Abstract
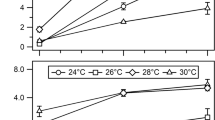
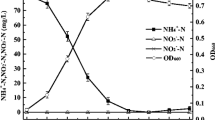
Azotobacter vinelandii was grown at constant growth rate in a chemostat with different molar ratios of sucrose to ammonium (C/N) in the influent media. Both compounds were consumed at essentially the same ratios as were present in the influent media. At low (C/N)-ratios, the cultures were ammonium-limited. At increased (C/N)-ratio ammonium-assimilating cultures additionally began to fix dinitrogen. The (C/N)-ratio at which nitrogenase activity became measurable, increased when the ambient oxygen concentration was increased. Immunoblotting revealed the appearance of nitrogenase proteins when the activity became detectable. Nitrogenase activity as determined either by acetylene reduction or by total nitrogen fixation gave constant relative activities of 1:3.8 (mol of N2 fixed per mol of acetylene reduced) under all sets of conditions used in this investigation. In spite of the oxygen dependent variation of the (C/N)-ratio, nitrogenase became active when the ammonium supply was less than about 14 nmol of ammonium per g of protein. This suggests that oxygen was not directly involved in the onset of dinitrogen fixation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beloserski AN, Proskurjakow L (1956) Praktikum der Biochemie der Pflanzen. Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschaften, Berlin, DDR
Bühler T, Monter U, Sann R, Kuhla J, Dingler C, Oelze J (1987) Control of respiration and growth yield in ammonium-assimilating cultures of Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Microbiol 148:242–246
Cejudo FJ, de la Torre A, Panque A (1984) Short-term ammonium inhibition of nitrogen fixation in Azotobacter. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 123:431–437
Drozd JW, Tubb RS, Postgate JR (1972) A chemostat study of the effect of nitrogen sources on nitrogen fixation, membranes and free amino acids in Azotobacter chroococcum. J Gen Microbiol 73:221–232
Gordon JK, Shah VK, Brill WJ (1981) Feedback inhibition of nitrogenase. J Bacteriol 148:884–888
Hardy RWF, Burns RC, Holsten RD (1973) Applications of the acetylene-ethylene assay for measurement of nitrogen fixation. Soil Biol Biochem 5:47–81
Kleiner D (1974) Quantitative relations for the repression of nitrogenase synthesis in Azotobacter vinelandii by ammonia. Arch Microbiol 101:153–159
Klugkist J, Haaker H (1984) Inhibition of nitrogenase activity by ammonium chloride in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol 157:148–151
Klugkist J, Haaker H, Wassink H, Veeger C (1985) The catalytic activity of nitrogenase in intact Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur J Biochem 146:509–515
Laane C, Krone W, Konings W, Haaker H, Veeger C (1980) Short-term effect of ammonium chloride on nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii and by bacteriods of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Eur J Biochem 103:39–46
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 327:680–685
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Nicholas DJD, Deering JV (1976) Repression, derepression and activation of nitrogenase in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Sci 29:147–161
Post E, Kleiner D, Oelze J (1983) Whole cell respiration and nitrogenase activities in Azotobacter vinelandii growing in oxygen-controlled continuous culture. Arch Microbiol 134:68–72
Postgate JR (1982) The fundamentals of nitrogen fixation. Cambridge University Press
Rivera-Ortiz JM, Burris RH (1975) Interactions among substrates and inhibitors of nitrogenase. J Bacteriol 123:537–545
Robson RL (1979) O2-Repression of nitrogenase synthesis in Azotobacter chroococcum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 5:259–262
Robson RL, Kennedy C, Postgate J (1983) Progress in comparative genetics of nitrogen fixation. Can J Microbiol 29:954–967
Shah VK, Davis LC, Brill WJ (1972) I. Repression and derepression of the iron-molybdenum and iron proteins of nitrogenase in Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta 253:498–511
Strandberg GW, Wilson PW (1968) Formation of the nitrogen fixation enzyme system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol 14:25–31
Tubb AS, Postgate JR (1973) Control of nitrogenase synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Gen Microbiol 79:103–117
Veeger C, Laane C, Scherings G, Haaker H, van Zeeland-Wolbers L (1980) Membrane energization and nitrogen fixation in Azotobacter vinelandii and Rhizobium leguminosarum. In: Newton WE, Orme-Johnson WH (eds) Nitrogen fixation, vol I. University Press, Baltimore, pp 111–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bühler, T., Sann, R., Monter, U. et al. Control of dinitrogen fixation in ammonium-assimilating cultures of Azotobacter vinelandii . Arch. Microbiol. 148, 247–251 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00414820
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00414820