. J.: Blockade of apomorphine's discriminative stimulus properties: relation to neuroleptic activity in neuropharmacological and biochemical assays. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 5, 671–679 (1976b)
Colpaert, F. C., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Janssen, P. A. J.: Cocaine cue in rats as it relates to subjective drug effects: a preliminary study. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 40, 195–199 (1976c)
Colpaert, F. C., Desmedt, L. K. C., Janssen, P. A. J.: Discriminative stimulus properties of benzodiazepines, barbiturates and pharmacologically related drugs: relation to some intrinsic and anticonvulsant effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 37, 113–123 (1976d)
Colpaert, F. C., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Janssen, P. A. J.: Haloperidol blocks the discriminative stimulus properties of lateral hypothalamic stimulation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 42, 93–97 (1977a)
Colpaert, F. C., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Janssen, P. A. J.: Differential haloperidol effect on two indices of fentanyl-saline discrimination. Psychopharmacology 53, 169–173 (1977b)
D'Mello, G. D., Stolerman, I. P.: Comparison of the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine and amphetamine in rats. Br. J. Pharmac. 61, 415–422 (1977)
Farnebo, L.-O., Fuxe, K., Hamberger, B., Ljungdahl, H.: Effect of some antiparkinsonian drugs on catecholamine neurons. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 22, 733–737 (1970)
Fischman, M. W., Schuster, C. R., Resnekov, L., Shick, J. F. E., Krasnegor, N. A., Fennell, W., Freedman, D. X.: Cardiovascular and subjective effects of intravenous cocaine administration in humans. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 33, 983–989 (1976)
Fouriezos, G., Wise, R. A.: Pimozide-induced extinction of intracrainal self-stimulation: response patterns rule out motor or performance deficits. Brain Res. 103, 377–380 (1976)
Gerner, R. H., Post, R. M., Bunney, W. E.: A dopaminergic mechanism in mania. Am. J. Psychiatry 133, 1177–1180 (1976)
Harris, R. T., Balster, R. L.: Discriminative control by dl-amphetamine and saline of lever choice and response patterning. Psychon. Sci. 10, 105–106 (1968)
Izquierdo, I., Cavalheiro, E. A.: Three main factors in rat shuttle behavior: their pharmacology and sequential entry in operation during a two-way avoidance session. Psychopharmacology 49, 145–157 (1976)
Janssen, P. A. J., The pharmacology of haloperidol. Int. J. Neuropsychiatry 3, 10–187 (1967)
Janssen, P. A. J., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Schellekens, K. H. L., Dresse, A., Lenaerts, F. M., Pinchard, A., Schaper, W. K. A., Van Nueten, J. M., Verbruggen, F. J.: Pimozide, a chemically novel, highly potent and orally long-acting neuroleptic drug. Arzneim.-Forsch. 18, 261–287 (1968)
Janssen, P. A. J., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Schellekens, K. H. L.: Is it possible to predict the clinical effects of neuroleptic drugs (major tranquillizers) from animal data? I. “Neuroleptic activity spectra” for rats. Arzneim.-Forsch. 15, 104–117 (1965)
Lichfield, J. T., Wilcoxon, F.: A simplified method for evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 96, 99–113 (1949)
Meltzer, H. Y., Stahl, S. M.: The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: a review. Schizophrenia Bull. 2, 19–76 (1976)
Post, R. M.: Cocaine psychoses: a continuum model. Am. J. Pschiatry 132, 225–231 (1975)
Schuster, C. R., Thompson, T.: Self administration of and behavioral dependence on drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 9, 483–502 (1969)
Siegel, S.: Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. New York: McGraw-Hill 1956
Silverman, P. B., Ho, B. T.: Characterization of discriminative response control by psychomotor stimulants. In: Discriminative stimulus properties of drugs, H. Lal, ed., pp. 107–119 New York: Plenum 1977
Usdin, E., Snyder, S. H. (eds.): Frontiers in catecholamine research, pp. 1219. New York: Pergamon 1973
Van Rossum, J. M.: The significance of dopamine-receptor blockade for the mechanism of action of neuroleptic drugs. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 160, 492–494 (1966)
Wauquier, A., Niemegeers, C. J. E.: Intracranial self-stimulation in rats as a function of various stimulus parameters. II. Influence of haloperidol, pimozide and pipamperone on medial forebrain bunde stimulation with monopolar electrodes. Psychopharmacologia 27, 191–202 (1972)
Yokel, R. A., Wise, R. A.: Increased lever pressing for amphetamine after pimozide in rats: implications for a dopamine theory of reward. Science 187, 547–549 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colpaert, F.C., Niemegeers, C.J.E. & Janssen, P.A.J. Neuroleptic interference with the cocaine cue: Internal stimulus control of behavior and psychosis. Psychopharmacology 58, 247–255 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427387
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427387