Summary
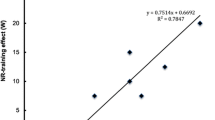
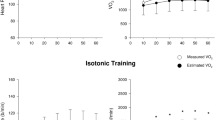
We recently observed that heart rate (HR) related methods for assessing physical fitness lead to an overestimation of endurance capacity in subjects treated with furosemide. To gain a more detailed description of this effect, the relationships between work load (WL), oxygen uptake (\(\dot V_{O_2 }\)), and HR were determined in the present study. To this end, nine healthy male subjects performed two incremental exercise tests (10 W increase per 30 s) on a bicycle ergometer. In one test 40 mg furosemide (Lasix®) was applied orally 90 min before exercise started. Compared with control conditions, furosemide led to a change in mean blood volume of −4.5% (range: +7.8% to −11.5%). Neither the maximal \(\dot V_{O_2 }\) (\(\dot V_{O_{2max} } \)) nor the maximal work load (WLmax) were significantly altered after furosemide application. Though the WL-\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) relationship was not significantly affected, the HR-\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) relationship showed significant alterations which depended on both the loss of blood volume (BV) and work intensity: When the reduction in BV was less than approximately 5%, HR was found to be lowered at all workloads. When the BV reduction was greater than about 5% HR was significantly reduced only in the lower ranges of work load but significantly increased at the higher work intensities. Since BV reductions are known to increase HR during exercise, our findings suggest that, in addition to the blood volume induced changes in HR, furosemide exerts further direct or indirect effects on heart rate adjustment.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Ekblom B, Goldbarg AN, Gullbring B (1972) Response to exercise after blood loss and reinfusion. J Appl Physiol 33:175–180
Forth W, Henschler D, Rummel W (1977) Allgemeine und spezielle Pharmakologie und Toxikologie. Bibliographisches Institut Mannheim, Wien, Zürich
Gaebelein CJ, Senay LC, Jr (1980) Influence of exercise type, hydration, and heart rate on plasma volume shifts in men. J Appl Physiol 49:119–123
Hnik P, Hudlicka D, Kucera J, Paine R (1969) Activation of muscle afferents by non propioceptive stimuli. Am J Physiol 217:1451–1454
Rost R, Hollmann W, Liesen H, Schulten D (1975) über den Einflu\ einer Erythrocyten-Retransfusion auf die kardiopulmonale LeistungsfÄhigkeit. Sportart Sportmed 7:137–144
Stegemann J, Kenner T (1971) A theory on heart rate control by muscular metabolic receptors. Arch Kreislaufforsch 64:185–214
Stegemann J (1976) Rechnergesteuerte Spiroergometrie nach der Methode der Einzelatemzuganalyse. Sportarzt Sportmed 27:1–7
Stegemann J, E\feld D (1984) Advantages of the computerized breath by breath method for the interpretation of spiroergometric data. In: Löllgen H, Mellerowicz H (eds) Progress in ergometry: quality control and test criteria. Fifth International Seminar on Ergometry: 30–35. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Thimm F, Tibes U (1978) Effects of K+, osmolality, lactic acid, orthophosphate and epinephrine on muscular receptors with group I, III, and IV afferents. J Physiol (Lond) 284:182–183
Tibes U, Haberkorn-Butendeich E, Hammersen F (1977) Effect of contraction on lymphatic, venous, and tissue electrolytes and metabolites in rabbit skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch 368:195–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baum, K., E\feld, D. & Stegemann, J. The influence of furosemide on heart rate and oxygen uptake in exercising man. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 619–623 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423206
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423206