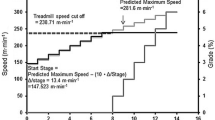
Summary
Previous studies have shown that true maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) obtained by means of cycle ergometer and step test are lower than the VO2max measured during uphill treadmill running. The predicted VO2max measured by ergometer was even lower. Four different methods for the determination of VO2max within the same group of examinees were compared: True VO2max by treadmill, ergometer, step test, and predicted VO2max (Astrand-Rhyming). This study was performed on 15 healthy non-professional sportsmen. They underwent progressive test protocols on alternating days and the results were as follows — VO2max expressed in ml O2 kg BW/min (mean±SD): treadmill running 63.8±4.7; ergometer cycling 60.2±5.6; step test 59.6±5.2 and predicted VO2max 59.9±6.9.
The VO2max as determined by uphill treadmill running was significantly higher than with the other methods. No significant difference was found between true VO2max determined by the ergometer and step test. However, step test and properly executed Astrand-Rhyming test again proved to be reliable and deviate from the treadmill test by only 6%. Maximal heart rate was sgnificantly higher in the treadmill and step tests than in the direct ergometer test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrand PO (1976) Quantification of exercise capability and evaluation of physical capacity in man. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 19: 51–67
Astrand I (1960) Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl 169] 49: 92
Bruce RA, Blackman JR, Jones JW (1963) Exercise testing in adult normal subjects and cardiac patients. Pediatrics 32: 742–755
Frolicher VF, Horner B, Garland D, Ignacio N, Alderus S, Malcolm CL (1974) A comparison of three maximal treadmill exercise protocols. J Appl Physiol 36: 720–725
Glassford RG, Baycroft GHY, Sedgwick AW, Macnab RBJ (1965) Comparison of maximal oxygen uptake values determined by predicted and actual methods. J Appl Physiol 20: 509–513
Hagberg JM, Giese MD, Schneider RB (1978) Comparison of three procedures for measuring VO2max in competitive cyclists. Eur J Appl Physiol 39: 47–52
Hermansen L, Saltin B (1969) Oxygen uptake during maximal treadmill and bycicle exercise. J Appl Physiol 26: 31–37
Kamon E, Pandolf KB: (1972) Maximal aerobic power during laddermill climbing, uphill running, and cycling. J Appl Physiol 32: 467–473
Kasch FW, Philips WH, Ross WD, Carter JEL, Boyer JL (1966) A comparison of maximal oxygen uptake by treadmill and step test procedures. J Appl Physiol 21: 1387–1388
Margaria R, Aghemo P, Rovelli E (1965) Indirect determination of maximal O2 consumption in man. J Appl Physiol 20: 1070–1073
Raskin H, Yatziv G (1968) A study on standardization of physical performance test for males and females aged 19–31. Int Committee on the Standardization of Physical Fitness Tests (ICSPFT), Wingate Institute, Israel, pp 1–30
Shephard RJ (1977) Endurance fitness, 2nd edn. University Toronto Press, Toronto, pp 104–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keren, G., Magazanik, A. & Epstein, Y. A comparison of various methods for the determination of VO2max. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 45, 117–124 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421319
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421319