Summary
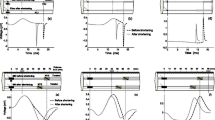
The dependence of extracellular action potentials (ECAPs) of single frog muscle fibres on intracellular action potentials (ICAPs) was studied during long-lasting (fatiguing) activity.
The conduction velocity, peak-to-peak amplitude and amplitudes of the separate phases of the first and second ICAP time derivatives decreased during long-lasting activity. The phases of the first and second ICAP space derivatives also decreased in amplitude and lengthened.
ECAPs near the membrane were similar in shape and proportional in amplitude to \(\frac{{\partial ^2 V}}{{\partial x^2 }}\) when recording at a distance from both the end of the fibre and the point of stimulation.
At long radial distances, the amplitudes of the separate ECAP phases depended on the amplitude and length of the corresponding phases of \(\frac{{\partial ^2 V}}{{\partial x^2 }}\).Thus the decrease in ECAP amplitude during long-lasting activity at long radial distances was less than at points close to the muscle fibre membrane.
The consequences of these findings for the changes in electromyograms recorded by needle or superficial electrodes during long-lasting (fatiguing) activity are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Etzensperger Y (1961) Renforcement de la secousse et modification des potentiels de repos et d'action provoques par l'activite prealable. Etude microphysiologique sur la fibre striee de grenouille, CR Soc Bil (Paris) 155:1336–1340
Freygang WH, Goldstein DA, Hellam DC (1964a) The afterpotential that follows trains of impulses in frog muscle fibres. J Gen Physiol 47:929–952
Freygang WH, Goldstein DA, Hellam DC, Peachey D (1964b) The relation between the late afterpotential and the size of the transverse tubular system of frog muscle. J Gen Physiol 48:235–263
Grabowski W, Lobsiger EA, Lüttgau HC (1972) The effect of repetitive stimulation at low frequences upon the electrical and mechanical activity of single muscle fibres. Pflügers Arch 334:222–239
Hanson J (1974a) The effects of repetitive stimulation on the action potential and the twitch of the rat muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 40:387–400
Hanson J (1974) Effects of repetitive stimulation on membrane potentials and twitch in human and rat intercostal muscle fibres. Acta Physiol Scand 92:239–248
Hanson J, Persson A (1971) Changes in the action potential and contraction of isolated frog muscle fibres after repetitive stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 81:340–348
Hodgkin AL, Horowitcz P (1957) The differential action of hypertonic solutions on the twitch and the action potential of a muscle fibre. J Physiol 136:17
Ishiko W, Sato N (1956) The negative afterpotential of skeletal muscle fibres. Kumamoto Med J 9:190–198
Katz B, Miledi R (1965) Propagation of electrical activity in motor nerve terminals. Proc Royal Soc B 985, 161:453–482
Lorente de No (1947) A study of nerve physiology. Studies from the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, v. 132, New York
Lüttgau HC (1965) The effect of metabolic inhibitors of the fatigue of the action potentials in single muscle fibres. J Physiol 178:45–67
Osborne MT (1958) Repetitive stimulation of muscle. Nature (Lond) 181:1798
Persson A (1963) The negative afterpotential of frog skeletal muscle fibres. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl. 205] 58
Plonsey R (1977) Action potential sources and their volume conductor fields. Proc IEEE 65:601–611
Schanne O, Kern R, Schafer B (1962) Zum Problem des Innerwiderstandes biologischer Zellen. Naturwissenschaften 49:161
Trautwein W, Zink K, Kayser K (1953) über Membran und Aktionpotentiale einzelner Fasern des Warmbluterskelettmuskels und ihre VerÄnderung bei der IschÄmie. Arch Ges Physiol 257:20–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radicheva, N., Gerilovsky, L. & Gydikov, A. Changes in the muscle fibre extracellular action potentials in long-lasting (fatiguing) activity. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 545–552 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421651
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421651