Summary
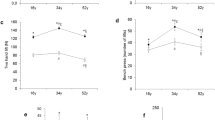
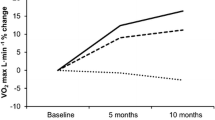
A young (¯X=36.8 years) and an old (¯X=52.9 years) group (n=12) matched for physical fitness performed a graded exercise test at the beginning and after a 4-month physical fitness program consisting of calisthenics, jogging, and recreational activities. The purpose of the study was to determine if there were any differences in response to physical training in the two age groups of similar fitness. Sixteen physiological and four biochemical variables were measured. There was no significant difference in \(\dot V\)O2 max between the young and old groups. Also, there were no significant differences between groups for serum total lipids, cholesterol, triglycerides, or glucose levels. The effects of the training program were similar for both the young and old groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, K. L., Hermansen, L.: Aerobic work capacity in middleaged Norwegian men. J. Appl. Physiol. 20, 432–436 (1965)
Astrand, I.: Aerobic work capacity in men and women with specific reference to age. Acta Physiol. Scand. 49 (Suppl. 169), 1–92 (1960)
Astrand, P. O., Christensen, E. H.: Aerobic work capacity. In: Oxygen in the Animal Organism (F. Dickens, E. Neil, W. F. Widdas, eds.), pp. 295–303. New York: Pergamon Press 1964
Astrand, I., Astrand, P. O., Hallback, I., Kilbom, A.: Reduction in maximal oxygen uptake with age. J. Appl. Physiol. 35, 649–654 (1973)
Barnicot, N. A., Bennett, F. J., Woodburn, J. C., Pilkington, T. R. E., Antonis, A.: Blood pressure and serum cholesterol in the Hadza of Tanzania. Hum. Biol. 44, 87–116 (1972)
Campbell, D. E.: Influences of diet and physical activity on blood serum cholesterol of young men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 18, 79–85 (1966)
Dade Laboratories. Total Lipids, Dade Division American Hospital Supply Corporation, Miami, Florida
Dehn, M. M., Bruce, R. A.: Longitudinal variations in maximal oxygen intake with age and activity. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 805–807 (1972)
Dill, D. B.: Marathoner De Mar: physiological studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 35, 185–190 (1965)
Dobelin, W. V., Astrand, I., Bergstrom, A.: An analysis of age and other factors related to maximal oxygen uptake. J. Appl. Physiol. 22, 934–938 (1967)
Faulkner, J. A., Montoye, H. J., Greey, G. W.: A comparison of executives with a total population in physical activity and other possible coronary heart disease risk factors. Med. Sci. Sports 1, 160–164 (1969)
Harleco: Glucose Determination. Philadelphia: Harleco Incorporated
Hollmann, W.: In: Körperliches Training als PrÄvention von Herz-Kreislauf-Krankheiten, p. 62. Stuttgart: Hippokrates 1965
Hycel Cholesterol Determinations: Houston, Texas: Hycel Incorporated
Ismail, A. H., Falls, H. B., MacLeod, D. F.: Development of a criterion for physical fitness tests from factor analysis results. J. Appl. Physiol. 20, 991–999 (1965)
Ismail, A. H., Corrigan, D. L., MacLeod, D. F., Anderson, V. L., Kasten, R. N., Elliott, P. W.: Biophysiological and audiological variables in adults. Arch. Otolaryngol. 97, 447–451 (1973)
Joseph, J. J.: Effects of calisthenics, jogging, and swimming on middle-aged men. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 14, 14–20 (1974)
Lowenstein, F. W.: Epidemiologic investigations in relation to diet in groups who show little atherosclerosis and are almost free of coronary ischemic heart disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 15, 175–186 (1964)
McDonough, J. R., Kusumi, F., Bruce, R. A.: Variations in maximal oxygen intake with physical activity in middle-aged men. Circulation 41, 743–751 (1970)
Mock, G. W.: The effects of a four-month physical fitness program on selected free fatty acids. Doctoral Dissertation, Purdue University, West Lafayette, 1972
Montoye, H. J., Van Huss, W. D., Brewer, W. D., Jones, E. M., Ohlson, M. A., Mahoney, E., Olson, H.: The effects of exercise on blood cholesterol in middle-aged men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 7, 139–145 (1959)
Oxford Laboratories: Tri-Chol Principle. Fostor City, California: Oxford Laboratory
Pollock, M. L., Miller, H. S., Jr., Wilmore, J.: A profile of a champion distance runner: age 60. Med. Sci. Sports 6, 118–121 (1974)
Pollock, M. L., Miller, H. S., Jr., Janeway, R., Linnerud, A. C., Robertson, B., Valentino, R.: Effects of walking on body composition and cardiovascular function of middle-aged men. J. Appl. Physiol. 30, 126–130 (1971)
Ribisl, P. M.: Effects of training upon the maximal oxygen uptake of middle-aged men. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. 27, 154–160 (1969)
Robinson, S.: Experimental studies of physica fitness in relation to age. Arbeitsphysiologie 10, 251–323 (1938)
Skinner, J. S., Hollosky, J. O., Cureton, T. K.: Effects of a program of endurance exercises on physical work. Am. J. Cardiol. 14, 747–752 (1964)
Taylor, H. L., Haskell, W., Fox III, S. M., Blackburn, H.: Exercise tests: A summary of procedures and concepts of stress testing for cardiovascular diagnosis and function evaluation. In: Measurement in Exercise Electrocardiography (H. Blackburn, ed.), pp. 259–305. Springfield: Thomas 1969
Teraslinna, P.: Effect of exercise on selected serum lipids and their relationships to certain variables of body structure and function. Doctoral Dissertation, Purdue University, West Lafayette, 1966
Wallin, C. C., Schendel, J. S.: Physiological changes in middle-aged men following a 10-week jogging program. Res. Q. Am. Assoc. Health Phys. Educ. 40, 600–606 (1969)
Wilmore, J. H., Behnke, A. R.: An anthrometric estimation of body density and lean body weight in young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 27, 25–31 (1969)
Wilmore, J. H., Girandola, R. N., Katch, F. I., Katch, V. L.: Physiological alterations resulting from a 10-week program of jogging. Med. Sci. Sports 2, 7–14 (1970)
Zauner, C. W., Swenson, E. W.: Exercise, diet and other factors on blood lipids. J. Fla. Med. Assoc. 57, 30–35 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, A.H., Montgomery, D.L. The effect of a four-month physical fitness program on a young and an old group matched for physical fitness. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 40, 137–144 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421158
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421158