Summary
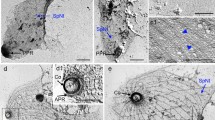
The electron-microscopical study of conventional fixed and contrasted Entamoeba histolytica-trophozoites from Diamonds monoxenic TTY-medium revealed “thick fibrils” in the vesicular cytoplasm of the parasites.
They are 9–14 nm in diameter and are therefore considered to be myosin-like filaments, that are spread mainly in the tail or the uroid of the moving ameba. No association with microfilaments (MF) or other organelles could be observed.
During the same investigation microtubules (MT) of variable length are described having a diameter of 35 nm, surrounded by a 19–25 nm wide capsule. They are distributed singly or in bundles with a maximal diameter of 350 nm. Some of the MT were coiled up to a helical shape.
Zusammenfassung
Im Cytoplasma intakter Kulturformen von zwei Entamoeba histolytica-Stämmen aus dem monoxenischen TTY-Medium nach Diamond wurden myosinähnliche Fibrillen in situ mit einem Durchmesser von 9–14 nm beobachtet.
Diese „dicken Fibrillen“ wurden vor allem im Hinterende der Amöben, die während aktiver Fortbewegung fixiert wurden, angetroffen, wo sie meist einzeln im Plasma zerstreut vorkommen. Eine Beziehung zu Mikrofilamenten vom Actintyp oder anderen Zellorganellen konnte nicht festgestellt werden.
Ebenfalls wurden bei den gleichen Trophozoiten Mikrotubuli mit einem Durchmesser von 35 nm beschrieben, die durch eine Hülle mit variablem Durchmesser von 19–25 nm umgeben sind. Die MT liegen einzeln oder in größeren Bündeln mit einem Durchmesser bis zu 350 nm unregelmäßig zerstreut zu Gruppen vereinigt in Cytoplasma. Als besondere Differenzierung werden spiralig gewundene MT dargestellt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Allerà, A., Wohlfahrt-Bottermann, K. E.: Weitreichende fibrilläre Protoplasmadifferenzierungen und ihre Bedeutung für die Protoplasmaströmung. IX. Aggregationszustände des Myosins und Bedingungen zur Entstehung von Myosinfilamenten in den Plasmodien von Physarum polycephalum. Cytobiologie 6, 261–286 (1972)
Behnke, O.: Mikrotubuli und Mikrofilamente. Triangel (De.) 13, 7–16 (1974)
Bhisey, A. N., Freed, J. J.: Altered movement of endosomes in Colchicin-treated cultured macrophages. Exp. Cell Res. 64, 430–438 (1971)
Bird, R. G., McCaul, T. F., Knight, R.: Rhabdo-virus-like particles of Entamoeba histolytica. Trans. roy. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg. 68, 2 (1974)
Bos, H. J.: The problem of pathogenicity in parasitic Entamoeba. Dissertation d. Rijksuniversiteit te Leiden (1973)
Camp, R. R., Mattern, C. F. T., Honigberg, B. M.: Study of Dientamoeba fragilis Jepps u. Dobell. I. Electronmicroscopic observations of the binucleate stages. II. Taxonomic position and revision of the genus. J. Protozool. 21, 69–82 (1974)
Daniels, E. W.: Ultrastructure. In: The biology of amoeba (K. W. Jeon, ed.), p. 125–168. New York and London: Academic Press 1973
Diamond, L. S.: Improved method for the monoxenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae with trypanosomatids. J. Parasit. 54, 715–719 (1968)
Diamond, L. S., Mattern, C. F. T., Bartgis, L. J.: Viruses of Entamoeba histolytica. I. Identification of transmissible virus-like agents. J. Virol. 9, 326–341 (1972)
Dobell, C.: Researches on the intestinal protozoa of monkeys and man. I. General introduction. II. Description of the whole life-history of Entamoeba histolytica in cultures. Parasitology 20, 357–412 (1928)
El Hashimi, Pittmann, W. F.: Ultrastructure of Entamoeba histolytica trophocoites obtained from the colon and from in vitro cultures. Amer. J. trop. Med. Hyg. 19, 215–226 (1970)
Feria-Velasco, A., Trevino, N.: The ultrastructure of trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with particular reference to spherical arrangements of osmiophilic cylindrical bodies. J. Protozool. 19, 200–211 (1972)
Gosh, T. N.: Observations on Entamoeba invadens Rodhain, 1934, in cultures. Arch. Protistenk. 112, 1–20 (1970)
Griffin, J. L.: In: Primitive motile systems in cell biology (R. D. Allen and N. Kamiya, eds.), p. 303–321. New York: Academic Press 1964
Griffin, J. L., Juniper, K.: Ultrastructure of Entamoeba histolytica from human amebic dysentery. J. Parasit. 54 (4), Section II, Part I, 124–125 (1970)
Lowe, C. Y., Maegraith, B. G.: Electron microscopy of an axenic strain of Entamoeba histolytica. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 64, 293–298 (1970)
Ludvik, J., Shipstone, A. C.: The ultrastructure of Entamoeba histolytica. Bull. Org. mond. Santé 43, 301–308 (1970)
Michel, R., Schupp, E.: Darstellung von Mikrofilamenten im Cytoplasma von Entamoeba histolytica. Z. Parasitenk. 43, 285–298 (1974)
Nachmias, V. T.: Fibrillar structures in the cytoplasm of Chaos chaos. J. Cell Biol. 23, 183 (1964)
Nachmias, V. T.: Further electron microscope studies on fibrillar organization of the ground cytoplasm of Chaos chaos. J. Cell Biol. 38, 40 (1968)
Nachmias, V. T.: Electron microscope observations on myosin from Physarum polycephalum, J. Cell Biol. 52, 648 (1972)
Pollard, T. D.: Progress in understanding amoeboid movement at the molecular level. In: The biology of amoeba (K. W. Jeon, ed.), p. 291–317. New York and London: Academic Press 1973
Pollard, T. D., Ito, S.: Cytoplasmic filaments of Amoeba proteus. I. The role of filaments in consistency changes and movement. J. Cell Biol. 46, 267–289 (1970)
Proctor, E. M., Gregory, M. A.: The ultrastructure of axenically cultivated trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with particular reference to an observed variation in structural pattern. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 66, 335–338 (1972a)
Proctor, E. M., Gregory, M. A.: The observation of a surface active lysosome in the trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica from the human colon. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 66, 339–342 (1972b)
Proctor, E. M., Gregory, M. A.: Ultrastructure of E. histolytica-strain NJH 200. Int. J. Parasit. 3, 457–460 (1973)
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as electronopaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Rosenbaum, R. M., Wittner, M.: Ultrastructure of bacterized and axenic trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with particular reference to helical bodies. J. Cell Biol. 45, 367–382 (1970)
Schäfer-Danneel, S.: Strukturelle und funktionelle Voraussetzung für die Bewegung von Amoeba proteus. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 441–462 (1967)
Taylor, D. L., Condeelis, J. S., Moore, P. L., Allen, R. D.: The contractile basis of amoeboid movement. I. The chemical control of mobility in isolated cytoplasm. J. Cell Biol. 59, 378–394 (1973)
Westphal, A., Michel, R.: Phagozytose und Pinozytose der Entamoeba histolytica. Z. Tropenmed. Parasit. 22, 82–91 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michel, R., Schupp, E. Fibrilläre und tubuläre Feinstrukturen im Cytoplasma von Entamoeba histolytica . Z. F. Parasitenkunde 47, 11–21 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00418061
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00418061