Abstract
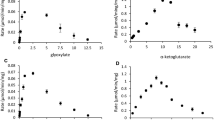
The incorporation of 14CO2 by an exponentially growing culture of the autotrophic bacterium Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum has been studied. The distribution of radioactivity during 2s–120s incubation periods has been analyzed by chromatography and radioautography. After a 2 s incubation most of the radioactivity of the ethanolsoluble fraction was present in the amino acids alanine, glutamate, glutamine and aspartate, whereas phosphorylated compounds were only weakly labelled. The percentage of the total radioactivity fixed, which was contained in the principal early labelled amino acid alanine, increased in the first 20 s and only then decreased, indicating that alanine is derived from primary products of CO2 fixation.
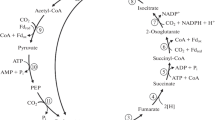
The labelling patterns of alanine produced during various incubation times have been determined by degradation. After a 2 s 14CO2 pulse, 61% of the radioactivity was located in C-1, 23% in C-2, and 16% in C-3. The results are consistent with the operation of a previously proposed autotrophic CO2 assimilation pathway which involves the formation of acetyl CoA from 2 CO2 via one-carbon unit intermediates, followed by the reductive carboxylation of acetyl CoA to pyruvate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassham JA, Calvin M (1960) The path of carbon in photosynthesis. In: Ruhland W (ed) Handbuch der Pflanzenphysiologie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, vol 5, part 1, pp 884–992
Bergmeyer HU, Möllering H (1970) Acetat. Bestimmung mit vorgeschalteter Indikatorreaktion. In: HU Bergmeyer (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, vol 2, p 1483
Calvin M, Bassham JA (1962) The photosynthesis of carbon compounds. Benjamin, New York
Cramer F (1954) Papierchromatographie, 3. ed. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Czok R, Lamprecht W (1970) Pyruvat, Phosphoenolpyruvat und D-Glycerat-2-Phosphat. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, vol 2, pp 1407–1411
Daniels L, Zeikus JG (1978) One-carbon metabolism in methanogenic bacteria: Analysis of short-term fixation products of 14CO2 and 14CH3OH incorporated into whole cells. J Bacteriol 136:75–84
Dawson R, Elliot DC, Elliot WH, Jones KM (eds) (1969) Data for biochemical research, 2. ed. Oxford University Press. London, p 526
Fuchs G, Stupperich E (1978) Evidence for an incomplete reductive carboxylic acid cycle in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol 118:121–125
Fuchs G, Stupperich E (1980) Acetyl CoA, a central intermediate of autotrophic CO2 fixation in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol 127:267–272
Fuchs G, Stupperich E, Thauer RK (1978a) Acetate assimilation and the synthesis of alanine, aspartate and glutamate in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol 117:61–66
Fuchs G, Stupperich E, Thauer RK (1978b) Function of fumarate reductase in methanogenic bacteria (Methanobacterium). Arch Microbiol 119:215–218
Fuchs G, Stupperich E, Eden G (1980a) Autotrophic CO2-fixation in Chlorobium limicola. Evidence for the operation of a reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle in growing cells. Arch Microbiol 128:64–71
Fuchs G, Stupperich E, Jaenchen R (1980b) Autotrophic CO2-fixation in Chlorobium limicola. Evidence against the operation of the Calvin cycle in growing cells. Arch Microbiol 128:56–63
Goebell H, Klingenberg M (1962) Dunnschlchtchromatographie von Tricarbonsäurezyklus-Substraten mit Autoradiographie. In: Chromatographie-Symposium. II. Société belge des sciences pharmaceutiques, Brüssel, pp 153–165
Grassl M (1970) L-Alanin-Bestimmung mit GPT und LDH. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, vol 2, pp 1637–1640
Hohorst HJ (1970) L-(+)-Lactat-Bestimmung mit Lactat-Dehydrogenase und NAD. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, vol 2, pp 1425–1429
Keltjens JT, Vogels GD (1981) Novel coenzymes of methanogens. In: Dalton H (ed) International Symposium “Microbial growth on C1-compounds”. Heyden & Son, London Philadelphia Rheine, pp 152–158
Kornberg HL (1958) The metabolism of C2 compounds in microorganisms. Biochem J 68:535–542
Lindley ND, Waites MJ, Quayle JR (1980) A modified pulse-labelling technique for the detection of early intermediates in microbial metabolism: Detection of 14C-Dihydroxyacetone during assimilation of 14C-methanol by Hansenula polymorpha. FEMS Microbiol Letters 8:13–16
Oberlies G, Fuchs G, Thauer RK (1980) Acetate thiokinase and the assimilation of acetate in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol 128:248–252
Quayle JR (1971) The use of isotopes in tracing metabolic pathways. In: Norris JR, Ribbons DW (eds) Methods in microbiology. Academic Press, New York London, vol 6B, pp 157–183
Schönheit P, Moll RK (1980) Growth parameters (Ks, μmax, Ys) of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol 127: 59–65
Simon H, Floss HG (1967) Anwendung von Isotopen in der Organischen Chemie und Biochemie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, vol 1, pp 23ff
Taylor GT, Kelly DP, Pirt SJ (1976) Intermediary metabolism in methanogenic bacteria. In: Schlegel HG, Gottschalk G, Pfennig N (eds) Proceedings of the Symposium “Microbial production and utilization of gases (H2, CH4, CO)”, Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen E. Goltze Verlag, Göttingen, pp 173–180
Trevelyan WE, Procter DP, Harrison JS (1950) Detection of sugars on paper chromatogramms. Nature 166:444–445
Uyeda K, Rabinowitz JC (1971) Pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase. IV. Studies on the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem 246:3120–3125
Wolfe RS (1979) Methanogens, a surprising microbial group. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 45:335–364
Zeikus JG, Fuchs G, Kenealy W, Thauer RK (1977) Oxidoreductases involved in cell carbon synthesis of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol 132:604–613
Zeikus JG, Wolfe RS (1972) Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol 109:707–713
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stupperich, E., Fuchs, G. Products of CO2 fixation and 14C labelling pattern of alanine in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum pulse-labelled with 14CO2 . Arch. Microbiol. 130, 294–300 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425943
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425943