Summary
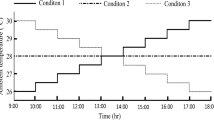
Rectal (Tre), oral (Tor) and oesophageal (Tes) temperatures were measured in five exercising subjects exposed for two hours to five conditions (1) a steady condition (WR) involving a constant work load (50 W) at a constant air temperature (Ta=36.5‡ C); (2) air temperature variations (δTa) between 28‡ C and 45‡ C and (3) between 23‡ C and 50‡ C at constant work load (50 W); (4) and (5) to work load variations (δW) between 25 W and 75 W at a constant Ta (=36.5‡ C). Oral temperature recordings were taken sublingually and were either continuous or discontinuous. When discontinuous, the time needed for Tor to stabilize after the mouth opening was taken into account. The respective reliability of Tor and Tre as estimates of Tes were compared in each condition. Results showed that the resting (Tor−Tes) difference (+0.12‡ C) was barely modified after two hours of exposure, whereas Tre overestimated Tes by 0.2‡ C to 0.4‡ C depending on the condition. The Tor variations were highly correlated with Tes variations under steady condition and under air temperature variations. In these conditions, Tor represented the best estimate of Tes. Under work-load variations, Tor was less closely related to Tes than was Tre. It is suggested that the relative inertia of Tor to step changes in exercise intensity could be ascribed to work induced variations in mouth blood flow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AikÄs E, Karvonen MJ, Piironen P, Ruosteenoja R (1962) Intramuscular, rectal and oesophageal temperature during exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 54: 366–370
Aulick LH, Robinson S, Tzankoff SP (1981) Arm and leg intravascular temperatures of men during submaximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 51: 1092–1097
Bardswell ND, Chapman JE (1911) Some observations upon the deep temperature of the human body at rest and after muscular exertion. Br Med J 1: 1106–1110
Bevegard BS, Shepherd JT (1967) Regulation of the circulation during exercise in man. Physiol Rev 47: 178–213
Brengelmann GL, Johnson JM, Hong PA (1979) Electrocardiographic verification of esophageal temperature probe position. J Appl Physiol 47: 638–642
Candas V, Sagot JC (1980) La température buccale: critère de température interne en conditions thermiques stables. J Physiol (Paris) 76: 44–45A
Carlsten A, Grimby G (1958) Rapid changes in human right heart blood temperature at variations in venous return. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 10: 397–401
Cooper KE, Kenyon JR (1957) A comparison of temperatures measured in the rectum, oesophagus, and on the surface of the aorta during hypothermia in man. Br J Surg 44: 616–619
Cranston WI, Gerbrandy J, Snell ES (1954) Oral, rectal and oesophageal temperatures and some factors affecting them in man. J Physiol (Lond) 126: 347–358
Edwards RJ, Belyavin AJ, Harrison MH (1978) Core temperature measurement in man. Aviat Space Environ Med 49: 1289–1294
Erickson R (1976) Thermometer placement for oral temperature measurement in febrile adults. Int J Nurs Stud 13: 199–208
Greenleaf JE, Castle BL (1972) External auditory canal temperature as an estimate of core temperature. J Appl Physiol 32: 194–198
Hellekant G (1972) Circulation of the tongue. In: Emmelin N, Zotterman Y (eds) Oral physiology. Pergamon Press, London, pp 127–137
McCaffrey TV, McCook RD, Wurster RD (1975) Effect of head skin temperature on tympanic and oral temperature in man. J Appl Physiol 39: 114–118
Marcus P (1973) Some effects of radiant heating of the head on body temperature measurement at the ear. Aerospace Med 44: 403–406
Mead J, Bonmarito CL (1949) Reliability of rectal temperatures as an index of internal body temperature. J Appl Physiol 2: 97–109
Nadel ER, Horvath SM (1970) Comparison of tympanic membrane and deep body temperatures in man. Life Sci 9: 869–875
Nichols GA, Kucha DH (1972) Taking adult temperatures: oral measurements. Am J Nurs 72: 1091–1093
Nielsen B (1968) Thermoregulatory responses to arm work, leg work and intermittent leg work. Acta Physiol Scand 72: 25–32
Nielsen B, Nielsen M (1962) Body temperature during work at different environmental temperatures. Acta Physiol Scand 56: 120–129
Sloan REG, Keatinge WR (1975) Depression of sublingual temperature by cold saliva. Br Med J 1: 718–720
Strydom NB, Wyndham CH, Williams CG, Morrison JF, Bredell GAG, Joffe A (1965) Oral/rectal temperature differences during work and heat stress. J Appl Physiol 20: 283–287
Wyndham CH, Strydom NB, Cooke HM, Maritz JS, Morrison JF, Fleming PW, Ward JS (1959) Methods of cooling subjects with hyperpyrexia. J Appl Physiol 14: 771–776
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the “Délégation Générale á la Recherche Scientifique et Technique contract no. 79.7.1126. Ph. Mairiaux was supported by a research grant of the “Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique” and by the Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene Department at the Catholic University of Louvain (U.C.L. Belgium)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mairiaux, P., Sagot, J.C. & Candas, V. Oral temperature as an index of core temperature during heat transients. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 50, 331–341 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423239
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423239