Abstract
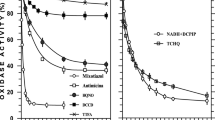
Assays were performed on the components of the respiratory chain enzyme complex and the citric acid cycle enzyme α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.4.2) from membrane preparations of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata grown in continuous culture. Cells were grown photoheterotrophically then switched to a chemoheterotrophic growth mode. NADH-and succinate-dependent oxygen uptake activities and cytochrome c oxidase (EC 1.9.3.1) activity were 5–6-fold higher in chemotrophically grown cells. The activities of NADH dehydrogenase (EC 1.6.99.3) and succinate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.1) did not differ greatly between the two growth modes, and it is suggested that in respiratory chain electron flow the cytochrome c oxidase segment catalyses the rate limiting step. In addition, a 5-fold increase in α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity was observed after the transition from a phototrophic to chemotrophic growth mode. Oxidase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activities increased 3–4-fold in phototrophically growing cultures exposed to a low partial pressure of oxygen (50 Pa; 1 atmosphere = 1.013×105 Pa). The data suggest that this small amount of oxygen exerts a significant effect on aerobic bioenergetic enzymes, even during phototrophic growth of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiking H, Sojka GA (1979) Response of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata to illumination and growth rate in a light limited continuous culture. J Bacteriol 139:530–536
Baccarini-Melandri A, Jones OTG, Hauska G (1978) Cytochrome c 2-an electron carrier shared by the respiratory and photosynthetic electron transport chain of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. FEBS Lett 86:151–154
Beatty JT, Gest H (1981) Biosynthetic and bioenergetic functions of citric acid cycle reactions in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol 148:584–593
Chappell JB (1964) The oxidation of citrate, iso-citrate and cis-aconitate by isolated mitochondria. Biochem J 90:225–237
Dierstein R, Drews G (1974) Nitrogen-limited continuous culture of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata growing photosynthetically or heterotrophically under low oxygen tensions. Arch Microbiol 99:117–128
Dierstein R, Drews G (1975) Control of composition and activity of the photosynthetic apparatus of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata grown in ammonium-limited continuous culture. Arch Microbiol 106:227–235
Firsow NN, Drews G (1977) Differentiation of the intracytoplasmic membrane of Rhodopseudomonas palustris induced by variations of oxygen partial pressure or light intensity. Arch Microbiol 115:299–306
Horio T, Bartsch RG, Kakuno T, Kamen MD (1969) Two reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenases from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem 244:5899–5909
Kaufmann N, Reidl HH, Golecki JR, Garcia AF, Drews G (1982) Differentiation of the membrane system in cells of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata after transition from chemotrophic to phototrophic growth conditions. Arch Microbiol 131:313–322
Keevil CW, Hough JS, Cole JA (1979) Regulation of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase synthesis in Citrobacter freundii by traces of oxygen and by glutamate. J Gen Microbiol 114:355–359
King TE (1963) Reconstitution of respiratory chain enzyme systems. XI. Use of artificial electron acceptors in the assay of succinate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 238:4032–4036
King MT, Drews G (1975) The respiratory electron transport of heterotrophically grown Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Arch Microbiol 102:219–231
Lampe H, Drews G (1972) Die Differenzierung des Membransystems von Rhodopseudomonas capsulata hinsichtlich seiner photosynthetischen und respiratorischen Funktionen. Arch Microbiol 84:1–19
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
Madigan MT, Gest H (1978) Growth of a photosynthetic bacterium anaerobically in darkness supported by “oxidant-dependent” sugar fermentation. Arch Microbiol 117:119–122
Madigan MT, Gest H (1979) Growth of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata chemoautotrophically in darkness with H2 as the energy source. J Bacteriol 137:524–530
Marrs BL, Stahl CL, Lien S, Gest H (1972) Biochemical physiology of a respiration deficient mutant of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:916–920
McCarthy JEG, Ferguson SJ (1982) Respiratory control and the basis of light induced inhibition of respiration in chromatophores from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 107:1406–1411
Melandri BA, Baccarini-Melandri A, San Pietro A, Gest H (1971) Interchangeability of phosphorylation coupling factors in photosynthetic and respiratory energy conversion. Science 174:514–516
Oelze J, Kamen MD (1975) Separation of respiratory reactions in Rhodospirillum rubrum: inhibitor studies with 2-hydroxydiphenyl. Biochim Biophys Acta 387:1–11
Oshima T, Drews G (1981) Isolation and partial characterisation of the membrane bound NADH dehydrogenase from the phototrophic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Z Naturforsch 36c:400–406
Thore A, Keister DL, San Pietro A (1969) Studies on the respiratory system of aerobically (dark) and anaerobically (light) grown Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Microbiol 67:378–396
Wakim B, Oelze J (1980) The unique mode of adjusting the composition of the photosynthetic apparatus to different environmental conditions by Rhodospirillum tenue. FEMS (Microbiol) Lett 7:221–223
Wakim B, Schrader M, Oelze J (1979) Characterization of cell envelope fractions of chemotrophically and phototrophically grown Rhodospirillum tenue. Arch Microbiol 123:287–293
Wakim B, Georg B, Oelze J (1980) Regulation of respiration and cytochrome c oxidase activity in Rhodospirillum rubrum and Rhodospirillum tenue during the reversible adaptation from phototrophic to chemotrophic conditions. Arch Microbiol 123:287–293
Weaver PF, Wall JD, Gest H (1975) Characterization of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Microbiol 105:207–216
Zannoni D, Jasper P, Marrs BL (1978) Light induced oxygen reduction as a probe of electron transport between respiratory and photosynthetic components in membranes of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Biochem Biophys 191:625–631
Zehnder AJB, Wuhrmann K (1976) Titanium (III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes. Science 194:1165–1166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cox, J.C., Beatty, J.T. & Favinger, J.L. Increased activity of respiratory enzymes from photosynthetically grown Rhodopseudomonas capsulata in response to small amounts of oxygen. Arch. Microbiol. 134, 324–328 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00407811
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00407811