Summary
Some unsolved problems in DNA alkylation by N-nitroso compounds are discussed in this overview. (1) Does O6 alkylation of guanine represent the initiating event exclusively or are O4 alkylation of thymidine and phosphate triester formation also involved in the initiating process? (2) Does the formation of rearranged DNA alkylation products by longer chained alkylnitroso compounds have any significance for the carcinogenic effects of these compounds? The concept of hard and soft acids and bases (HSAB principle) as a qualitative model can predict the changes in the DNA alkylation pattern by branched carbenium ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boiteux S, Laval F (1985) Repair of O6 methylguanine, by mammalian cell extracts, in alkylated DNA and poly (dG-m5dC) (poly dG-m5dC) in B and Z forms. Carcinogenesis 6:805–807
Briscoe WT, Cotter L (1985) DNA sequence has an effect on the extent and kinds of alkylation of DNA by a potent carcinogen. Chem Biol Interact 56:321–331
Coles B (1984–85) Effects of modifying structure on electrophilic reactions with biological nucleophiles. Drug Metab Rev 15:1307–1334
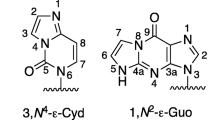
Chung F, Hecht SS (1983) Formation of cyclic 1,N2-adducts by reaction of deoxyguanosine with α-Acetoxy-N-nitrosopyrolidine, 4-(carbethoxynitrosamino)butanol, or Crotonaldelyde. Cancer Res 43:1230–1235
Dolan ME, Pegg AE (1985) Extent of formation of O4-methylthymidine in calf thymus DNA methylated by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea and lack of repair of this product by rat liver O6-alkyl-guanine-DNA-alkyl-transferase. Carcinogenesis 6:1611–1614
Furois-Corbin S, Pullmann B (1985) Specificity in carcinogen-DNA interaction: a theoretical exploration of the factors involved in the effect of neighbouring bases on N-methyl-N-nitrosourea alkylation of DNA. Chem Biol Interact 54:9–13
Ho T (1977) Hard and soft acids and bases principle in organic chemistry. Academic Press, New York
Ho T, Ho HG, Hamilton LD (1978) Biochemical significance of the hard and soft acids and bases principle. Chem Biol Interact 23:65–84
Izatt RM, Christensen JJ, Rytting JH (1971) Sites and thermodynamic quantities associated with proton and metal ion interaction with ribonucleic acid, deoxyribonucleic acid and their constituent bases, nucleosides and nucleotides. Chem Rev 71:439–481
Kadlubar FF, Beranek DT, Weis CC, Evans FE, Cox R, Irving CC (1984) Characterisation of the purine ring-opened 7-methyl guanine and its persistence in rat bladder epithelial DNA after treatment with the carcinogen N-methylnitrosourea. Carcinogenesis 5:587–592
Kirmse W (1976) Stickstoff als Abgangsgruppe: Aliphatische Diazonium Ionen. Angew Chem 88:273–283
Lown JW, Chauhan SMS, Koganty RR, Sapse AM (1984) Alkyldinitrogen species implicated in the carcinogenic, mutagenic, and anticancer activities of N-nitroso compounds: Characterization by 15N-NMR of 15N enriched compounds and analysis of DNA base. J Am Chem Soc 106:6401–6408
Morimoto K, Dolan ME, Sciechitano D, Pegg AE (1985) Repair of O6-propylguanine and O6-butylguanines in DNA by O6-alkylguanine DNA alkyltransferases from rat liver and E. Coli. Carcinogenesis 6:1027–1031
Moss RA (1974) Some chemistry of alkanediazotates. Accounts Chem Res 7:421–427
Ortlieb H, Kleihues P (1980) Reaction of N-n-butyl-N-nitrosourea with DNA in vitro. Carcinogenesis 1:849–854
Park KK, Wishnok JS, Archer MC (1977) Mechanism of alkylation by N-nitroso compounds: detection of rearranged alcohol in the microsomal metabolism of N-nitroso-n-propylamine and base catalyzed decomposition of N-n-propyl-N-nitrosourea. Chem Biol Interact 18:349–354
Pearson RG (1966) Acids and bases. Science 151:172–177
Pegg AE (1984) Methylation of the O6 position of guanine in DNA is the most likely initiating event in carcinogenesis by methylating agents. Cancer Invest 2:223–231
Richardson FC, Dyroff MC, Boucheron JA, Swenberg JA (1985) Differential repair of O4-alkylthymidine following exposure to methylating and ethylating hepatocarcinogens. Carcinogenesis 6:625–629
Saffhill R (1984) In vitro reaction of N-n-butyl-N-nitrosourea and n-butylmethanesulphonate with guanine and thymine bases of DNA. Carcinogenesis 5:621–625
Saffhill R, Margison GP, O'Connor PJ (1985) Mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by alkylating agents. Biochim Biophys Acta 823:111–145
Saville B (1967) Anwendungen des Konzepts der harten und weichen Säuren und Basen auf Vielzentrenreaktionen. Angew Chem 79:966–977
Scribner JD, Ford GP (1982) n-Propyldiazonium ion alkylates O6 of guanine with rearrangement, but alkylates N7 without rearrangement. Cancer Lett 16:51–56
Singer B (1984) Alkylation of the O6 of guanine is only one of many chemical events that may initiate carcinogenesis. Cancer Invest 2:233–238
Singer B, Grunberger D (1983) Molecular biology of mutagens and carcinogens. Plenium Press, New York
Singer B, Spengler SJ, Fraenkel-Conrat H, Kusmierek JT (1986) O4-Methyl-ethyl or-isopropyl substituents on thymidine in poly (dA-dT) all lead to transitions upon replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:28–32
Swenberg JA, Dyroff MC, Bedell MA, Popp JA, Huh N, Kirstein U, Rajewsky M (1984) O4-Ethyldeoxythymidine but not O6-ethyldeoxyguanosine accumulates in hepatocyte DNA of rats exposed continuously to diethylnitrosamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1692–1695
Wiessler M, Pool BL (1984) Mutagenic properties of N-cyclopropyl and N-allyl-N-nitroso compounds. Studies on the nature of alkylating species 5:635–639
Zarbl H, Sukumar S, Arthur AV, Martin-Zanca D, Barbacid M (1985) Direct mutagenesis of Ha-ras-1 oncogenes by N-nitroso-N-methylurea during initiation of mammary carcinogenesis in rats. Nature 315:382–385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiessler, M. DNA adducts by N-nitroso compounds. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 112, 81–84 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404386
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404386