Summary
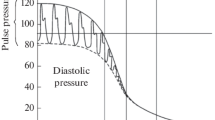
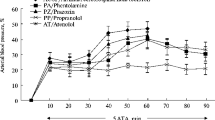
Clonidine was administered into the left vertebral artery of anesthetized cats. A dose-response curve of the lowering effect on intraocular pressure (IOP) has been made and compared with the dose-response curve obtained after intravenous administration. A more pronounced decrease in IOP after the first route of administration became evident. The effect is not secondary to a stronger reduction of blood pressure by centrally injected clonidine.
Distribution experiments with 14C-clonidine revealed no direct connection between the vertebral arteries and the blood supply of the eye. For 2 h the concentrations in the eye are somewhat lower than after intravenous administration. Therefore, the IOP-lowering effect is not due to a direct influence of clonidine on the eye.
It is submitted that the clonidine-induced reduction in IOP is at least in part due to a central mechanism, in which the stimulation of central α-adrenoceptors and adrenergic neurons may be involved. The relevance of this hypothesis with regard to a possible central regulation of IOP is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R.C., Langham, M.B.: The intraocular pressure response of conscious rabbits to clonidine. Invest. Ophthalmol. 15, 815–823 (1976)
Bill, A., Heilmann, K.: Ocular effects of clonidine in cats and monkeys (Macaca irus). Exp. Eye Res. 21, 481–488 (1975)
Darda, S.: Pharmacokinetics of clonidine. In: Recent Advances in Hypertension, P. Milliez and M. Safar, eds., pp. 375–388. Reims: Société Alinéa 1975
Edelhauser, E., Nemetz, U.: Zur intraocularen Drucksenkung mit Clonidin. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 160, 188–193 (1972)
Gloster, J., Greaves, D.P.: Effect of diencephalic stimulation upon intraocular pressure. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 41, 513–532 (1957)
Innemee, H.C., van Zwieten, P.A.: An increase in intraocular pressure due to clonidine. Albrecht von Graefes Arch. Klin. Ophthalmol. 207, 149–156 (1978 a)
Innemee, H.C., van Zwieten, P.A.: The distribution in the eye and the effect on intraocular pressure of clonidine. Albrecht von Graefes Arch. Klin. Ophthalmol. (in press 1978b)
Jünemann, G., Paust, E.: Über Wirkungsweise und Wirkungsprinzip des Catapresan in der Glaukomtherapie. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 158, 501–513 (1971)
Jünemann, G., Schmidt, G.: Zur Catapresanwirkung am glaukomatösen Auge. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 157, 193–201 (1970)
Krieglstein, G.K., Langham, M.E., Leydhecker, W.: The peripheral and central neural actions of clonidine in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Invest. Ophthalmol. 17, 149–158 (1978)
Leydhecker, W., Hertlein, E.: Senkt Catapresan den I.O. Druck unabhängig vom Blutdruck? Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 159, 574–577 (1971)
Reneman, R.S., Wellens, D., Jageneau, A.H.M., Stynen, L.: Vertebral and carotid blood distribution in the brain of the dog and the cat. Cardiovasc. Res. 8, 15–72 (1974)
Sallmann von, L., Lowenstein, O.: Responses of intraocular pressure, blood pressure and cutaneous vessels to electric stimulation in the diencephalon. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 39 (II) 11–29 (1955)
Sattler, R.W., van Zwieten, P.A.: Acute hypotensive action of 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline hydrochloride (St 155) after infusion into the cat's vertebral artery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2, 9–13 (1967)
Schmitt, H.: Actions des α-sympathomimétiques sur les structures nerveuses. Actual. Pharmacol (Paris). 24, 93–191 (1971)
Schmitt, H., Schmitt, H.: Interactions between 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline (St 155, Catapresan®) and adrenergic blocking drugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 9, 7–13 (1970)
Schmitt, H., Schmitt, H., Fénard, S.: Evidence for an α-sympathomimetic component in the effects of catapresan on vasomotor centers: antagonism by piperoxane. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 14, 98–100 (1971)
Sherbini-Schepers el, M.A., Innemee, H.C., van Zwieten, P.A.: Enhanced depressor effect of clonidine after modification of the vertebral artery infusion technique. Proc. Joint Meetings of the Dutch Medical and Biological Societies, Leiden 1977
Zwieten van, P.A.: Antihypertensive drugs with a central action. Progress in Pharmacol. 1, 1–63 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Innemee, H.C., van Zwieten, P.A. The central ocular hypotensive effect of clonidine. Albrecht von Graefes Arch. Klin. Ophthalmol. 210, 93–102 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409995
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409995