Abstract
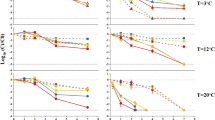
The survival of an E. coli strain in water samples from the Butrón river has been studied. The input of E. coli cells in the aquatic system breaks down the established balance among the components of the natural microbiota: E. coli becomes the object of the active protozoal predation whereas the autochtonous heterotrophic community become alternative preys. As a result of this new situation, the natural microbiota increases but returns to the initial values once the E. coli cells have been removed from the system. The effect of the temperature of incubation on the survival is exerted through the effect of this parameter on the predatory activity of the protozoa. Light has a lethal and direct action on the E. coli cells, the effect of this parameter is even superior to that of predation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. C., Rhodes, M. W. & Kator, K. I. (1983) Seasonal variation in survival of E. coli exposed ‘in situ’ membrane diffusion chambers containing filtered and non filtered estuarine water. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 45: 1877–1883
Cabridence, R. & Lepailleur, H. (1969) Rôle des alges dans l'épuration biologique des eaux. Terres et eaux 58: 12–18
Costerton, J. W. & Colwell, R. R. (1979) Native aquatic bacteria: enumeration, activity and ecology. ASTM special technical publication 695. Costerton & Colwell Ed.
Danso, S. K. A. & Alexander, M. (1975) Regulation of predation by prey density: the protozoan-Rhizobium relationship. Appl. Microbiol. 29: 515–521
Davenport, C. V., Sparrow, E. B. & Gordon, R. C. (1976) Fecal indicator bacteria persistence under natural conditions in an ice-covered river. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 32: 527–536
Dive, D. (1973) La nutrition holozoîque des protozoaires ciliés. Ses consequences dans l'épuration naturelle et artificielle. A. N. N. Biol. 12: 343–380
Enzinger, R. M. & Cooper, R. C. (1976) Role of bacteria and protozoa in the removal of E. coli from estuarine waters. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 31: 758–763
Gameson, A. L. H. (1984) Investigations of sewage discharges to some british coastal waters. Bacterial mortality, 1. Wat. Res. Cent.: 1–34
Grigsby, P. & Calkins, J. (1979) The inactivation of a natural population of coliform bacteria by sunlight. Photochem. Photobiol. 31: 291–294
Habte, M. & Alexander, M. (1978) Protozoan density and the coexistence of protozoan predator and bacterial prey. Ecology 59: 140–146
Jagger, J. (1975) Inhibition by sunlight of the growth of E. coli B/r. Photochem. Photobiol. 22: 67–70
Jannasch, H. W. (1968) Competitive elimination of Entero-bacteriaceae from seawater. Appl. Microbiol. 16: 1616–1618
Kapuscinski, R. B. & Mitchell, R. (1981) Solar radiation induces sublethal injury in E. coli in sea water. Appl. Microbiol. 41: 670–674
Kittrell, F. W. & Furfari, S. A. (1963) Observations of coliform bacteria in streams. J. Wat. Pollut. Cont. Fed. 35: 1361–1385
Lechevalier, M. W. & McFeters, G. A. (1985) Interactions between heterotrophic plate count bacteria and coliform organisms. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 49: 1338–1341
McCambridge, J. & McMeekin, T. A. (1979) Protozoan predation of E. coli in estuarine waters. Wat. Res. 13: 659–663
McCambridge, J. & McMeekin, T. A. (1980) Relative effects of bacterial and protozoan predators on survival of E. coli in estuarine water samples. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 40: 907–911
McCambridge, J. & McMeekin, T. A. (1981) Effect of solar radiation and predacious microorganisms on survival of fecal and other bacteria. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 41: 1083–1087
McFeters, G. A. & Stuart, D. G. (1972) Survival of coliform bacteria in natural waters: field and laboratory studies with membrane-filters chambers. Appl. Microbiol. 24: 805–811
Saz, A. K., Watson, S., Brown, S. R. & Lowery, D. C. (1963) Antimicrobial activity of marine waters. Macromolecular nature of antistaphylococcae factor. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8: 63–66
Sieburth, J. McN. & Pratt, D. M. (1962) Anticoliform activity of sea water associated with the termination of Skeletonema costatum blooms. Trans. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 24: 495–501
Singh, B. N. (1955) Culturing soil protozoa and estimating their numbers in soil. In: D. K. M. Kevan (ed), Soil zoology. Butterworths Scientific Publications, London
Stolp, H. & Starr, M. P. (1963) Bdellovibrio bacteriovorous gen. et sp. n., a predatory, ectoparasitic and bacteriolytic microorganism. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 29: 217–248
Taylor, W. D. (1978) Growth responses of ciliate protozoa to the abundance of their bacterial prey. Microbiol. Ecology 4: 207–214
Verstraete, W. & Voets, J. P. (1976) Comparative study of E. coli survival in two aquatic ecosystems. Wat. Res. 10: 129–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barcina, I., Arana, I., Iriberri, J. et al. Influence of light and natural microbiota of the Butrón river on E. coli survival. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 52, 555–566 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423416
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423416