Summary
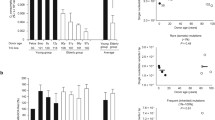
The normal senescent fibroblasts in culture accumulate a significantly high proportion of altered enzymes, and the alterations are considered to be the manifestation of ageing in molecular terms. To detect the possible molecular alterations in patients with De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome, the severest form of xeroderma pigmentosum, in which repair processes to UV light-damaged DNA are defective and the neurologic abnormalities are considered to reflect accelerated ageing, we studied the heat stability of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) in crude extracts of cultured skin fibroblasts. Three patients with the syndrome were the center of our investigation. Even at early passage in culture the heat-labile portion of G6PD was increased in the cells from patients in comparison to normal controls.
The life span of the cells in culture from patients was not reduced below normal age-matched controls, and no appreciable senescent appearance was observed. The increase in the heat-labile portion of G6PD from cells of De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome patients to reflect that defective repair of DNA damage occurs, rather than being a direct result of ageing of cultured cells.
Zusammenfassung
Die normalen gealterten Fibroblasten zeigen einen signifikanten hohen Anteil veränderter Enzyme. Diese Veränderungen werden als molekularbiologische Zeichen des Alterns betrachtet. Um die möglichen moleckularen Veränderungen mit De Sanctis-Cacchione-Syndrom, der schwersten Form des Xeroderma pigmentosum, bei dem Repair-Mechanismen auf UV der DNA defekt sind und die neurologischen Abnormalitäten offenbar einen beschleunigten Altersvorgang belegen, wurde die Hitzestabilität der Glucose-6-Phosphat-Dehydrogenase in rohen Extrakten von Hautfibroblastenkulturen untersucht. Es standen drei Patienten zur Untersuchung zur Verfügung. Bei den frühesten kulturellen Passagen zeigte sich der hitzelabile Anteil der Glucose-6-Phosphat-Dehydrogenase in den Zellen der Patienten vermehrt im Vergleich mit den normalen Kontrollen. Die Überlebenszeit der Zellkulturen zeigten keinen Unterschied zu den der Kontrollen. Es wurden keine bemerkenswerte Alterserscheinungen beobachtet. Der Anstieg der hitzelabilen Glucose-6-Phosphat-Dehydrogenase in Zellen der Patienten mit De Sanctis-Cacchione-Syndrom scheinen mehr direkt auf einen defekten Repair-Mechanismus der DNA hinzuweisen als sich aus dem Altern der Zellkulturen ableiten zu lassen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarkson JM, Evans HJ (1972) Unscheduled DNA synthesis in human leucocytes after exposure to UV light, r-rays and chemical mutagens. Mut Res 14:413–430
Cleaver JE (1968) Defective repair replication of DNA in seroderma pigmentosum. Nature 218:652–656
Cleaver JE (1973) DNA repair with purines and pyrimidines in radiation and carcinogen-damaged normal and xeroderma pigmentosum human cells. Cancer Res 33:362–369
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis. II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann NY Acad Sci 121:404–427
Dreyfus JC, Rubinson H, Shapira F, Weber A, Marie J, Kahn A (1977) Possible molecular mechanisms of ageing. Gerontol 23:211–218
Fujiwara Y, Higashikawa T, Tatsumi M (1977) A retarded rate of DNA replication and normal level of DNA repair in Werner's syndrome fibroblasts in culture. J Cell Physiol 92:365–374
Gershon D, Gershon H (1976) An evaluation of the “error catastrophe” theory of ageing in the light of recent experimental results. Gerontol 22:212–219
Goldstein S, Moerman EJ (1975) Heat-labile enzymes in Werner's syndrome fibroblasts. Nature 255:159
Goldstein S, Moerman EJ (1975) Heat-labile enzymes in skin fibroblasts from subjects with progeria. N Engl J Med 292:1305–1309
Goldstein S, Singal M (1974) Alteration of fibroblast gene products in vitro from a subject with Werner's syndrome. Nature 251:719–721
Hart RW, Setlow RB (1974) Correlation between deoxyribonucleic acid excision-repair and life span in number of mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:2169–2173
Hizi A, Yagil G (1974) On the mechanism of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase regulation in mouse liver. Eur J Biochem 45:201–209
Holliday R, Tarrant GM (1972) Altered enzymes in ageing human fibroblasts. Nature 238:26–30
Holliday R, Porterfield JS, Gibbs DD (1974) Premature ageing and occurrence of altered enzymes in Werner's syndrome fibroblasts. Nature 248:762–763
Kuhnlein U, Pemhoet EE, Linn S (1976) An altered apurinic DNA endonuclease activity in group A and group D xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:1169–1173
Lambert B, Ringborg U, Skoog L (1979) Age-related decrease of ultraviolet light-induced DNA repair synthesis in human leucocytes. Cancer Res 39:2792–2795
Lewis CM, Tarrant GM (1972) Error theory and ageing in human diploid fibroblasts. Nature 239:316–318
Orgel LE (1963) The maintenance of the accuracy of protein synthesis and its relevance to ageing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 49:517–521
Ornstein L (1964) Disc electrophoresis. I. Back ground and theory. Ann NY Acad Sci 121:321–349
Reed WB, Sugarman GI, Mathis RA (1977) De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome. Arch Dermatol 113:1561–1563
Robbins JH, Kraemer KH, Lutzner MA, Festoff BW, Coon HG (1974) Xeroderma pigmentosum: an inherited disease with sun sensitivity, multiple cutaneous neoplasms, and abnormal DNA repair. Ann Int Med 80:221–248
Rothstein M (1979) The formation of altered enzymes in ageing animals. Mech Ageing Dev 9:197–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, N., Kitano, Y. Heat-labile glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in cultured fibroblasts from patients with De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome. Arch Dermatol Res 271, 341–346 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409462
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409462