Abstract
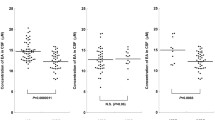
Rubidium concentration was measured in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of depressed patients. During pre-rubidium placebo periods the endogenous concentration of rubidium in CSF was significantly reduced as compared to plasma. In 5 patients who received oral loading doses of rubidium, the steady state relationships between rubidium and potassium were altered and the increases in plasma and erythrocyte rubidium concentrations were greater than the increase in CSF rubidium concentration. Measurement of rubidium concentrations in plasma adequately reflected the CSF concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradbury, M. W. B.: The effect of rubidium on the distribution and movement of potassium between blood, brain, and cerebrospinal fluid in the rabbit. Brain Res. 24, 311 (1970)
Feighner, J. P., Robins, E., Guze, S. B., Woodruff, R. A., Jr., Winokur, G., Munoz, R.: Diagnostic criteria for use in psychiatric research. Arch. gen. Psychiat. 26, 57 (1972)
Fieve, R. R., Meltzer, H. L., Taylor, R. M.: Rubidium chloride ingestion by volunteer subjects: initial experience. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 20, 307 (1971)
Fieve, R. R., Meltzer, H., Dunner, D. L., Levitt, M., Mendlewicz, J., Thomas, A.: Rubidium: biochemical, behavioral, and metabolic studies in humans. Amer. J. Psychiat. 130, 55 (1973)
Lieberman, K. W., Meltzer, H. L.: Determination of rubidium in biological materials by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Anal. Letters 4, 547 (1971)
Meltzer, H. L., Taylor, R. M., Platman, S. R., Fieve, R. R.: Rubidium: a potential modifier of affect and behavior. Nature (Lond.) 223, 321 (1969)
Meltzer, H. L., Lieberman, K. W., Shelley, E. M., Stallone, R., Fieve, R. R.: Metabolism of naturally occurring Rb in the human: the constancy of urinary Rb/K. Biochem. Med. 7, 218 (1973)
Sheard, M. H.: Effect of lithium on foot shock aggression in rats. Nature (Lond.) 228, 284 (1970)
Stolk, J. M., Nowack, W. J., Barchas, J. D.: Brain Norepinephrine: enhanced turnover after rubidium treatment. Science 168, 501 (1970)
Stolk, J. M., Conner, R. L., Barchas, J. D.: Rubidium-induced increase in shockelicited aggression in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 250 (1971)
Yamagata, N.: Balance of K, Rb, and Cs between Japanese people and diet and assessment of their biological half times. J. Radiat. Res. 8, 100 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Aspects of this study were reported at the Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, Honolulu, Hawaii, May 1973.
Principal Research Scientist.
Associate Research Scientist.
Chief of Clinical Research, Metabolic Unit and Lithium Outpatient Clinic.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunner, D.L., Meltzer, H.L. & Fieve, R.R. Cerebrospinal fluid rubidium metabolism in depression. Psychopharmacologia 37, 7–13 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426677
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426677