Abstract
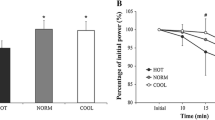
The effect of an increased body temperature (T r) elicited by prolonged heavy exercise at normal ambient temperature in absence of any heat stress, on the maximal aerobic power (\(\dot V_{O_2 \max } \)) and on heart rate (HR) has been studied. The prolonged exercise consisted in running for 1 hr on a motor driven treadmill, this leading to an average increase of T r of 1.2° C. Oxygen consumption (\(\dot V_{O_2 } \)), ventilation (V I ), HR and T r were measured at rest and every 10 min during the prolonged exercise. Before and after this exercise indirect measurement of \(\dot V_{O_2 \max } \) were made.
After the exercise, HR in submaximal exercise was increased, the increase being less pronounced the heavier the exercise. The HR increment was 17.5 beats/min per 1° C rise in T r in the exercise involving an oxygen comsumption of 22 ml/kg·min and it dropped to 7.5 b/min · °C when the O2 consumption increased to 32.4 ml/kg · · min.
\(\dot V_{O_2 \max } \) as calculated indirectly from HR values in submaximal exercise remained essentially the same before and after the treadmill run.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouha, L., Smith, P. E., de Lanne, R., Maxfield, M. E.: Physiological reaction of men and women during muscular activity and recovery in various environments. J. appl. Physiol. 16, 133–140 (1961)
Damato, A. N.: Cardiovascular response to acute thermal stress (hot environment) in unacclimatized normal subjects. Amer. Heart J. 76 (6), 769–774 (1968)
Friedrich, H.: Einfluß des Klimas auf Körpertemperatur und Kreislauf bei Ruhe und Arbeit. Arch. Kreisl.-Forsch. 13, 351–361 (1944)
Grimby, G.: Exercise in man during pyrogen-induced fever. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 14 (Suppl. 67), 1–112 (1962)
Grimby, G., Nilsson, N. J.: Cardiac output during exercise in pyrogen-induced fewer. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 15 (Suppl. 69), 44–61 (1963)
Klausen, K., Dill, D. B., Phillips, E. E., Jr., McGregor, D.: Metabolic reactions to work in the desert. J. appl. Physiol. 22, 292–296 (1967)
Kronfeld, D. S., MacFarlane, W. V., Harvey, N., Howard, B., Robinson, K. W.: Strenous exercise in a hot environment. J. appl. Physiol. 13, 425–429 (1958)
Lazarovici, V., Moldovan, L., Popescu, A., Nuca, F., Vraciu, D., Sac, A.: L'influence de la temperature ambient sur la capacité d'effort physique des mineurs occupés à l'extraction des métaux non ferreux. Ergonomics and Physical Environmental Factors, International Labor Office, pp. 352–357, Geneva 1970
Margaria, R., Aghemo, P., Rovelli, E.: Indirect determination of maximal O2 consumption in man. J. appl. Physiol. 20, 1070–1973 (1965)
Margaria, R., Meschia, G., Marro, F.: Determination of O2 consumption with a Pauling oxygen meter. J. appl. Physiol. 6, 776–780 (1954)
Nielsen, M.: Die Regulation der Körpertemperatur bei Muskelarbeit. Skand. Arch. Physiol. 79, 193–230 (1938)
Pellegrini, G., Riva, A., Margaria, R.: La termoregolazione nel lavoro muscolare. Arch. Fisiol. 46, 111–133 (1947)
Pirnay, F., Deroanne, R., Petit, J. M.: Maximal oxygen consumption in a hot environment. J. appl. Physiol. 28, 642–645 (1970)
Piwonka, R. W., Robinson, S., Gay, V. L., Manalis, R. S.: Preacclimatisation of man to heat by training. J. appl. Physiol. 20, 379–384 (1965)
Rowell, L. B., Blackmon, J. R., Martin, R. H., Mazzarella, J. A., Bruce, R. A.: Hepatic clearance of indocyanine green in man under thermal and exercise stress. J. appl. Physiol. 20, 384–394 (1965)
Rowell, L. B., Brengelmann, G. L., Murray, J. A., Kraning II, K. K., Kusumi, F.: Human metabolic response to hyperthermia during mild to maximal exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 26, 395–402 (1969)
Rowell, L. B., Marx, H. J., Bruce, R. A., Conn, R. D., Kusumi, F.: Reduction of cardiac output, central blood volume, and stroke volume with thermal stress in normal man during exercise. J. clin. Invest. 45, 1801–1816 (1966)
Saltin, B.: Circulatory response to submaximal and maximal exercise after thermal dehydration. J. appl. Physiol. 19, 1125–1132 (1964)
Saltin, B., Gagge, A. P., Bergh, U., Stolwjik, J. A. J.: Body temperatures and sweating during exhaustive exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 32, 635–643 (1972)
Saltin, B., Gagge, A. P., Stolwjik, J. A. J.: Muscle temperature during submaximal exercise in man. J. appl. Physiol. 25, 679–688 (1968)
Tanner, J. M.: The relationship between the frequency of the heart, oral temperature and rectal temperature in man at rest. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 115, 391–409 (1957)
Wenzel, H. G.: Über die Beziehungen zwischen Körperkerntemperatur und Pulsfrequenz des Menschen bei körperlicher Arbeit unter warmen Klimabedingungen. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 26, 43–94 (1968)
Williams, C. G., Bredell, G. A. G., Wyndham, C. H., Strydom, N. B., Morrison, J. F., Peter, J., Fleming, P. W., Ward, J. S.: Circulatory and metabolic reactions to work in heat. J. appl. Physiol. 17, 625–638 (1962)
Wyndham, C. H.: The physiology of exercise under heat stress. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 35, 193–220 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was conducted during Richard A. Mostardi's tenure as a Post Doctoral Fellow of the National Institute of Health, Heart and Lung Division, No. 1F03 HE 51569-01. Present address: Department of Biology, University of Akron, Akron, Ohio 44304.
This work has been supported in part by a grant from the Italian National Research Council (CNR).
On leave from Department of Physiology, Higher School of Physical Education, Cracow, Poland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostardi, R., Kubica, R., Veicsteinas, A. et al. The effect of increased body temperature due to exercise on the heart rate and on the maximal aerobic power. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 237–245 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421151
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421151