Summary
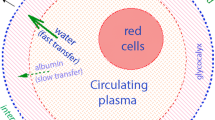
High precision blood and plasma densitometry was used to measure transvascular fluid shifts during water immersion to the neck. Six men (28–49 years) undertook 30 min of standing immersion in water at 35.0±0.2‡ C; immersion was preceded by 30 min control standing in air at 28±1‡ C. Blood was sampled from an antecubital catheter for determination of blood density (BD), plasma density (PD), haematocrit (Ht), total plasma protein concentration (PPC), and plasma albumin concentration (PAC).
Compared to control, significant decreases (p<0.01) in all these measures were observed after 20 min immersion. At 30 min, plasma volume had increased by 11.0±2.8%; the average density of the fluid shifted from extravascular fluid into the vascular compartment was 1006.3 g · l−1; albumin moved with the fluid and its albumin concentration was about one-third of the plasma protein concentration during early immersion. These calculations are based on the assumption that the F-cell ratio remained unchanged. No changes in erythrocyte water content during immersion were found.
Thus, immersion-induced haemodilution is probably accompanied by protein (mainly albumin) augmentation which accompanies the intravascular fluid shift.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crane MG, Harris JJ (1974) Suppression of plasma aldosterone by partial immersion. Metabolism 23: 359–368
Epstein M (1978) Renal effects of head-out water immersion in man: Implications for an understanding of volume homeostasis. Physiol Rev 58: 529–581
Epstein M, Duncan DC, Fishman LM (1972) Characterization of the natriuresis caused in normal man by immersion in water. Clin Sci 43: 275–287
Greenleaf JE (1984) Physiological responses to prolonged bed rest and fluid immersion in humans. J Appl Physiol 57: 619–633
Greenleaf JE, Morse JT, Barnes PR, Silver J, Keil LC (1983) Hypervolemia and plasma vasopressin response during water immersion in man. J Appl Physiol 55: 1688–1693
Greenleaf JE, Shvartz E, Keil LC (1981) Hemodilution, vasopressin suppression, and diuresis during water immersion in man. Aviat Space Environ Med 58: 328–336
Greenleaf JE, Shvartz E, Kravik S, Keil LC (1980) Fluid shifts and endocrine responses during chair rest and water immerison in man. J Appl Physiol 48: 78–88
Harrison MH, Keil LC, Wade CA, Silver JE, Geelen G, Greenleaf JE (1986) Effect of hydration on plasma volume and endocrine responses to water immersion. J Appl Physiol 61: 1410–1417
Harrison MH (1985) Effects of thermal stress and exercise on blood volume in humans. Physiol Rev 65: 169–209
Hinghofer-Szalkay H (1986) Method of high-precision microsample blood and plasma mass densitometry. J Appl Physiol 60: 1082–1088
Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Moser M (1986) Fluid on protein shifts after postural changes in humans. Am J Physiol 250 (Heart Circ Physiol 19): H68-H75
Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Leopold H, Kenner T, Holzer H (1980) On the coefficient of thermal expansion of blood and its constituents. Biomed Techn (Berlin) 25: 151–157
Kaiser D, Linkenbach HJ, Gauer OH (1969) Change of plasma volume in man during immersion in a thermoindifferent water bath. Pflügers Arch 308: 166–173
Khosla SS, Du Bois SB (1981) Osmoregulation and interstitial fluid pressure changes in humans during water immersion. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 51: 686–692
Khosla SS, Du Bois SB (1979) Fluid shifts during initial phase of immersion diuresis in man. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 46: 703–708
Kratky O, Leopold H, Stabinger H (1966) Dichtemessung an Flüssigkeiten und Gasen auf 10−6 g/cm3 bei 0,6 cm3 Probenvolumen. Z Angew Physik 27: 273–277
McCally M (1964) Plasma volume response to water immersion: Implications for space flight. Aerosp Med 35: 130–132
Miki K, Hajduczok G, Hong SK, Krasney JA (1986) Plasma volume changes during head-out water immersion in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 251 (Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 20): R582-R590
Risch WD, Koubenec H-J, Gauer OH, Lange S (1978) Time course of cardiac distension with rapid immersion in a thermo-neutral bath. Pflügers Arch 374: 119–120
Von Diringshofen H (1948) Die Wirkungen des hydrostatischen Druckes des Wasserbades auf den Blutdruck in den Kapillaren und die BindegewebsentwÄsserung. Z Kreis-laufforsch 37: 382–390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinghofer-Szalkay, H., Harrison, M.H. & Greenleaf, J.E. Early fluid and protein shifts in men during water immersion. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 56, 673–678 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424809
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424809