Abstract
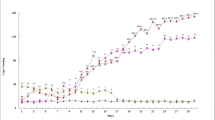
In the absence of scheduled shocks cyclazocine (2.5 mg/kg) severely depressed avoidance responding. No behavioural excitation was observed. Behavioural excitation is observed after cyclazocine (2.5 mg/kg) injection, in the presence of scheduled shocks. The excitatory phase associated with the drug is dependent on the presence of the aversive stimulus. Thus, behaviour/drug interaction is dependent on environmental factors. The interaction of stress on psychotomimetic drug-action allows one to formulate a mechanism whereby environmental stress can play a crucial role in the genesis and underlying mechanism of schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaton, J. M., Smythies, J. R., Benington, F., Monn, R. D., Clark, L. C., Jr.: Behavioural effects of some 4-substituted amphetamines. Nature (Lond.) 220, 800–881 (1968).
Bliss, D. L., Ailion, J., Zwanziger, J.: Metabolism of norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine in rat brain with stress. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 164, 122–134 (1968).
Bridger, W. H., Mandel, I. J.: Excitatory and inhibitory effects of mescaline on shuttle avoidance in the rat. Biol. Psychiat. 3, 379–385 (1971).
Kety, S. S., Smythies, J. R.: General discussion in: The mode of action of psychotomimetic drugs, pp. 107–115, J. R. Smythies (Chairman). Neurosci. Res. Progr. Bull. 8, No. 1 (1970).
McNemar, Q.: Psychological statistics, Third Edit. New York-London: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 1962.
Sidman, M.: Some properties of the warning stimulus in avoidance behaviour. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 48, 444–450 (1955).
Smythies, J. R., Sykes, E. A.: The effect of mescaline upon the conditioned avoidance response in the rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 6, 163–172 (1964).
Smythies, J. R., Bradley, R. J., Johnston, V. J.: Interaction of “stress” and the response to mescaline. Nature (Lond.) 215, 1179–1180 (1967).
Smythies, J. R., Sykes, E. A., Lord, C. P.: Structure activity relationship studies on mescaline (11.) Tolerance and non-tolerance between mescaline and its analogues in rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 9, 434–446 (1966).
Welch, B. L., Welch, A. S.: Fighting: Preferential lowering of norepinephrine and dopamine in brainstem, concomitant with a depletion of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla. Commun. Behav. Biol. 3, 125–130 (1969).
Wray, S. R.: Correlative evaluation of cyclazocine, LSD and naloxone on continuous discriminated avoidance in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 26, 29–43 (1972a).
Wray, S. R.: An experimental analysis of behavioural effects induced by narcotic antagonists with psychotomimetic properties. Unpublished Ph. D. Thesis, University of Hull, Yorkshire, England (1972b).
Wray, S. R.: Possible catecholamine mediation of levallorphan-induced behavioural disruption in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 30, 251–262 (1973).
Wray, S. R., Cowan, A.: The behavioural effects of levallorphan, cyprenorphine (M295) and amphetamine on repeated Y-maze performance in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 21, 257–267 (1971a).
Wray, S. R., Cowan, A.: The effects of naloxone, chlorpromazine, and haloperidol pre-treatment on levallorphan-induced disruption of rats' operant behaviour. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 261–270 (1971b).
Wray, S. R., Cowan, A.: Correlation between animal and clinical findings with a psychotomimetic anticholinesterase. Neuropharmacology (in press) (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wray, S.R. Interaction of stress and psychotomimetic drug-action: Possible implication for psychosis. Psychopharmacologia 30, 263–268 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422872
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422872