Summary
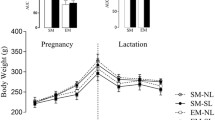
Changes of selected indicators of lipid metabolism in the liver of the offspring of rat mothers exercised during pregnancy and of control mothers were followed up. Male offspring of exercised mothers were heavier at the age of 35 days and lighter at the age of 90, 100, and 108 days. The concentration of total lipids and fatty acids was raised in female offspring at the age of 35 and 90 days, and did not differ or was reverse (i.e., lower) in male offspring of exercised mothers compared to controls. The cholesterol concentration in the liver was increased in both female and male offspring of exercised mothers. The liposynthesis (studied in vivo after injection of Na-acetate-1-14C) tended to be lower in female offspring, and varied in male offspring of exercised mothers. In a subsequent in vitro study (incubation of liver slices with Na-acetate-1-14C) a lower total lipid and fatty acid concentration in the liver of male offspring of exercised mothers (108 days old) was found together with higher level of serum free fatty acids and unchanged liposynthesis. Finally, a higher concentration of cholesterol, higher synthesis of fatty acids and lower cholesterogenesis in small intestine in male offspring of exercised mothers 100 days old compared to those of control mothers was shown. As follows, daily work load during pregnancy results in significant changes of lipid metabolism in the liver and small intestine of the offspring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell, L. L., Levy, B. B., Brodie, B. B., Kendall, F. E.: A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specifity. J. biol. Chem. 195, 357–366 (1952)
Avoy, D. R., Swyryd, E. A., Gould, G.: Effects of α-p-chlorophenoxybutyryl ethyl ester (CPIB) with and without androsterone on cholesterol biosynthesis in rat liver. J. Lipid Res. 6, 369–376 (1965)
Dancis, R.: Transfer of free fatty acids across human placenta. In: Early diabetes in early life. (R. A. Camerini-Davalos, H. S. Cole, eds.), pp. 233–236. New York: Academic Press 1975
Freinkel, H., Metzger, B. E.: Some considerations of fuel economy in fed state during late human pregnancy. In: Early diabetes in early life. (R. A. Camerini-Davalos, H. S. Cole, eds.), pp. 289–302. New York: Academic Press 1975
PaŘízková, J.: Impact of daily work load during pregnancy on the microstructure of the rat heart in male offsprings. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 34, 1–4 (1975)
PaŘízková, J.: Body fat and physical activity. (Martinus Nijnhoff, ed.). The Netherlands: The Hague 1977
PaŘízková, J., Poledne, R.: Consequences of long-term hypokinesia as compared to mild exercise in lipid metabolism of the heart, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 33, 331–338 (1974)
Paul, P.: Effects of long lasting physical exercise and training on lipid metabolism. In: Metabolic adaptations to prolonged physical exercise. (H. Howald, J. R. Poortmans, eds.), pp. 156–193. Basel: BirkhÄuser 1975
Petrásek, R., PaŘízková, J.: Cholesterol formation in rat liver induced by various levels of physical activity. Physiol. bohemoslov. 24, 462 (1975)
Szabo, A. J., Opperman, W., Hanover, B., Gugliucci, C., Szabo, O.: Fetal adipose development: Relationship to maternal free fatty acid levels. In: Early diabetes in early life. (R. A. Camerini-Davalos, H. S. Cole, eds.), pp. 167–176. New York: Academic Press 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PaŘízková, J., Petrásek, R. The impact of daily work load during pregnancy on lipid metabolism in the liver of the offspring. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 39, 81–87 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421712
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421712