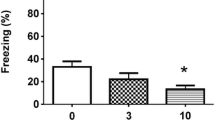
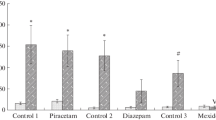
Abstract
Naloxone impairs acquisition of shuttle avoidance behavior (0.8 mg/kg IP) and habituation to a rearing response to a tone (1.6 mg/kg IP) in rats. β-Endorphin (2 μg/kg IP) has no effect on acquisition, but, when given prior to test sessions, facilitates retrieval of the two tasks. Naloxone has no effect of its own upon retrieval. In addition to these effects, the pretraining administration of β-endorphin disrupts, and that of naloxone facilitates retention of the two tasks. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that these two forms of learning are state-dependent on the release of β-endorphin (and, perpaps, of other opiate peptides as well), that this substance is released during training in a sufficient amount for this purpose, and that, in addition, there is a physiological amnesic mechanism mediated by opiate peptides. Furthermore, the results are also consistent with previous observations that β-endorphin is released from the rat brain during training, but not during test sessions of the two tasks (Izquierdo et al., 1980b). The possibility is discussed that state-dependency and the amnesic effect comprise one single, rather than two separate mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisman, H.: Aversively motivated behavior as a tool in psychopharmacologic analysis. In: Psychopharmacology of aversively motivated behavior, H. Anisman, G. Bignami, eds., pp. 1–62. New York: Plenum 1978
Belleville, R. E.: Control of behavior by drug-produced internal stimuli. Psychopharmacologia 5, 95–105 (1964)
Bliss, C. I.: Statistics in biology, vol. 1. New York: McGraw-Hill 1967
Cavalheiro, E. A., Izquierdo, I.: Effect of hippocampal and neocortical spreading depression on rat shuttle behavior in four different behavioral tests. Physiol. Behav. 18, 1011–1016 (1977)
DeWied, D., Bohus, B., van Ree, J. M., Urban, I.: Behavioral and electrophysiological effects of peptides related to lipotropin (β-LPH). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 204, 570–580 (1978)
Evangelista, A. M., Izquierdo, I.: The effect of pre- and post-trial amphetamine injections on avoidance responses of rats. Psychopharmacologia 20, 42–47 (1971)
Evangelista, A. M., Izquierdo, I.: Effects of atropine on avoidance conditioning: Interaction with nicotine and comparison with N-methylatropine. Psychopharmacologia 27, 241–248 (1972)
Fulginiti, S., Molina, V. A., Orsingher, O. A.: Inhibition of catecholamine biosynthesis and memory processes. Psychopharmacology 51, 65–69 (1976)
Goldstein, A., Pryor, G. T., Otis, L. S., Larsen, F.: On the role of endogenous opioid peptides: Failure of naloxone to influence shock escape threshold in the rat. Life Sci. 18, 599–604 (1976)
Hernández-Peón, R., Brust-Carmona, H.: Functional role of subcortical structures in habituation and conditioning. In: Brain mechanisms and learning, A. Fessard, R. W. Gerard, J. Konorski, J. F. Delafresnaye, eds., pp. 393–408. Oxford: Blackwell 1961
Izquierdo, I.: Effect of naloxone and morphine on various forms of memory in the rat: Possible role of endogenous opiate mech-anisms in memory consolidation. Psychopharmacology 66, 199–203 (1979)
Izquierdo, I., Beamish, D. G., Anisman, H.: Effect of an inhibitor of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase on the acquisition and retention of four different avoidance tasks in mice. Psychopharmacology 63, 173–178 (1979)
Izquierdo, I., Cavalheiro, E. A.: Three main factors in rat shuttle behavior: Their pharmacology and sequential entry in operation during a two-way avoidance session. Psychopharmacology 49, 145–157 (1976)
Izquierdo, I., Graudenz, M.: Memory facilitation by naloxone is due to release of dopaminergic and beta-adrenergic systems from tonic inhibition. Psychopharmacology 67, 265–268 (1980)
Izquierdo, I., Paiva, A. C. M., Elisabetsky, E.: Post-training intraperitoneal administration of leu-enkephalin and beta-endorphin causes retrograde amnesia for two different tasks in rats. Behav. Neural Biol. 28, 246–250 (1980a)
Izquierdo, I., Souza, D. O., Carrasco, M. A., Dias, R. D., Perry, M. L., Eisinger, S., Elisabetsky, E., Vendite, D. A.: Beta-endorphin causes retrograde amnesia and is released from the rat brain by various forms of training and stimulation. Psychopharmacology, in press (1980b)
Kapp, B. S., Gallagher, M.: Opiates and memory. Trends Neurosci. 2, 177–179 (1979)
Katz, R. J., Gelbart, J.: Endogenous opiates and behavioral responses to environmental novelty. Behav. Biol. 24, 338–348 (1978)
McGaugh, J. L., Herz, M. J.: Memory consolidation. San Francisco: Albion 1972
Messing, R. B., Jensen, R. A., Martinez, J. L., Jr., Spiehler, V. R., Vasquez, B. J., Soumireu-Mourat, B., Liang, K. C., McGaugh, J. L.: Naloxone enhancement of memory. Behav. Neural Biol. 27, 266–275 (1979)
Mondadori, C., Waser, P. G.: Facilitation of memory processing by post-trial morphine: Possible involvement of reinforcement mechanisms? Psychopharmacology 63, 297–300 (1979)
Pavlov, I. P.: Conditioned reflexes: An investigation of the physiological activity of the cerebral cortex. Oxford: Oxford University Press 1927
Solomon, P. R.: Role of the hippocampus in blocking and conditioned inhibition of the rabbit's nictitating membrane response. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 91, 407–417 (1977)
Stein, L., Belluzzi, J. D.: Brain endorphins and the sense of well-being: A psychobiological hypothesis. Adv. Biochem. Pharmacol. 18, 299–311 (1978)
Zornetzer, S. F.: Neurotransmitter modulation and memory: A new neuropharmacological phrenology? In: Psychopharmacology: A generation of progress, M. A. Lipton, A. DiMascio, K. F. Killam, eds., pp. 637–649. New York: Raven 1978
Zornetzer, S. F., Gold, P. E., Hendrickson, J.: Alpha-methyl-P-tyrosine and memory: State-dependency and memory failure. Behav. Biol. 12, 135–141 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Izquierdo, I. Effect of β-Endorphin and naloxone on acquisition, memory, and retrieval of shuttle avoidance and habituation learning in rats. Psychopharmacology 69, 111–115 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426531
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426531