Summary
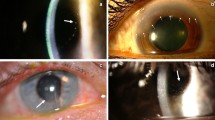
A case of conjunctivitis ligneosa in an otherwise healthy man of 18 was successfully treated by removal of the thick pseudomembrane and subsequent conjunctival graft. The graft was taken from a cadaver eye. Eleven months later necrosis of the transposed conjunctiva suddenly developed, starting 6 days after the extirpation of a neighbouring epidermoid cyst. After general treatment with corticosteroids, the graft revascularized, with the exception of a small central defect. This was closed by a second graft, taken from the upper fornix of the patient's eye. There were no postoperative complications during a total follow-up period of 2 years.
Histochemical and electron-microscope findings indicated the presence of abundant acid mucopolysaccharides. Electron microscope investigation gave further proof of severely disturbed glycosaminoglycane-collagen interactions in that there was evidence of changes in the collagen fibril diameter and of ring- and hookshaped structures lying between the single fibrils and positively stained with ruthenium red.
The most striking finding was an increased urinary excretion of total hydroxyproline, ranging between 65 and 127 mg per day.
It appears that conjunctivitis ligneosa is a local symptom of a general disturbance in glycosaminoglycane and collagen metabolism.
Zusammenfassung
Bei einem 18 Jahre alten Mann mit Konjunctivitis lignosa wurde die Pseudomembran excidiert und der Defekt durch Leichenbindehaut gedeckt. Elf Monate später Nekrose des Transplantats, ausgelöst durch Entfernung einer benachbarten Bindehautcyste. Nach Kortikosteroidbehandlung und nochmaliger Bindehautstransplantation (vom Patientenauge) komplikationsloser Verlauf. Nachbeobachtungszeit insgesamt zwei Jahre.
Histochemisch und elektronenmikroskopisch ergaben sich Hinweise für eine vermehrte Produktion von Glykosaminoglykanen sowie für Veränderungen der Glykosaminoglykan-Kollagenbeziehungen. Die Hydroxyprolinausscheidung war erhöht. Demnach dürfte es sich bei der Konjunctivitis lignosa um das lokale Symptom einer allgemeinen Störung des Mucopolysaccharid- und Kollagenstoffwechsels handeln.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Borel, M. G.: Un nouveau syndrome palpébral. Bull. Soc. franç. Ophtal. 46, 168–180 (1933)
Bottermann, P., Oberländer, J.: Hydroxyprolin-Bestimmung: Diagnostische Bedeutung und klinische Relevanz. Diagnostik 6, 552–555 (1973)
François, J., Victoria-Troncoso, V.: La conjonctivite ligneuse. Ophthalmologica. (Basel) 154, 470–482 (1967)
François, J., Victoria-Troncoso, V.: Treatment of ligneous conjunctivitis. Amer J. Ophthal. 65, 674–678 (1968)
Frimodt-Møller, J.: Conjunctivitis lignosa combined with a dental affection. Report of a case. Acta ophthal. (Kbh.) 51, 34–38 (1973)
Gärtner, J.: The normal fine structure and aging changes of the human zonular fibers. With special regard to the degeneration of collagen in senile ciliary body and in pinguecula. Z. Zellforsch. 114, 281–300 (1971)
Gieseking, R.: Mesenchymale Gewebe und ihre Reaktionsformen im elektronenoptischen Bild. Veröffentlichungen aus der morphologischen Pathologie, H. 72. Stuttgart: Fischer 1966
Holzmann, H., Morsches, B., Gebhardt, R., Liedtke, F.: Zum „Collagen-like protein“-Gehalt im Serum von Psoriatikern. Klin. Wschr. 48, 1197–1198 (1970)
Kanai, A., Polack, F. M.: Histologic and electron microscope studies of ligneous conjunctivitis. Amer. J. Ophthal. 72, 909–916 (1971)
Krause, E.-G.: Polysaccharide In: Molekulare Biologie der Zelle (H. Bielka, Hrgs.), 2., überarb. Aufl. Stuttgart: Fischer 1973
Luft, J. H.: Electron microscopy of cell extraneous coats as revealed by ruthenium red staining. J. Cell Biol. 23, 54 A (1964)
Luft, J. H.: The fine structure of hyaline cartilage matrix following ruthenium red fixation and staining. J. Cell Biol. 27, 61 A (1965)
Mawas, E., Tremoulet, O., Moulinard, L., Morard, J.-Cl.: Evolution d'une conjunctivite ligneuse. Bull. Soc. Ophtal. Fr. 71, 1068–1077 (1971)
Merker, H. J., Günther, Th.: Die elektronenmikroskopische Darstellung von Glykosaminoglykanen im Gewebe mit Rutheniumrot. Histochemie 34, 293–303 (1973)
Morsches, B.: Persönliche Mitteilung (1973)
Nemetschek, Th.: Verlauf der Quellung beim Kollagen. Kolloid-Z. Polymere 187, 109–120 (1963)
Nemetschek, Th.: Altersabhängige Abläufe am Kollagen. In: Altern und Entwicklung — Aging and development (H. Bredt und J. W. Rohen, Hrsg.), Bd. 3. Stuttgart-New York: Schattauer 1971
Nemetschek, Th., Gansler, H.: Quellung von Kollagen. Reaktionen mit anorganischen und organischen Kationen. Z. Naturforsch. 16b, 496–509 (1961)
Nover, A.: Über die als Conjunctivitis lignosa bezeichnete chronische pseudomembranöse Bindehautentzündung. Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk. 145, 221–233 (1964)
Pearse, E. A. G.: Histochemistry: Theoretical and applied, 3rd ed. London: Churchill 1968
Pease, D. C., Bouteille, M.: The tridimensional ultrastructure of native collageneous fibrils, cytochemical evidence for a carbohydrate matrix. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 35, 339–358 (1971)
Pilgrim, U., Vogel, A., Meves, C.: Elektronenoptische Faserstrukturen beim Skleromyxödem und beim Skleroedema adultorum. Dermatologica (Basel) 147, 46–63 (1973)
Revel, J. P.: Role of the golgi apparatus of cartilage cells in the elaboration of matrix glycosaminoglycans. In: Chemistry and molecular biology of the intercellular matrix (E. A. Balazs, ed.), vol. 3. London and New York: Academic Press 1970
Ross, R.: The connective tissue forming cell. In: Treatise on collagen, vol. 2 (B. S. Gould, ed.), part A. London and New York: Academic Press 1968
Schreck, E.: Mündliche Mitteilung. Zit. bei Nover (1964)
Silberth, J. E.: Biosynthesis of mucopolysaccharides. In: Molecular pathology of connective tissues (Tamayo, R. P., and Rojkind, M., eds.). New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc. 1973
Spencer, L. M., Straatsma, B. R., Foos, R. Y.: Ligneous Conjunctivitis. Arch. Ophthal. 80, 365–367 (1968)
Trojan, H.: Beitrag zur Histologie der Conjunctivitis lignosa. Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk. 158, 551–554 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit dankenswerter Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gärtner, J. Zur Therapie und Pathogenese der Konjunctivitis lignosa. Albrecht v. Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal. 190, 229–245 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00407097
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00407097