Abstract
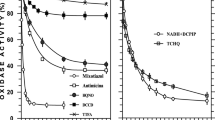
The specific inhibitory effect of benzhydroxamic acid on the cyanide-insensitive respiration could be reversed in whole cells of the yeast Saccharomycopsis lipolytica, by addition of Fe(III), in a way suggesting a competition between the added iron and an enzyme-bound metallic ion, both central atoms for the ligand benzhydroxamic acid. The possibility that added metal ions modify the penetration of BHAM into the cells was ruled out. Co(II), Cu(II) and Al(III) could substitute for Fe(III). A linear relation between the concentration in added Fe(III) and the reversed respiration rate was observed. At a given cell concentration. the reversion by added Fe(III) of the inhibitory effect of benzhydroxamic acid on the alternative respiration appeared more related to the degree of inhibition rather than to the concentration in added inhibitor. Increasing cell concentrations required increasing amounts of Fe(III) to reach the same level of reversion. No reversal occurred at concentrations in added Fe(III) lower than 0.1 mM, whatever the benzhydroxamic concentration, the cell concentration or the yeast batch.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bittel, J. E., Koeppe, D. E., Miller, R. J.: Sorption of heavy metal cations by corn mitochondria and the effects on electron and energy transfer reactions. Physiol. Plant. 30, 226–230 (1974)
Estabrook, R. W.: Mitochondrial respiratory control and the polarographic measurement of ADP: O ratios. In: Methods in enzymology, Vol. 10 (R. W. Estabrook, M. E. Pullman, eds.), pp. 41–47. New York: Academic Press 1967
Henry, M.-F., Hamaide-Deplus, M.-C., Nyns, E.-J.: Cyanide-insensitive respiration of Candida lipolytica. Antonie v. Leeuwenhoek 40, 79–91 (1974)
Henry, M.-F., Nyns, E.-J.: Cyanide-insensitive respiration. An alternative mitochondrial pathway. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 4, 1–65 (1975)
Neilands, J. B.: Naturally occurring non-porphyrin iron compounds. Structure and Bonding 1, 59–108 (1966)
Neilands, J. B.: Hydroxamic acids in nature. Science 156, 1443–1447 (1967)
Neilands, J. B.: Evolution of biological iron binding centers. Structure and Bonding 11, 145–170 (1972)
Nyns, E.-J., Auquière, J.-P., Chiang, N., Wiaux, A. L.: Comparative growth of Candida lipolytica on glucose and n-hexadecane. Nature (Lond.) 215, 177–178 (1967)
Schonbaum, G. S., Bonner, W. D., Jr., Storey, B. T., Bahr, J. T.: Specific inhibition of the cyanide-insensitive respiratory pathway in plant mitochondria by hydroxamic acids. Plant Physiol. 47, 124–128 (1971)
Umbreit, W. W., Burris, R. H., Stauffer, J. F.: Manometric techniques, 4th ed. Minneapolis: Burgess 1964
Yarrow, D.: Four new combinations in yeasts. Antonie v. Leeuwenhoek 38, 357–360 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henry, M.F., Nyns, E.J. Reversion by Fe(III) of the inhibition by hydroxamic acids of the cyanide-Insensitive respiration in the yeast Saccharomycopsis lipolytica . Arch. Microbiol. 114, 171–174 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410780
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410780