Abstract
Undesirable side effects have limited the use of adrenaline/guanethidine combinations in the usual concentrations in the treatment of chronic simple glaucoma. Better tolerance to lower concentrations has already been demonstrated in other studies.
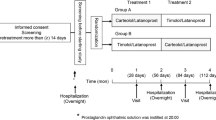
In the double-blind study described here, three different combinations (adrenaline 1%, 0.5% and 0.2% combined respectively with guanethidine 5%, 3% and 1%) were compared in respect of their depressive action on intraocular pressure and the tolerance shown to them. All three combinations were found to be effective.
The combination with the lowest concentration was significantly less hypotensive in its effect than the other two but the number of patients treated was too small to allow a clear distinction to be made between the effects of the other two combinations. Nevertheless, there was a tendency for the effectiveness to fall with decreasing concentration. As far as tolerance was concerned, there was little difference between the middle and lowest concentrations, the latter being that best tolerated. The excellent effect of the strongest concentration was impaired by the poor tolerance shown to it.
The comparison between the three combinations was followed by a study of the diurnal pressure changes in patients during the course of the treatment. The slow rise up to midday and the abrupt afternoon fall remain unexplained. The low concentration of the preparation had a better hypotensive action than pilocarpine, while the middle concentration proved even a little better than the beta-blocker Timolol.
Zusammenfassung
Die bisher meist verwendeten Konzentrationen von Adrenalin-Guanethidin-Kombinationen in der Behandlung des Glaucoma chronicum simplex waren wegen unangenehmen Nebenwirkungen in ihrer Anwendbarkeit begrenzt. Andere Studien zeigten die bessere Verträglichkeit schwächerer Konzentrationen.
In unserer Doppelblindstudie verglichen wir die drucksenkende Wirkung und Verträglichkeit drei verschiedener Dosen der Kombination (Adrenalin 1%, 0.5% und 0.2% kombiniert mit Guanethidin 5%, 3% und 1%). Alle drei Konzentrationen waren wirksam.
Die schwächste Konzentration ist signifikant weniger hypotensiv als die zwei anderen. Infolge eines zu kleinen Patientenkollektives konnte die mittlere Konzentration nicht eindeutig von der starken Konzentration abgegrenzt werden. Jedoch zeigt sich die Tendenz der abnehmenden Wirksamkeit mit fallender Konzentration. In Bezug auf Verträglichkeit steht die mittlere Konzentration nahe bei der schwachen, am besten ertragenen. Die gute Wirkung der starken Konzentration wird beeinträchtigt durch die schlechte Verträglichkeit.
Im Anschluß an den Vergleich der drei Dosen wurde der Tagesdruckverlauf unter Z 15000 untersucht. Der langsame Anstieg gegen Mittag und brüske Abfall am Nachmittag ist noch unerklärt. Die schwache Konzentration senkt den Druck besser als der Betablocker Timolol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anselmi, P., Bron, A.J., Maurice, D.M.: Action of drugs on the aqueous flow in man measured by fluorophotometry. Exp. Eye Res., 7, 487–496 (1968)
Becker, B., Pettit, T.H., Gay, A.J.: Topical Epinephrine Therapy of Open-Angle Glaucoma. Arch. Ophthal., 66, 219–224 (1961)
Bischoff, P.: Erfahrungen mit Timolol in der Glaukomtherapie. Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk. 173, 2, 202–207 (1978)
Bonomi, L., Di Comite, P.: Effect of guanethidine and other sympatholytic drugs. Upon the pupillary response to electrical stimulation of the sympathetic system in rabbits. Amer. J. Ophthal., 61, 544–546 (1966)
Boura, A.L.A., Green, A.F.: Comparison of bretylium and guanethidine. Tolerance, and effects on adrenergic nerve function and responses to sympathomimetic amines. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 19, 13–41 (1962)
Bron, A.J.: Sympathetic control of aqueous secretion in man. Brit. J. Ophthal. 165, 344–349 (1969)
Cannon, W.B.: A law of denervation. Amer. J. med. Sci., 198, 737–750 (1939)
Collignon, J., Prijot, E.: La guanethidine a-t-elle une place dans le traitement d'hypertension oculaire? Bull. Soc. Belge d'Ophtal. 165, 344–349 (1973)
Crombie, A.L.: Adrenergic hypersensitization as a therapeutic tool in glaucoma. Trans. ophthal. Soc. U.K., 94, 570–572 (1974)
Eltz, H., Aeschlimann, J., Gloor, B.: A double-blind clinical trial of a guanethidine/adrenaline combination, compared with the two separate components, in glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmologica, 56, 191–200 (1978)
Gloster, J.: Guanethidine and glaucoma. Trans. ophthal. Soc. U.K., 94, 573–575 (1974)
Green, A.F., Robson, R.D.: Adrenergic neurone blocking agents: tolerance and hypersensitivity to adrenaline and noradrenaline. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 25, 497–506 (1965)
Hendly, E.D., Eakins, K.E.: The mechanism of action of guanethidine on aqueous humour dynamics. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 150, 393–397 (1965)
Hoyng, Ph.F.J., Dake, C.L., Greve, E.L.: A double-blind short-term trial of guanethidine 3% and adrenaline 0.5% combined in one eye drop. Albrecht v. Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal. 203, 73–80 (1977)
Hoyng, Ph.F.J., Dake, C.L.: The combination of guanethidine 3% and adrenaline 0.5% in 1 eyedrop (GA) in glaucoma treatment. Brit. J. Ophthal. 63, 56–62 (1979)
Jones, D.E.P., Norton, D.A., Harvey, J., Davies, D.J.G.: Effect of adrenaline and guanethidine in reducing intraocular pressure in rabbits' eyes. Brit. J. Ophthal. 59, 304–307 (1975)
Jones, D.E.P., Norton, D.A., and Davies, D.J.G.: Low dosage combined adrenaline-guanethidine formulations in the management of chronic simple glaucoma. Trans. ophthal. Soc. U.K. 97, 192–195 (1977)
Küchle, H.J.: Zur lokalen Wirkung von Guanethidin (Ismelin) auf das gesunde und glaukomkranke Auge. Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk. 139, 224–234 (1961)
Kutschera, E.: Klinische Erfahrungen mit Ismelin. Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk. 139, 234–241 (1961)
Lamble, J.W.: Some factors affecting the ocular hypotensive and mydriatic responses of the rabbit to topically applied 1-adrenaline bitartrate. Exp. Eye Res. 19, 79–89 (1974)
Langham, M.E.: The responses of the pupil and intraocular pressure of conscious rabbits to adrenergic drugs following unilateral superior cervical ganglionectomy. Exp. Eye Res. 4, 381–389 (1965)
Mills, K.B., Ridgway, A.E.A.: A double-blind comparison of guanethidine and adrenaline drops with 1% adrenaline alone in chronic simple glaucoma. Brit. J. Ophthal. 62, 320–323 (1978)
Nagasubramanian, S., Tripathi, R.C., Poinoosawny, D., Gloster, J.: Low concentration guanethidine and adrenaline therapy of glaucoma. Trans. Ophthal. Soc. U.K. 96, 179–183 (1976)
Obstbaum, S.A., Kolker, A.E., Phelpps, C.D.: Low-dose epinephrine effect on intraocular pressure. Arch. Ophthal. 92, 118–120 (1974)
Oosterhuis, J.A.: Guanethidine (Ismelin) in ophthalmology. Observations in rabbits. Arch. Ophthal. 67, 592–599 (1962)
Paterson, G.D., Paterson, G.: Drug therapy of glaucoma. Brit. J. Ophthal. 56, 288–294 (1972)
Romano, J.: Use of guanethidine 5 per cent and adrenaline 1 per cent in the treatment of severe open angle glaucoma. Trans. Ophthal. Soc. U.K. 97, 196–201 (1977)
Roth, J.A.: Guanethidine and adrenaline used in combination in chronic simple glaucoma. Brit. J. Ophthal. 3, 157–163 (1973)
Sears, M.L., Sherk, T.E.: The trabecular effect of noradrenaline in the rabbit eye. Invest. Ophthal. 3, 157–163 (1964)
Sears, M.L.: The mechanism of action of adrenergic drugs in glaucoma. Invest. Ophthal. 5, 2, 115–119 (1966)
Siegel, S.: Nonparametric statistics for the behavioural sciences. Mc. Graw-Hill, 166–173 (1956)
Sneddon, J.M., Turner, P.: The effect of local guanethidine on the palpebral fissure and the pupil in thyreotoxicosis, and its interaction with sympathomimetic amines. J. Physiol. (London) 189, 20–23 (1967)
Zimmermann, T.J., Kaufmann, H.E.: Timolol: Dose response and duration of action. Arch. Ophthal. 95, 605 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Urner-Bloch, U., Aeschlimann, J.E. & Gloor, B.P. Treatment of chronic simple glaucoma with an adrenaline/guanethidine combination at three different dosages (comparative double-blind study). Albrecht von Graefes Arch. Klin. Ophthalmol. 213, 175–185 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410987
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410987