Summary
Antiendomysial antibodies (EmA) of the IgA class are directed against reticulin components of the primate smooth muscle and are markers of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. These antibodies occur in essentially all active cases of celiac disease and in about 70% of dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) patients. IgA deposits in the dermal papillae of the skin are the hallmark of DH and are employed routinely in establishing its diagnosis. The incidence of IgA deposits in skin varies depending upon the site and type of biopsy specimen taken.
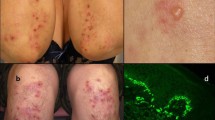
We studied sera and skin biopsy specimens for EmA and for IgA deposits in the skin from 11 DH patients. EmA were detected in the sera of 10 of the 11 cases. Of these 11 patients, 9 were positive for IgA deposits in their skin, as revealed by direct immunofluorescence (IF). The immune deposits were detected in the normal, and not in the lesional skin. DH cases that were initially negative on biopsy and serum positive for EmA were found to be positive when a repeat biopsy of the normal skin was performed. Thus, serological studies in conjunction with direct IF studies of the normal skin are useful in making a diagnosis of DH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accetta P, Kumar V, Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Helm F (1986) Antiendomysial antibodies: a serological marker for dermatitis herpetiformis. Arch Dermatol 122:459–462
Beutner EH, Nisengard RJ, Kumar V (1979) Defined immunofluorescence: basic concepts and their application to clinical immunodermatology. In: Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Bean SF (eds) Immunopathology of the skin, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 29–75
Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Kumar V, et al. (1986) Sensitivity and specificity of IgA class anti-endomysial antibodies for dermatitis herpetiformis and findings relevant to their pathogenic significance. J Am Acad Dermatol 15:464–473
Beutner EH, Kumar V, Krasny S, et al. (1987) Defined IF in immunodermatology. In: Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Kumar V (eds) Immunopathology of the skin, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 3–40
Chorzelski TP, Beutner EH, Jablonska S, et al. (1971) Immunofluorescence studies in the diagnosis of dermatitis herpetiformis and its differentiation from bullous pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol 56:373–380
Chorzelski TP (1983) Workshop on: Immunofluorescent and immunoelectron microscopy techniques. Proceedings of the XVIth International Congress of Dermatologists. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, pp 593–597
Chorzelski TP, Sulej J, Tchorzewska H, et al. (1983) IgA class endomysium antibodies in dermatitis herpetiformis and celiac disease. In: Beutner EH, Nisengard RJ, Albini B (eds) Defined immunofluorescence and related cytochemical methods. NY Acad Sci, New York, pp 325–334
Chorzelski TP, Beutner EH, Sulej J, et al. (1984) IgA antiendomysium antibody. A new immunological marker of dermatitis herpetiformis and coeliac disease. Br J Dermatol 111:395–402
Fry L, Seah PP (1974) Dermatitis herpetiformis: an evaluation of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol 90:137–146
Kapuscinska A, Zalewski T, Chorzelski TP, et al. (1987) Disease specificity, sensitivity and dynamics of changes in IgA class antiendomysial antibodies in celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 6:529–534
Katz SI, Hall RP, Lawley TP, et al. (1980) Dermatitis herpetiformis: the skin and the gut. Ann Intern Med 93:857–874
Kieffer M, Barnetson RstC (1983) Increased gliadin antibodies in dermatitis herpetiformis and pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol 108:673–678
Kumar V, Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP (1984) Distribution of monkey esophagus antigens reactive with IgA class antibodies in the sera of dermatitis herpetiformis patients. Arch Dermatol Res 276:293–296
Kumar V, Jain N, Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP (1987) Detection of anti-gliadin antibodies in bullous diseases and their recognition of similar antigenic polypeptides. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 83:155–159
Leonhard JN, Chorzelski TP, Beutner EH, et al. (1985) IgA antiendomysial antibody detection in the serum of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis following gluten challenge. Arch Dermatol Res 277:349–351
Ljunghall K, Scheynius A, Forsum U (1979) Circulating reticulin autoantibodies of IgA class in dermatitits herpetiformis. Br J Dermatol 100:173–176
Meer JB van der (1969) Granular deposits of immunoglobulins in the skin of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. An immunofluorescent study. Br J Dermatol 81:493–503
Moi H (1984) Incidence and prevalence of dermatitis herpetiformis in a county in central Sweden, with comments on the course of the disease and IgA deposits as diagnostic criterion. Acta Derma Venereol 64:144–150
Seah PP, Fry L (1975) Immunoglobulins in the skin in dermatitis herpetiformis and their relevance in diagnosis. Br J Dermatol 92:157–166
Seah PP, Fry L, Hoffbrand AV, et al. (1971) Tissue antibodies in dermatitis herpetiformis and adult coeliac disease. Lancet 1:834–836
Unsworth DJ, Leonhard JN, McMinn RMH, et al. (1981) Anti-gliadin antibodies and small intestinal mucosal damage in dermatitis herpetiformis. Br J Dermatol 105:653–658
Zone JJ, Carioto LA, LaSalle BA, et al. (1985) Granular IgA is decreased or absent in never involved skin in dermatitis herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol 84:332 (Abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Beutner, E.H. & Chorzelski, T.P. Antiendomysial antibody — useful serological indicator of dermatitis herpetiformis. Arch Dermatol Res 279, 454–458 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412591
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412591