Abstract
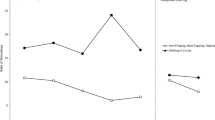
The effects of short-term treatment of dextroamphetamine on hyperkinetic children were investigated on twenty children who were enrolled in a normal school setting. The study was carried out double-blind. Students were evaluated medically, psychiatrically, neurologically, and administered psychological testing consisting of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children and Wide Range Achievement Test. Parents and teachers also evaluated the child on questionnaires. Students were given 5 mg of dextroamphetamine in the morning by a nurse, and this was increased 5 mg weekly until the maximum dose of 15 mg was reached in the third week.
Results indicated that there was a significant difference at the p<0.05 level in classroom behavior and attitude toward authority on teacher's ratings. No significant differences were found on variables measured by the parents' questionnaires. WISC results indicated significant differences on pre-post measurements for placebo and drug; however, there were no significant differences in improvement scores when between group comparisons were made. WRAT results also remained unchanged.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradley, C., Bowen, M.: School performance of children receiving amphetamine sulfate. Amer. J. Orthopsychiat. 10, 782–788 (1940).
—, Green, E.: Psychometric performance of children receiving amphetamine sulfate. Amer. J. Orthopsychiat. 97, 388–394 (1940).
Conners, C. K.: A factor analysis of parent ratings of symptom patterns in hyperkinetic, neurotic, and normal children. Child Develop. 41, 667–682 (1970).
—: A Teacher's rating scale for use in drug studies with children. Amer. J. Psychiat. 126, 152–156 (1969).
—, Borcai, A.: Effect of dextroamphetamine on children: Studies on subjects with learning disabilities and school behaviour problems. Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 17, 478–485 (1967).
—, Rothschild, G., Eisenberg, L.: Effects of dextroamphetamine on intelligence and achievement of children with learning disorders. Arch. gen. Psychiat. 21, 182 to 190 (1969).
Eisenberg, L., Lachmann, R., Molling, P. A., Lockner, A., Mizelle, J. D., Conners, C. K.: A psychopharmacologic experiment in a training school for delinquent boys. Amer. J. Orthopsychiat. 33, 431–447 (1963).
Jastak, J., Bijou, S., Jastak, S.: Wide range achievement test. Guidance Association (1965).
Molitch, M., Eccles, J. P.: Effect of benzedrine sulfate on the intelligence scores of children. Amer. J. Psychiat. 94, 587–590 (1937).
Wechsler, D.: Wechsler adult intelligence scale manual. New York: Psychological Corp. 1955.
Zrull, J. P., Westman, J. C., Arthur, B., Rice, D. L.: A comparison of diazepam, D-amphetamine and placebo in the treatment of the hyperkinetic syndrome in children. Amer. J. Psychiat. 121, 188–189 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Carried out under N.I.M.H. grant 16128 Boston State Hospital, 591 Morton Street, Boston, Mass. Medication supplied by Smith, Kline & French.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finnerty, R.J., Soltys, J.J. & Cole, J.O. The use of d-amphetamine with hyperkinetic children. Psychopharmacologia 21, 302–308 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403869
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403869