Abstract
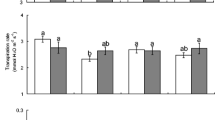
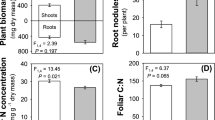
Rising atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration is expected to increase plant productivity, but little evidence is available regarding effects on insect feeding or growth. Larvae of the soybean looper, a noctuid moth, were fed leaves of soybean plants grown under three carbon dioxide regimes (350, 500 and 650 μl·l-1). Larvae fed at increasingly higher rates on plants from elevated carbon dioxide atmospheres: 30% greater on leaves from the 650 μl·l-1 treatment than on leaves from the 350 μl·l-1 treatment. When variation in larval feeding was related to the leaf content of nitrogen and water, there was no significant remaining effect of carbon dioxide treatment. The principal effect on herbivores of increasing the carbon supply of leaves appeared to be reduction of leaf nutrient concentration. This study suggests that feeding by herbivores on the leaves of C3 plants may increase as the level of atmospheric carbon dioxide rises.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazzaz FA, Carlson RW (1984) The response of plants to elevated CO2. I. Competition among an assemblage of annuals at two levels of soil moisture. Oecologia (Berlin) 62:196–198
Burkett BN, Schneiderman HA (1974) Roles of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the control of spiracular function in Cecropia pupae. Biol Bull 147:274–293
Butler GD, Kimball BA, Mauney JR (1986) Populations of Bemisia tabaci (Genn.). (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) grown in open-top field CO2-enriched chambers. Southwestern Entomologist (in press)
Carlson RW, Bazzaz FA (1980) The effects of elevated CO2 concentrations on growth, photosynthesis, transpiration, and water use efficiency of plants. In Environmental and Climatic Impact of Coal Utilization, JJ Singh and A Deepack, Eds Academic Press, New York
Clark WC (1983) Ed. Carbon Dioxide Review 1982. Oxford Univ. Press, New York
Fraenkel GS (1959) The raison d'etre of secondary plant substanes. Science 129:1466–1470
Greene GL, Leppla NC, Dickerson WA (1976) Velvetbean caterpillar rearing procedure and artificial medium. J Econ Entomol 69:487–488
Huber SC, Isreal DW (1982) Biochemical basis for partitioning of photosynthetically fixed carbon between starch and sucrose in soybean (Glycine max Merr.) leaves. Plant Physiol 69:691–696
Kimball BA (1983) Carbon dioxide and agricultural yield: an assemblage and analysis of 430 prior observations. Agron J 75:779–788
Kimball BA, Mauney JR, Guinn G, Nakayama FS, Pinter PJ, Clawson KL, Idso SB, Butler GD, Radin JR (1984) Effects of increasing atmospheric CO2 on the yield and water use of crops. US Water Conservation Laboratory (Phoenix, Arizona) 1984 Annual Report, pp 178–239
Kogan M, Cope D (1974) Feeding and nutrition of insects associated with soybeans. 3. Food intake, utilization, and growth in the soybean looper, Pseudoplusia includens. Ann Entomol Soc Am 67:66–72
Kramer PJ (1981) Carbon dioxide concentration, photosynthesis and dry matter production. Bioscience 31:29–33
Lincoln DE, Newton TS, Ehrlich PR, Williams KS (1982) Coevolution of the checkerspot butterfly Euphydryas chalcedona and its larval food plant Diplacus aurantiacus: larval response to protein and leaf resin. Oecologia (Berlin). 52:216–223
Lincoln DE, Sionit N, Strain BR (1984) Growth and feeding response of Pseudoplusia includens to host plants grown in controlled carbon dioxide atmospheres. Env Ent 13:1527–1530
Rogers HH, Thomas JF, Bingham GE (1983) Response of agronomic and forest species to elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide. Science 220:428–429
Scriber JM (1982) The behavior and nutritional physiology of southern armyworm larvae as a function of plant species consumed in earlier instars. Entomol Exp Appl 31:359–369
Scriber JM, Slansky F (1981) The nutritional ecology of immature insects. Ann Rev Entomol 26:183–211
Shour MH, Sparks TC (1981) Biology of the soybean looper, Pseudoplusia includens: characterization of last-stage larvae. Ann Entomol Soc Am 74:532–535
Sionit N (1983) Response of soybean to two levels of mineral nutrition in CO2-enriched atmosphere. Crop Sci 23:329–333
Sionit N, Strain BR, Hellmers M, Riechers GM, Jaeger CH (1985) Long term atmospheric CO2 enrichment affects the growth and development of Liquidambar styraciflua and Pinus taeda seedlings. Can J For Res 15:468–471
Sionit N, Rogers HH, Bingham GE, Strain BR (1984) Photosynthesis and stomatal conductance with CO2 enrichment of container- and field-grown soybeans. Agron J 76:447–451
Slansky F, Feeny P (1977) Stabilization of the rate of nitrogen accumulation by larvae of the cabbage butterfly on wild and cultivated food plants. Ecol Monogr 47:209–228
Strain BR, Bazzaz F (1983) Terrestrial plant communities. In CO2 and Plants: The Response of Plants to Rising Levels of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide. AAAS Selected Symposium 84. Westview Press. Boulder
Waldbauer GP (1968) The Consumption and Utilization of Food by Insects. Adv Insect Physiol 5:229–288
Wong SC (1979) Elevated atmospheric partial pressure of CO2 and plant growth. Oecologia (Berlin) 44:68–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lincoln, D.E., Couvet, D. & Sionit, N. Response of an insect herbivore to host plants grown in carbon dioxide enriched atmospheres. Oecologia 69, 556–560 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410362
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410362