Abstract
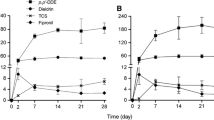
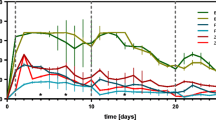
In earlier work, we found that leeches from an industrially polluted creek bioaccumulated chlorophenols to much higher concentrations than other resident benthic invertebrates and fish. We suggested that leeches may have significant potential as biomonitors for these and other organic contaminants in the environment. In this study, we compared the bioaccumulation and depuration of 16 organic compounds, including eight chlorophenols (CPs), lindane, DDT and four derivatives, benzothiazole (BT) and 2-(Methylthio)benzothiazole (MMBT) for three species of leeches. Dina dubia had the highest bioaccumulation capacity for most contaminants, but residues persisted longest in Erpobdella punctata. Helobdella stagnalis appeared capable of degrading some compounds. Half lives of CPs, DDT and DDT derivatives were generally longer than one month. In contrast, half lives were only 1 day for lindane, 1–2.5 days for MMBT and 7 days for BT despite very high initial tissue concentrations of the latter two compounds. Bioconcentration factors for contaminants in leeches were higher than those reported for other aquatic organisms. Half lives for lindane, DDT and DDT derivatives were consistent with the literature for other organisms, but half lives for CPs were much longer. The results suggest that leeches would be excellent biomonitors of both continuous and intermittent contamination of a waterway with CPs and DDT, as they retain these compounds for long periods after exposure. Their usefulness as a screening tool for lindane and benzothiazoles would be limited to chronically contaminated environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton, D. R. and Metcalfe, J. L.: 1986, ‘Life Cycles, Reproduction, and Diets of Dina dubia and Erpobdella punctata (Hirudinea: Erpobdellidae) in Canagagigue Creek, Ontario’, Can. J. Zool. 64, (3), 640–648.
Bjerk, J. E. and Brevik, E. M.: 1980, ‘Organochlorine Compounds in Aquatic Environments’, Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 9, 743–750.
Brownlee, B., Carey, J. H., and Fox, M. E.: 1981, A Review of Benzothiazoles in the Aquatic Environment, Scientific Series No. 126, Environment Canada, Inland Waters Directorate, Burlington, Ontario, 5 pp.
Butler, G. C., Bennett, B. G., Miller, D. R., Piotrowski, J. K., and Sors, A.: 1985, ‘Methods for Estimating Exposure to Chemicals’, in Vouk, V. B., Butler, G. C., Hoel, D. G. and Peakall, D. B. (eds.), Methods for Estimating Risk of Chemical Injury: Human and Non-human Biota and Ecosystems, John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 7–28.
Call, D. J., Brooke, L. T., and Lu, P-Y.: 1980, ‘Uptake, Elimination, and Metabolism of Three Phenols by Fathead Minnows’, Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 9, 699–714.
Carey, J. H., Fox, M. E., Brownlee, B. G., Metcalfe, J. L., Mason, P. D., and Yerex, W. H. 1983, The Fate and Effects of Contaminants in Canagagigue Creek 1. Stream Ecology and Identification of Major Contaminants', Scientific Series No. 135, Environment Canada, Inland Waters Directorate, Burlington, Ontario, 37 pp.
Carey, J. H., Fox, M. E., Brownlee, B. G., Metcalfe, J. L., and Platford, R. F.: 1984, ‘Disappearance Kinetics of 2,4- and 3,4-Dichlorophenol in a Fluvial System’, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 62,(8), 971–975.
Chiou, C. T., Freed, V. H., Schmedding, D. W., and Kohnert, R. L.: 1977, ‘Partition Coefficient and Bioaccumulation of Selected Organic Chemicals’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, (5), 475–478.
Davies, R. W., Wrona, F. J., and Linton, L.: 1979, ‘A Serological Study of Prey Selection by Helobdella stagnalis (Hirudinoidea)’, J. Animal Ecol. 48, 181–194.
de laCruz, A. A. and Naqvi, S. M.: 1973, ‘Mirex Incorporation in the Environment: Uptake in Aquatic Organisms and Effects on the Rates of Photosynthesis and Respiration’, Arch. Environm Contam. Toxicol. 1, (3), 255–264.
Ernst, W.: 1977, ‘Determination of the Bioconcentration Potential of Marine Organisms.- A Steady State Approach. I. Bioconcentration Data for Seven Chlorinated Pesticides in Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and their Relation to Solubility Data’, Chemosphere 11, 731–740.
Ernst, W.: 1979, ‘Factors Affecting the Evaluation of Chemicals in Laboratory Experiments Using Marine Organisms’, Ecotoxicol. Environm. Safety 3, (1), 90–98.
Ernst, W. and Weber, K.: 1978, ‘Chlorinated Phenols in Selected Estuarine Bottom Fauna’, Chemosphere 11, 867–872.
Folke, J., Birklund, J., Sorensen, A. K., and Lund, U.: 1983, ‘The Impact on the Ecology of Polychlorinated Phenols and Other Organics Dumped at the Bank of a Small Marine Inlet’, Chemosphere 12, (9), 1169–1181.
Gakstatter, J. H. and Weiss, C. M.: 1967, ‘The Elimination of DDT-C14, Dieldrin-C14, and Lindane-C14 from Fish Following a Single Sublethal Exposure in Aquaria’, Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 96, (3), 301–307.
Glickman, A. H., Statham, C. N., Wu, A., and Lech, J. J.: 1977, ‘Studies on the Uptake, Metabolism, and Disposition of Pentachlorophenol and Pentachloroanisole in Rainbow Trout’, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 41, 649–658.
Jacob, C.: 1986, ‘Use of the Bioconcentration Capability of Leeches to Evaluate Chlorophenol Pollution’, M. Sc. Thesis, The University of British Columbia, 181 pp.
Jones, P. A.: 1981, ‘Chlorophenols and Their Impurities in the Canadian Environment’, Economic and Technical Review Report EPS 3-EC-81-2, Environment Canada, Environmental Protection Service, Ottawa, Canada, 434 pp.
Kaila, K. and Saarikoski, J.: 1977, ‘Toxicity of Pentachlorophenol and 2,3,6-Trichlorophenol to the Crayfish (Astacus fluviatilis L.)’, Environ. Pollut. 12, 119–123.
Kenaga, E. E. and Goring, C. A. I.: 1978, ‘Relationship between Water Solubility, Soil-Sorption, Octanol-Water Partitioning, and Bioconcentration of Chemicals in Biota’, in Proceedings of the Third Aquatic Toxicology Symposium, American Society for Testing and Materials, New Orleans, LA., 63 pp.
Kobayashi, K. and Akitake, H.: 1975, ‘Studies on the Metabolism of Chlorophenols in Fish-I. Absorption and Excretion of Pentachlorophenol by Goldfish’, Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fisheries 41, (1), 87–92.
Landner, L., Lindstrom, K., Karlsson, M., Nordin, J., and Sorensen, L.: 1977, ‘Bioaccumulation in Fish of Chlorinated Phenols from Kraft Pulp Mill Bleachery Effluents’, Bull. Environm Contam. Toxicol. 18, (6), 663–673.
Leo, A., Hansch, C., and Elkins, D.: 1971, ‘Partition Coefficients and their Uses’, Chem. Rev. 71 (6), 525–616.
Meeks, R. L.: 1968, ‘The Accumulation of 36Cl Ring-Labeled DDT in a Freshwater Marsh’, J. Wildl. Mgmt. 32, (2), 376–398.
Metcalfe, J. L., Fox, M. E., and Carey, J. H.: 1984, ‘Aquatic Leeches (Hirudinea) as Bioindicators of Organic Chemical Contaminants in Freshwater Ecosystems’ Chemosphere 13, (1), 143–150.
Metcalfe, J. L., Fox, M. E., Coletta, P. A., and Carey, J. H.: 1985, Chlorophenol Levels in Aquatic Leeches from Selected Sites in Southwestern New Brunswick, Contribution No. 85-61, Environment Canada, Inland Waters Directorate, National Water Research Institute, Burlington, Ontario, 11 pp.
Naqvi, S. M. and de laCruz, A.: 1973, ‘Mirex Incorporation in the Environment: Residues in Nontarget Organisms-1972’, Pestic. Monit. J. 7, (12), 104–111.
Niimi, A. J. and McFadden, C. A.: 1982, ‘Uptake of Sodium Pentachlorphenate (NaPCP) from Water by Rainbow Trout (Salmo gairdneri) Exposed to Concentrations in the ng L-1 Range’, Bull. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 11–19.
Paasivirta, J., Heinola, K., Humppi, T., Karjalainen, A., Knuutinen, J., Mantykoski, K., Paukku, R., Piilola, T., Surma-Aho, K., Tarhanen, J. Welling, L., Vihonen, H., and Sarkka, J.: 1985, ‘Polychlorinated Phenols, Guaiacols and Catechols in Environment’, Chemosphere 14, (5), 469–491.
Pruitt, G. W., Grantham, B. J., and Pierce, R. H.Jr.: 1977, ‘Accumulation and Elimination of Pentachlorophenol by the Bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus’, Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 106, (5), 462–465.
Sawyer, R. T.: 1974, ‘Leeches (Annelida: Hirudinea)’, in Hart, C. W.Jr. and Fuller, S. L. H. (eds.), Pollution Ecology of Freshwater Invertebrates, Academic Press, New York, pp. 81–142.
Schimmel, S. C., Patrick, J. M.Jr., and Forester, J.: 1977, ‘Toxicity and Bioconcentration of BHC and Lindane in Selected Estuarine Animals’, Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 6, 355–363.
Trujillo, D. A., Ray, L. E., Murray, H. E., and Giam, C. S.: 1982, ‘Bioaccumulation of Pentachlorophenol by Killifish (Fundulus similus)’, Chemosphere 11, (1), 25–31.
Virtanen, M. T. and Hattula, M-L.: 1982, ‘The Fate of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol in an Aquatic Continuous-Flow System’, Chemosphere 11, (7), 641–649.
Webster, E. J.: 1967, ‘An Autoradiographic Study of Invertebrate Uptake of DDT-Cl36’, Ohio J. Sci. 67, (5), 300–307.
Weil, V. L., Dure, G., and Quentin, K-E.: 1974, ‘Wasserloslichkeit von insektiziden chlorierten Kohlenwasserstoffen und polychlorierten Biphenylen im Hinblick auf eine Gewasserbelastung mit diesen Stoffen’, Wasser und Abwasser-Forschung 7, (6), 169–175.
Yamato, Y., Kiyonaga, M., and Watanabe, T.: 1983, ‘Comparative Bioaccumulation and Elimination of HCH Isomers in Short-Necked Clam (Venerupis japonica) and Guppy (Poecilia reticulata)’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 352–359.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metcalfe, J.L., Fox, M.E. & Carey, J.H. Freshwater leeches (Hirudinea) as a screening tool for detecting organic contaminants in the environment. Environ Monit Assess 11, 147–169 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401727
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401727