Summary
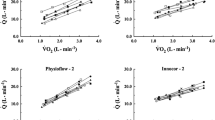
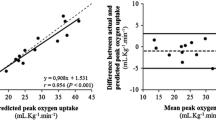
A one-step CO2 rebreathing method for the determination of cardiac output and stroke volume (SV) has been evaluated by comparison with the direct Fick technique during recumbent exercise (10–90 W) in 13 patients. In an initial analysis, the influence of different rebreathing times and of correction for haemoglobin concentration was studied. The best correlation with the direct Fick technique was obtained with the longest analysis time, i. e. 21 s, and correction for variations in haemoglobin concentration further improved the correlation. Consequently, an analysis time of 21 s and correction for haemoglobin have been used. At low cardiac outputs, the CO2-rebreathing method overestimated the flow compared to the Fick technique. The correlation between the methods, however, was so good that a valid estimate of cardiac output could be obtained from the CO2 rebreathing method with appropriate corrections (Cardiac output, CO2 method=2.7+0.77. Cardiac output, Fick; r=0.91; Residual Standard deviation (SD res) =0.77 l · min−1). Stroke volumes measured with the CO2 rebreathing method did not differ significantly from those obtained with the direct Fick technique, although there was a tendency to overestimate stroke volume with the CO2 rebreathing method (SV, CO2 method=12+0.89 · SV, Fick; r=0.82; SD res=11 ml).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler J (1965) Measurement of cardiac output using soluble gases. In: Fenn WO, Rahn H (eds) Handbook of physiology, sect. 3: respiration, vol. II. Am Physiol Soc, Washington DC, pp 1489–1503
Clausen JP, Larsen OA, Trap-Jensen J (1970) Cardiac output in middle aged patients determined with CO2 rebreathing method. J Appl Physiol 28:337–342
Farhi LE, Nesarajah MS, Olszowka AJ, Metildi LA, Ellis AK (1976) Cardiac output determination by simple one-step rebreathing technique. Respirat Physiol 28:141–159
Hamilton WF (1962) Measurement of cardiac output. In: Hamilton WF, Dow P (eds) Handbook of physiology, sect. 2: circulation, vol. 1. Am Physiol Soc, Washington DC, pp 551–584
Hargreaves M, Jennings G (1983) Evaluation of the CO2 rebreathing method for the noninvasive measurement of resting cardiac output in man. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 10:609–614
Linnarsson D, Larsson H (1985) Pulmonary blood flow determination with selective rebreathing of CO2. Clin Physiol [Suppl 3] 5:39–48
Matalon S, Dashkoff N, Nesarajah MS, Klocke FJ, Farhi LE (1982) Effects of hyperventilation on pulmonary blood flow and recirculation time of humans. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exerc Physiol 52:1161–1166
McHardy GJR (1967) The relationship between the differences in pressure and content of carbon dioxide in arterial and venous blood. Clin Sci 32:299–309
New York Heart Association (1973) Diseases of the heart and blood vessels. 7th edn. Little, Brown & Co., Boston
Ohlsson J, Wranne B (1986) Noninvasive assessment of valve area in patients with aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 7:501–508
Ohlsson J, Hlastala MP, Tranesjö J, Wranne B (1983) Noninvasive determination of effective stroke volume. Evaluation of a CO2 rebreathing method in normal subjects and patients. Clin Physiol 3:9–18
Ohlsson J, Wranne B, Marklund T (1985) Non-invasive assessment of aortic and mitral regurgitation. Eur Heart J 6:851–857
Paterson DH, Cunningham DA (1976) Comparison of methods to calculate cardiac output using the CO2 rebreathing method. Eur J Appl Physiol 35:223–230
Reybrouck T, Amery A, Billiet L, Fagard R, Stijns H (1978) Comparison of cardiac output determined by a carbon dioxide-rebreathing and direct Fick method at rest and during exercise. Clin Sci Mol Med 55:445–452
Stewart RI, Lewis CM (1983) The reliability of the carbon dioxide rebreathing, indirect Fick method of cardiac output determination in patients with pulmonary disease. Clin Sci 64:289–293
Wigle RD, Hamilton PD, Parker JO (1979) Measurement of cardiac output by carbon dioxide rebreathing. Can J Applied Sport Sci 4:135–139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohlsson, J., Wranne, B. Non-invasive assessment of cardiac output and stroke volume in patients during exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 538–544 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421650
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421650