Summary
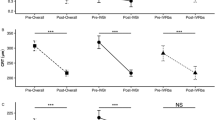
Bupranolol 0.5% oily solution applied topically lowered intraocular pressure of glaucomatous eyes significantly. The pressure decrease is related to pre-treatment pressure levels. The maximum effect occurred within 4 hours and lasted for more than 24 hours. No objective or subjective irritation could be attributed to the ophthalmic preparation. There was no significant effect on outflow facility, on blood pressure or tear flow. However, bupranolol produces local anesthesia on the eye. The problem of tachyphylaxis is discussed in the treatment of glaucoma with bupranolol eye drops.
Zusammenfassung
Die ölige Lösung von 0,5% Bupranolol bewirkt bei lokaler Applikation am Auge eine signifikante Augendrucksenkung um durchschnittlich 42 % des Ausgangsdruckes. Das Maximum der Drucksenkung war nach 4 Stunden zu beobachten, die Drucksenkung nach einmaliger Applikation dauerte mehr als 24 Stunden. Die verwendeten Bupranolol-Augentropfen führten zu keiner Reizung der vorderen Augenabschnitte. Es fand sich kein signifikanter Effekt auf die Abflußleichtigkeit, auf den Blutdruck oder den Tränenfluß. Bupranolol bewirkt jedoch eine Lokalanaesthesie am Auge. Das Problem eines langsamen Wirkungsverlustes von Bupranolol-Augentropfen als Glaukom-Therapeutikum wird diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonomi, I., Steindler, P.: Effect of pindolol on intraocular pressure. Brit. J. Ophthal. 59, 301–303 (1975)
Elliot, M.J., Cullen, P.M., Philipps, C.I.: Ocular hypotensive effect of atenolol (Tenormin, I.C.I.). Brit. J. Ophthal. 59, 296–300 (1975)
Katz, I.M., Hubbard, W.A., Getson, A.J., Gould, A.L.: Intraocular pressure decrease in normal volunteers following timolol ophthalmic solution. Invest. Ophthal. 15, 489–492 (1976)
Rahi, A.H.S., Chapman, C.M., Gerner, A., Wright, P.: Pathology of practolol-induced ocular toxicity. Brit. J. Ophthal. 60, 312–323 (1976)
Sharaf, E.D., Haroun, E.A., Ishaac, Z., El Shewy, T.M., Nassel, A.E.H.: The effect of some β-adrenergic blockers on human intraocular pressure. Exp. Eye Res. 19, 223–225 (1974)
Vale, J., Gibbs, A.C.C., Philipps, C.I.: Topical propranolol and ocular tension in the human. Brit. J. Ophthal. 56, 770–775 (1972)
Waterloh, E., Rittel, H.-F., Leide, E.: Untersuchungen über 1-(6′-Chlor-3′-methylphenoxy)-3-tert.-butylamino-propan-2-ol-hydrochlorid (KL 255). Arzneimittel-Forsch. 19, 153–156, 330–333 (1969)
Willems, D., Frisch, P., Klepzig, H.: Behandlung von Angina pectoris und Herzrhytmusstörungen mit einem Beta-Rezeptorenblocker. Zeitschr. Kreislaufforsch. 60, 309–318 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are indebted to Dr. Winzer, chem.-pharm. Fabrik, Konstanz, for a generous supply of bupranolol in oily solution (OphthoreninR), and to Ms. E. Profitlich for able technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krieglstein, G.K., Sold-Darseff, J. & Leydhecker, W. The intraocular pressure response of glaucomatous eyes to topically applied bupranolol. Albrecht von Graefes Arch. Klin. Ophthalmol. 202, 81–86 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410994
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410994